|
Zhankuic Acid
Zhankuic acids are sterols isolated from the fungus ''Taiwanofungus camphoratus''. Zhankuic acid C possesses ''in vitro'' anti-inflammatory properties due to its role as a selective TLR4/ MD-2 antagonist An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist. Etymology The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, riv .... File:Zhankuic acid A.svg, Zhankuic acid A File:Zhankuic acid B.svg, Zhankuic acid B File:Zhankuic acid C.svg, Zhankuic acid C References External links Zhankuic acid A - PubChem [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to cell membrane structure, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids (fats in the broader sense of the term). Types Sterols of plants are called ''phytosterols'' and sterols of animals are called ''zoosterols''. The most importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwanofungus Camphoratus
''Taiwanofungus camphoratus'', also known as stout camphor fungus, is a species of fungus that is endemic to Taiwan, where it grows only on the endemic aromatic tree ''Cinnamomum kanehirae'', causing a brown heart rot. Traditional medicine It is used in Taiwanese traditional medicine as a purported remedy for cancer, hypertension, and hangover. The annual market is worth over $100 million (US) in Taiwan alone. The 32.15 Mb genome containing 9,254 genes has been sequenced. ''Taiwanofungus camphoratus'' has been found to produce anti-obesogenic, anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic effects in high-fat diet-fed mice. Chemical constituents Antcin B, antrodioxolanone, antrocamphin B, antroquinonol, antrocamphins, zhankuic acids, and other antcins have been reported as constituents of ''Taiwanofungus camphoratus''. Ecological concern Because of its use as an herbal remedy, fruiting bodies of the fungus can fetch high prices. Good quality fruiting bodies were reported to cost as m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
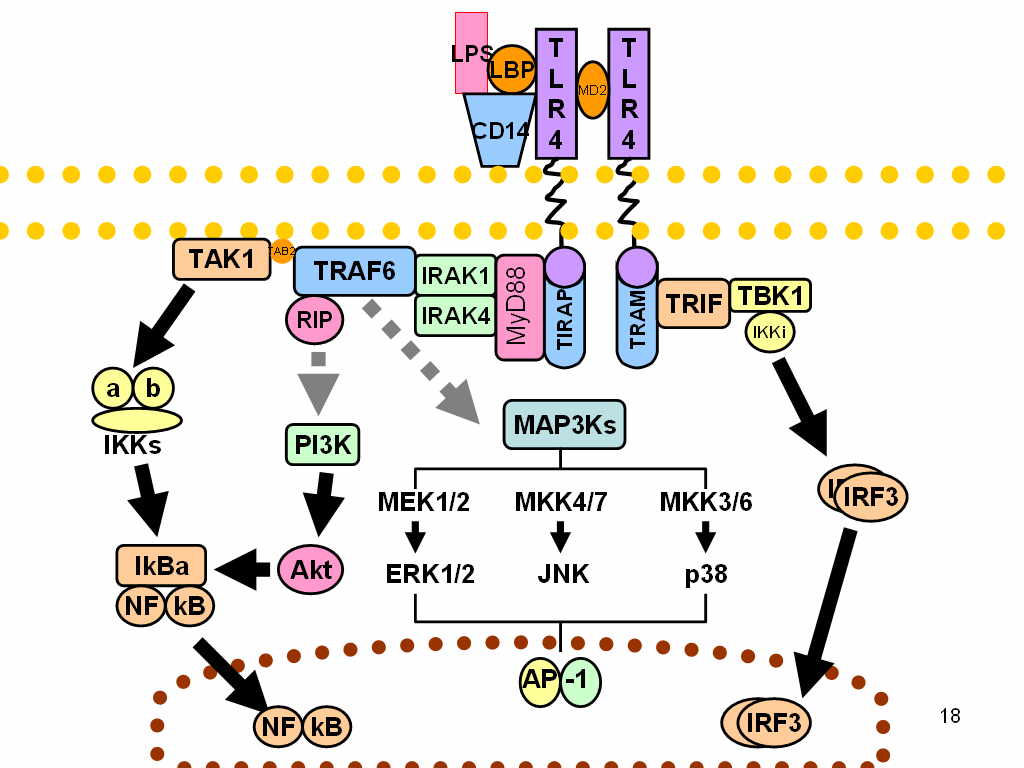
TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system. TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid (erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid (T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS. It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid and lauric acid a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte Antigen 96
Lymphocyte antigen 96, also known as "Myeloid Differentiation factor 2 (MD-2)," is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LY96'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in binding lipopolysaccharide with Toll-Like Receptor (TLR4). Function The MD-2 protein appears to associate with toll-like receptor 4 on the cell surface and confers responsiveness to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), thus providing a link between the receptor and LPS signaling. That is, the primary interface between TLR4 and MD-2 is formed before binding LPS and the dimerization interface is induced by binding LPS. Structure MD-2 has a β-cup fold structure composed of two anti-parallel β sheets forming a large hydrophobic pocket for ligand binding. Interactions Lymphocyte antigen 96 has been shown to interact with TLR 4. When LPS binds to a hydrophobic pocket in MD-2, it directly mediates dimerization of the two TLR4-MD-2 complexes. Thus, MD-2 form a heterodimer that recognizes a common pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |