|
Zengő
Zengő (; ) is the highest mountain in Mecsek Mountains in southern Hungary – its height is 682 metres.Pierre Jolivet, Jorge Santiago-Blay, Michael Schmitt, Research of chrysomelidae, BRILL, 2009 p. 23/ref> The peak is situated in the southeastern part of the range. On its top, along with a look-out tower, stand the ruins of a small medieval castle, which was probably built on the site of an earlier guard tower of the Roman Empire. The peak can be most easily reached from Pécsvárad or Hosszúhetény. Name Its name literally translates as ''"resonant"''. According to the local legend the noise heard from the mountain from time to time is caused by treasure hunters who entered the mountainside hundreds of years ago and could never come out again. Radar plan In 2005 the Hungarian government abandoned a plan to build a NATO radar on the peak after fierce resistance to the plan from locals and green groups who argued that the radar and the adjacent road construction woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecsek
Mecsek (; ; Serbian language, Serbian: ''Meček'' or Мечек; ) is a mountain range in southern Hungary. It is situated in the Baranya (region), Baranya region, in the north of the city of Pécs. Etymology The Hungarian toponym "Mecsek" derives from the sobriquet version of the name Mihály (Michael). Originally applied only to the hills adjacent to Pécs, the name Mecsek was first mentioned in 16th century. Geography The mountains cover an area of approximately 500 km2. The highest peak in the mountain range is Zengő (literally translates to 'resonant'), which has an elevation of 682 metres (2,238 feet). The Mecsek Hills consist of plateau-like block mountains of a broken, folded structure. Its basis is crystalline rock of Variscan origin surmounted by Triassic and Jurassic limestone and dolomite and Tertiary formations that form the main block. The mountains are divided by a structural fault running NW to SE. The eastern part consists mainly of high ridges of sedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pécsvárad
Pécsvárad (; ) is a town in Baranya County, southern Hungary. Geography Pécsvárad is on the southern slope of the Mecsek mountains, in particular the part called Kelet-Mecsek. It's at the foot of the Zengő, the highest peak of these mountains at 682 metres. The Danube is about 25 kilometers to the east-southeast. Pécs is 19 kilometers to the south-southwest. Lake Dombay is in the western outskirts of the town. about two kilomters from the center. It is a man made lake and recreational area. History The medieval history of Pécsvárad is closely connected to the medieval Pécsvárad Abbey, an abbey and castle that dominated the town. It was founded by Stephen I of Hungary in 1015. From here, bishop Astrik was later said to have left for Rome to collect the Holy Crown of Hungary, Crown of Hungary. Later kings expanded its possessions. After the 1526 Battle of Mohács and subsequent Ottoman invasion, the abbey was destroyed. The Ottoman occupation During the Turkish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hosszúhetény
Hosszúhetény (, ) is the most populous village in Baranya county, southwest Hungary, a significant centre of village tourism. It is located 18 kilometres northeast to Pécs, the county capital, in a valley between the feet of Zengő, the highest peak of the Mecsek mountains and the peak called :hu:Hármashegy, Hármashegy. It has a population of 3424 (as of 1 January 2010) and an area of . The valley has been inhabited since the Stone Age. Two other nearby villages belong to the administration of Hosszúhetény: :hu:Püspökszentlászló, Püspökszentlászló and Kisújbánya. Located in an environmentally protected area, a special microclimate producing rare flower species like ''Peony, Paeonia officinalis ssp'', among picturesque mountains, the three villages are popular among tourists who arrive from all parts of Hungary and abroad. One of the main sites is the arboretum of the episcopal castle in Püspökszentlászló. Tourism gives an increasing portion of the villagers' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Hungary
Hungary (Hungarian language, Hungarian: Magyarország) is a landlocked country in southeastern Central Europe, on the Eurasian Steppe. Situated in the Carpathian Basin, it has a land area of 93,030 square km, measuring about 250 km from north to south and 524 km from east to west. It has 2,106 km of boundaries, shared with Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia to the south and southwest, Slovenia to the west and southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary's modern borders were first established after World War I when, by the terms of the Treaty of Trianon in 1920, it lost more than 71% of what had formerly been the Kingdom of Hungary, 58.5% of its population, and 32% of the Hungarians. The country secured some boundary revisions from 1938 to 1941: In 1938 the First Vienna Award gave back territory from Czechoslovakia, in 1939 Hungary occupied Carpatho-Ukraine. In 1940 the Second Vienna Awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paeonia Officinalis
''Paeonia officinalis'', the common peony, or garden peony, is a species of flowering plant in the family (biology), family Paeoniaceae, native plant, native to mainly mountainous areas of Southern Europe and introduced in Central Europe, Central and Western Europe, Western Europe and North America. ''Paeonia officinalis'' was first used for medicinal purposes, then grown as an ornamental. Many selections are now used in horticulture, though the typical species is uncommon. ''Paeonia officinalis'' is still found wild in Europe. The cultivar 'Rubra Plena' (deep crimson double flowered) has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Description It is a herbaceous plant, herbaceous perennial plant, perennial growing to tall and wide, with leaves divided into 9 leaflets, and bowl-shaped deep pink or deep red flowers, in diameter, in late spring (May in the Northern Hemisphere). Distribution The common peony is native to Europe in Spain, northern Portugal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( ; , or ', ) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary. Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and east), the Drava and Mur River, Mura rivers (south), and the foothills of the Alps roughly along the border between Hungary and Austria (west). Transdanubia comprises the counties of Győr-Moson-Sopron, Komárom-Esztergom, Fejér, Veszprém (county), Veszprém, Vas, Zala County, Zala, Somogy County (former), Somogy, Tolna (county), Tolna, Baranya (county), Baranya and the part of Pest (county), Pest that lies west of the Danube. (In the early Middle Ages the latter was known as Pilis county.) This article deals with Transdanubia in this geographical meaning. Territorial changes While the northern, eastern and southern borders of the region are clearly marked by the Danube and Drava rivers, the western border was always identical with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Socialist Party
The Hungarian Socialist Party (, ), commonly known by its acronym MSZP (), is a centre-left to left-wing social-democratic and pro-European political party in Hungary. It was founded on 7 October 1989 as a post-communist evolution and one of two legal successors of the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party (MSZMP). Along with its conservative rival Fidesz, MSZP was one of the two most dominant parties in Hungarian politics until 2010; however, the party lost much of its popular support as a result of the Őszöd speech, the consequent 2006 protests in Hungary, and then the 2008 financial crisis. Following the 2010 election, MSZP became the largest opposition party in parliament, a position it held until 2018, when it was overtaken by the former far and now centre-right Jobbik. History The MSZP evolved from the communist Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party (or MSZMP), which ruled Hungary between 1956 and 1989. By the summer of 1989, the MSZMP was no longer a Marxist–Leninist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
László Sólyom
László Sólyom (, ; 3 January 1942 – 8 October 2023) was a Hungarian politician, lawyer, and librarian who was President of Hungary from 2005 until 2010. Previously he was the first president of the Constitutional Court of Hungary from 1990 to 1998. A prominent jurist and pro-democracy activist, Sólyom became the first president of the Constitutional Court at a time when the country was in the final years of its democratic transition after Hungarian People's Republic, decades of communist rule. During his mandate, the Court declared the Capital punishment in Hungary, death penalty unconstitutional, strengthened the protection of freedom of expression and conscience, and legitimated the domestic partnerships of homosexuals. Later, 2005 Hungarian presidential election, in 2005, he was elected president of Hungary, a largely ceremonial position, as an independent candidate. He held this office until 2010. Early life László Sólyom was born on 3 January 1942 in Pécs, Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmentalist
Environmentalism is a broad Philosophy of life, philosophy, ideology, and social movement about supporting life, habitats, and surroundings. While environmentalism focuses more on the environmental and nature-related aspects of Green politics, green ideology and politics, ecologism combines the ideology of Social ecology (theory), social ecology and environmentalism. ''Ecologism'' is more commonly used in continental European languages, while ''environmentalism'' is more commonly used in English but the words have slightly different connotations. Environmentalism advocates the preservation, restoration and improvement of the natural environment and critical Earth system science, earth system elements or processes such as the climate, and may be referred to as a movement to control pollution or protect plant and animal biodiversity, diversity. For this reason, concepts such as a land ethics, environmental ethics, biodiversity, ecology, and the biophilia hypothesis figure predomina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, modified leaves; corolla, the petals; androecium, the male reproductive unit consisting of stamens and pollen; and gynoecium, the female part, containing style and stigma, which receives the pollen at the tip of the style, and ovary, which contains the ovules. When flowers are arranged in groups, they are known collectively as inflorescences. Floral growth originates at stem tips and is controlled by MADS-box genes. In most plant species flowers are heterosporous, and so can produce sex cells of both sexes. Pollination mediates the transport of pollen to the ovules in the ovaries, to facilitate sexual reproduction. It can occur between different plants, as in cross-pollination, or between flowers on the same plant or even the same f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
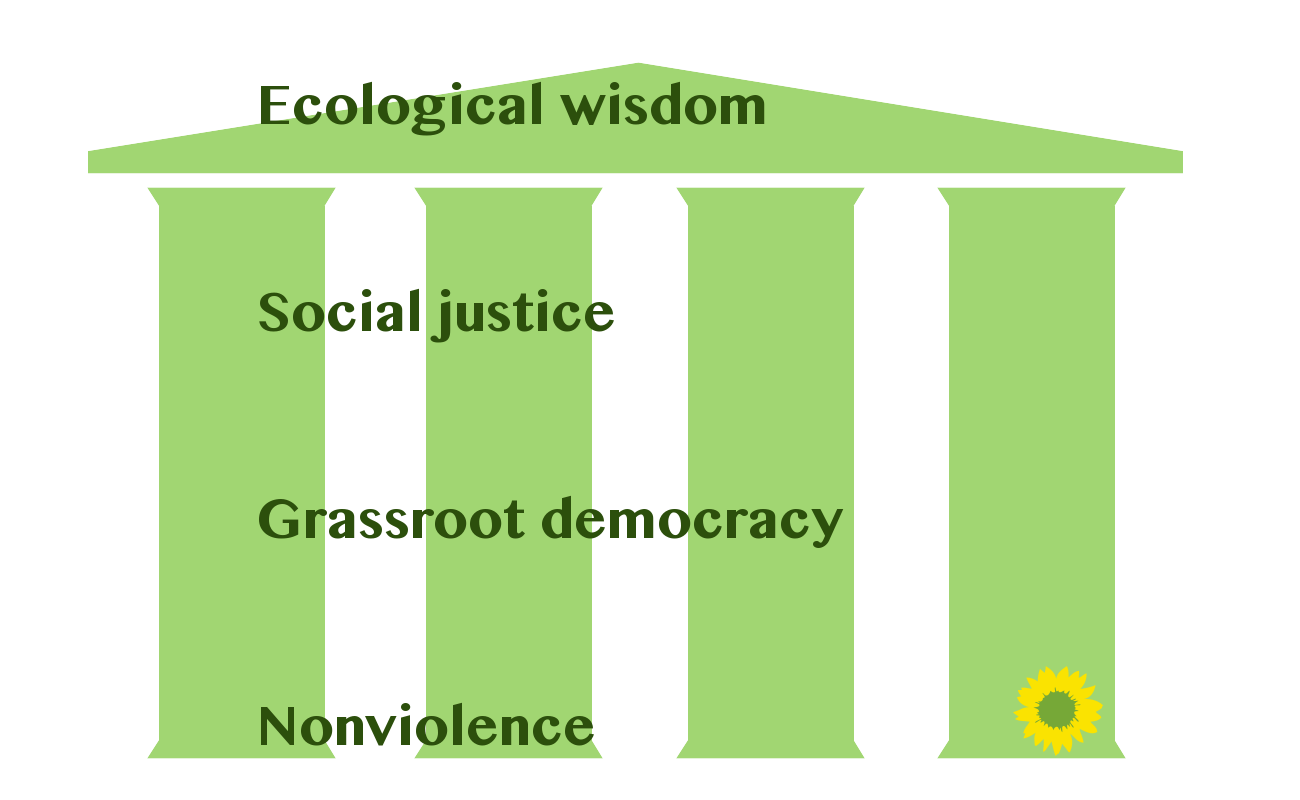
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |