|
Zheng Yi (author)
''Scarlet Memorial: Tales of Cannibalism in Modern China'' is a book of reportage literature (''baogao wenxue'') by the Chinese novelist Zheng Yi (郑义; born 1947). Zheng and a group of writers under the joint pseudonym "T. P. Sym" translated and abridged it from the Chinese work 红色 纪念碑 ''Hongse jinianbei'' (''Red monument''; Taipei: Huashi, 1993). Zheng uses local government documents, eye-witness accounts and confessions to describe the factional violence and even cannibalism that occurred in the Guangxi Massacre during the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976). Zheng blames the savagery and cannibalism on "class struggle" and "revolutionary revenge". The book received praise for revealing the nature of Mao's regime and also criticism for giving the impression that cannibalism was systematic and widespread. Development Background Zheng Yi was born in Chongqing, Sichuan, in 1947, and went to Beijing to attend the middle school attached to Qinghua University, China's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zheng Scarlet Memorial Cover
Zheng may refer to: *Zheng (surname), Chinese surname (鄭, 郑, ''Zhèng'') *Zheng County, former name of Zhengzhou, capital of Henan, China *Guzheng (), a Chinese zither with bridges *Qin Shi Huang (259 BC – 210 BC), emperor of the Qin Dynasty, whose name was Zheng (政) Historical regimes *Zheng (state) (806 BC–375 BC), an ancient state in China *Zheng (619–621), a state controlled by rebel leader Wang Shichong during the Sui–Tang transition *House of Koxinga (1655–1683), Ming partisans who ruled Taiwan during the early Qing See also *Cheng (other) *Sheng (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Economic Reform
The Chinese economic reform or reform and opening-up (), known in the West as the opening of China, is the program of economic reforms termed " Socialism with Chinese characteristics" and "socialist market economy" in the People's Republic of China (PRC). Led by Deng Xiaoping, often credited as the "General Architect", the reforms were launched by reformists within the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) on December 18, 1978, during the "Boluan Fanzheng" period. The reforms went into stagnation after the military crackdown on 1989 Tiananmen Square protests, but were revived after Deng Xiaoping's Southern Tour in 1992. In 2010, China overtook Japan as the world's second-largest economy by nominal GDP and in 2017 overtook the United States by becoming the world's largest economy by GDP (PPP). Prior to the reforms, the Chinese economy was dominated by state ownership and central planning. From 1950 to 1973, Chinese real GDP per capita grew at a rate of 2.9% per year on average, albei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 Non-fiction Books
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peacefully dissolved into the Czech Republic and Slovakia; In the United States, the ATF besieges a compound belonging to David Koresh and the Branch Davidians in a search for illegal weapons, which ends in the building being set alight and killing most inside; Eritrea gains independence; A major snow storm passes over the United States and Canada, leading to over 300 fatalities; Drug lord and narcoterrorist Pablo Escobar is killed by Colombian special forces; Ramzi Yousef and other Islamic terrorists detonate a truck bomb in the subterranean garage of the North Tower of the World Trade Center in the United States., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Oslo I Accord rect 200 0 400 200 1993 Russian constitutional crisis rect 400 0 600 200 Dissol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Terrill
Ross Terrill (b. 1938 Melbourne) is an Australian-born American political scientist and historian. He specializes in the history of China, especially the history of the People's Republic of China. He has made several public appearances in order to testify in front of the United States Congress, and he has also written numerous articles and nine books. For many years he has been a research associate at Harvard's Fairbank Center for Chinese Studies, and recently, he was a visiting professor at the University of Texas at Austin as well as a visiting professor at Monash University in Australia. Early life Ross Terrill was born in Melbourne, Australia in 1938 to Miriel (Lloyd) Terrill and Frank Gregston. Terrill attended Wesley College in Melbourne, where he became Dux in 1956. In 1962 Terrill attended the University of Melbourne where he completed his Honours in history and political science. In 1965, shortly after completing his honours degree, Terrill immigrated to the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Studies In Society And History
''Comparative Studies in Society and History'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal published quarterly by Cambridge University Press Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing hou ... on behalf of the Society for Comparative Study of Society and History. It was established in 1958. References External links *Journal online History journals Publications established in 1958 Quarterly journals English-language journals Cambridge University Press academic journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies {{history-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diary Of A Madman (Lu Xun)
"Diary of a Madman", also translated as "A Madman's Diary" () is a short story by the Chinese writer Lu Xun, published in 1918. It was the first and most influential work written in vernacular Chinese in republican era China, and would become a cornerstone of the New Culture Movement. Lu Xun's stories often critiqued early 20th century Chinese society, and "Diary of a Madman" established a new language and revolutionary figure of Chinese literature, an attempt to challenge conventional thinking and traditional understanding. The diary form and the idea of the madman who sees reality more clearly than those around him were inspired by Nikolai Gogol's short story " Diary of a Madman". Lu Xun's "madman" sees "cannibalism" both in his family and the village around him, and he then finds cannibalism in the Confucian classics which had long been credited with a humanistic concern for the mutual obligations of society, and thus used to justify the superiority of Confucian civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
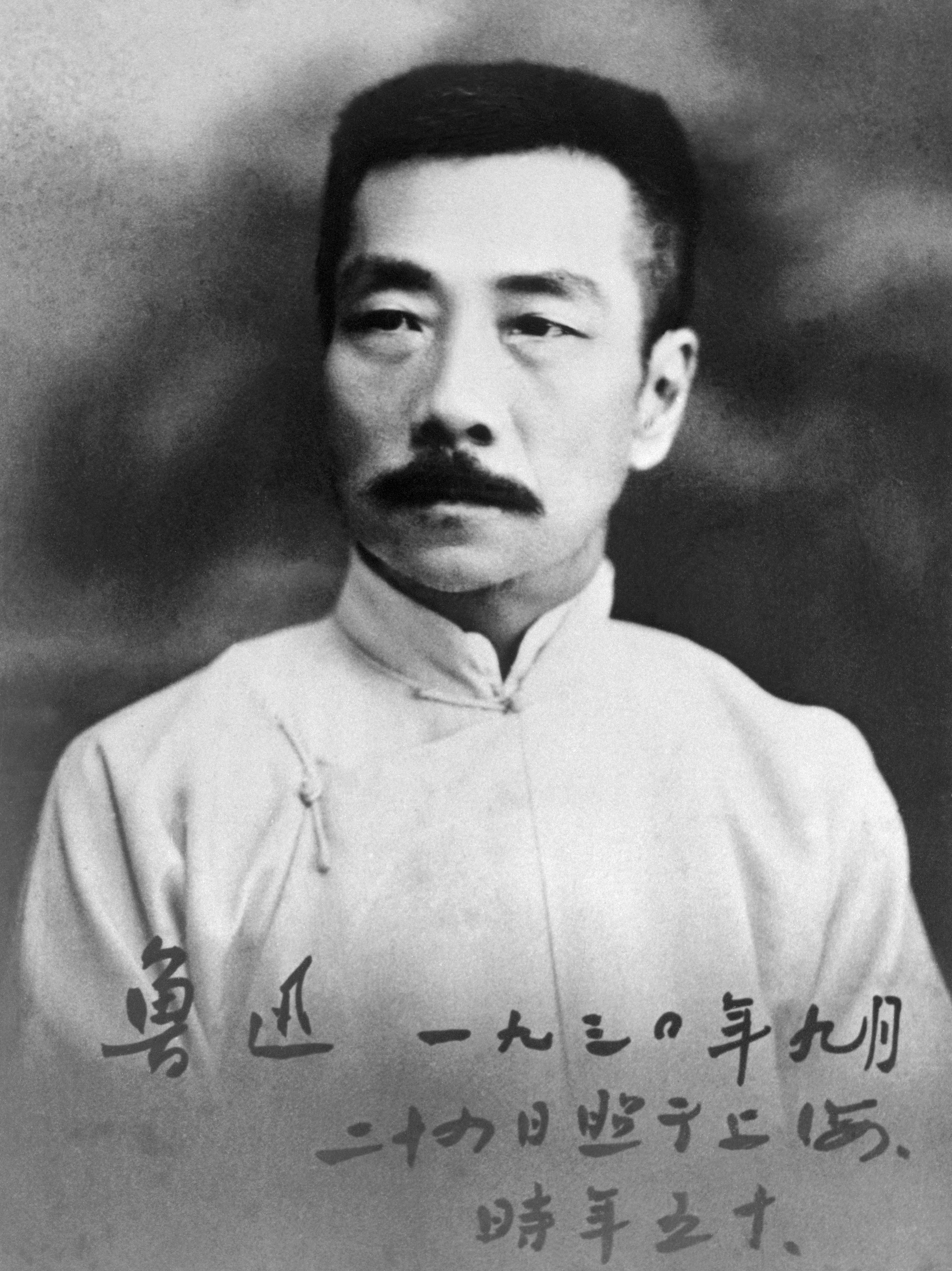
Lu Xun
Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. He was a leading figure of modern Chinese literature. Writing in vernacular Chinese and classical Chinese, he was a short story writer, editor, translator, literary critic, essayist, poet, and designer. In the 1930s, he became the titular head of the League of Left-Wing Writers in Shanghai during republican era China (1912-1949). Lu Xun was born into a family of landlords and government officials in Shaoxing, Zhejiang; the family's financial resources declined over the course of his youth. Lu aspired to take the imperial examinations, but due to his family's relative poverty he was forced to attend government-funded schools teaching "Western education". Upon graduation, Lu went to medical school in Japan but later dropped out. He became interested in studying literature but was eventually f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. Ethnography in simple terms is a type of qualitative research where a person puts themselves in a specific community or organization in attempt to learn about their cultures from a first person point-of-view. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation—on the researcher participating in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–49)
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the island around 6, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Investigation And Statistics
The National Bureau of Investigation and Statistics (Military Commission), (NBIS or BIS) (), commonly known as Juntong (), was the military intelligence agency of the Republic of China before 1946. It was devoted to intelligence gathering and covert spying operation for purposes of national security and defense. It was originally headed by Dai Li, and after 1946 he was succeeded by Mao Renfeng. This bureau was largely superseded by the Military Intelligence Bureau under Ministry of National Defense in Taiwan today. The NBIS had a great influence amongst the Nationalist Government's military, police, administration, and transportation agencies, as well as embassies and consulates abroad during the Political Tutelage period (1928-1946) of Republic of China. It was often criticized by the political dissidents as a "secret police" involved in covert and espionage operation, including surveillance, kidnapping, assassinations, elimination and house-arrest against Chinese communis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roderick MacFarquhar
Roderick "Rod" Lemonde MacFarquhar (2 December 1930 – 10 February 2019) was a British China scholar, politician, and journalist. MacFarquhar had a varied career. He was founding editor of ''China Quarterly'' in 1959. He served as a Member of Parliament in the 1970s, then joined the BBC .In the 1980s, he became a professor at Harvard University, where he served several terms as director of the Fairbank Center for Chinese Studies. He was best known for his studies of Maoist China, the three-volume ''The Origins of the Cultural Revolution'' and ''Mao's Last Revolution''. Family and early life MacFarquhar was born in Lahore, British India (now Pakistan). His father was Sir Alexander MacFarquhar, a member of the Indian Civil Service and later a senior diplomat at the United Nations. His mother was Berenice (née Whitburn). He was educated at the Aitchison College in Lahore and Fettes College, an independent school in Edinburgh. Academic and journalistic career After spending part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821) are published by Times Newspapers, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'', which do not share editorial staff, were founded independently and have only had common ownership since 1966. In general, the political position of ''The Times'' is considered to be centre-right. ''The Times'' is the first newspaper to have borne that name, lending it to numerous other papers around the world, such as ''The Times of India'', ''The New York Times'', and more recently, digital-first publications such as TheTimesBlog.com (Since 2017). In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as , or as , although the newspaper is of nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |