|
Zemo Nikozi Church Of The Deity
The Zemo Nikozi church of the Deity ( ka, ზემო ნიქოზის ღვთაების ეკლესია, tr), also known as Ghvtaeba (ღვთაება), is a medieval Georgian Orthodox cathedral in the Gori Municipality, in Georgia's east-central region of Shida Kartli. It is part of the complex which also includes a bell-tower, an episcopal palace, and a circuit wall. The complex is inscribed on the list of Georgia's Immovable Cultural Monuments of National Significance. The complex stands in what is now the village of Zemo Nikozi—an "upper" part of the historical settlement of Nikozi—on the right bank of the Greater Liakhvi River, in the immediate proximity of the South Ossetia conflict zone, some 2 km south of the disputed entity's capital of Tskhinvali. The episcopal palace was badly damaged in fighting during the August 2008 Russo-Georgian War and subsequently underwent an emergency stabilization program. The Zemo Nikozi church is the seat of a bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zemo Nikozi
Zemo Nikozi is a village in central Georgia (shida kartli) near the Russian and south Ossetian military forces' check-point. It is the birthplace of Patriarch Kyrion II of Georgia. Nikozi is One of Georgia's oldest villages and home to early Christian churches and historical monuments. Nikozi is selected for the 5th Animation International Film Festival September. 2015. The annual Nikozi International Animated Film Festival will be held at the Episcopal Palace of the Nikozi Monastery. The Palace was completely destroyed in the 2008 August war however the festival has given the area new life and become a cultural centre for the town's youth. There is Nikozi Art School in the city. See also * Zemo Nikozi church of the Deity * Zemo Nikozi church of the Archangel See also * Shida Kartli Shida Kartli ( ka, შიდა ქართლი, , ; "Inner Kartli") is a landlocked administrative region (''Mkhare'') in eastern Georgia. It comprises a central part of the historical-ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razhden The Protomartyr
Razhden ( ka, რაჟდენი, tr, also transliterated as Ražden or Rajden; died ) was a 5th-century Persian people, Persian nobleman in the service of the Georgia (country), Georgian king Vakhtang I of Iberia and a convert to Christianity who was executed by the Sassanid Empire, Sassanid military in Kingdom of Iberia (antiquity), Iberia. He was canonized by the Georgian Orthodox Church as St. Razhden the Protomartyr (რაჟდენ პირველმოწამე, ''razhden pirvelmotsame''), with his feast day marked on August 16 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), August 16 (Old Style, O.S. August 3).Machitadze, Archpriest Zakaria (2006)"St. Razhden, Protomartyr of the Georgian Church (†457)" i''The Lives of the Georgian Saints''. ''pravoslavie.ru''. Retrieved on 2011-12-18. History The earliest mention of Razhden is found in the ''History of King Vakhtang Gorgasali'', part of the medieval The Georgian Chronicles, Georgian historical compendium, composed in the 8th or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleography
Palaeography ( UK) or paleography ( US; ultimately from grc-gre, , ''palaiós'', "old", and , ''gráphein'', "to write") is the study of historic writing systems and the deciphering and dating of historical manuscripts, including the analysis of historic handwriting. It is concerned with the forms and processes of writing; not the textual content of documents. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of scriptoria. The discipline is one of the auxiliary sciences of history. It is important for understanding, authenticating, and dating historic texts. However, it generally cannot be used to pinpoint dates with high precision. Application Palaeography can be an essential skill for historians and philologists, as it tackles two main difficulties. First, since the style of a single alphabet in each given langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asomtavruli
The Georgian scripts are the three writing systems used to write the Georgian language: #Asomtavruli, Asomtavruli, #Nuskhuri, Nuskhuri and #Mkhedruli, Mkhedruli. Although the systems differ in appearance, their Letter (alphabet), letters share the same names and alphabetical order and are written horizontally from Writing system#Directionality, left to right. Of the three scripts, Mkhedruli, once the civilian royal script of the Kingdom of Georgia and mostly used for the royal charters, is now the standard script for modern Georgian and its related Kartvelian languages, whereas Asomtavruli and Nuskhuri are used only by the Georgian Orthodox Church, in ceremonial religious texts and Iconography#Christian iconography, iconography. Georgian scripts are unique in their appearance and their exact origin has never been established; however, in strictly structural terms, their alphabetical order largely corresponds to the Greek alphabet, with the exception of letters denoting uniquely G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-in-square
A cross-in-square or crossed-dome floor plan, plan was the dominant architectural form of middle- and late-period Byzantine Empire, Byzantine church architecture, churches. It featured a square centre with an internal structure shaped like a cross, topped by a dome. The first cross-in-square churches were probably built in the late 8th century, and the form has remained in use throughout the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox world unto the present day. In the West, Donato Bramante's first design (1506) for St. Peter's Basilica was a centrally planned cross-in-square under a dome and four subsidiary domes. In German, such a church is a , or ‘cross-dome church’. In French, it is an , ‘church with an inscribed figure, inscribed cross’. Architecture Architectural form A cross-in-square church is centered around a quadratic cella, naos (the ‘square’) which is divided by four columns or piers into nine bay (architecture), bays (divisions of space). The inner five divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikozi Belltower (Photo A
Zemo Nikozi is a village in central Georgia (shida kartli) near the Russian and south Ossetian military forces' check-point. It is the birthplace of Patriarch Kyrion II of Georgia. Nikozi is One of Georgia's oldest villages and home to early Christian churches and historical monuments. Nikozi is selected for the 5th Animation International Film Festival September. 2015. The annual Nikozi International Animated Film Festival will be held at the Episcopal Palace of the Nikozi Monastery. The Palace was completely destroyed in the 2008 August war however the festival has given the area new life and become a cultural centre for the town's youth. There is Nikozi Art School in the city. See also * Zemo Nikozi church of the Deity * Zemo Nikozi church of the Archangel See also * Shida Kartli Shida Kartli ( ka, შიდა ქართლი, , ; "Inner Kartli") is a landlocked administrative region (''Mkhare'') in eastern Georgia. It comprises a central part of the historical-geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikozi Cathedral
Zemo Nikozi is a village in central Georgia (shida kartli) near the Russian and south Ossetian military forces' check-point. It is the birthplace of Patriarch Kyrion II of Georgia. Nikozi is One of Georgia's oldest villages and home to early Christian churches and historical monuments. Nikozi is selected for the 5th Animation International Film Festival September. 2015. The annual Nikozi International Animated Film Festival will be held at the Episcopal Palace of the Nikozi Monastery. The Palace was completely destroyed in the 2008 August war however the festival has given the area new life and become a cultural centre for the town's youth. There is Nikozi Art School in the city. See also * Zemo Nikozi church of the Deity * Zemo Nikozi church of the Archangel See also * Shida Kartli Shida Kartli ( ka, შიდა ქართლი, , ; "Inner Kartli") is a landlocked administrative region (''Mkhare'') in eastern Georgia. It comprises a central part of the historical-geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a population of approximately 675 million; it operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros. The organisation is distinct from the European Union (EU), although it is sometimes confused with it, partly because the EU has adopted the original Flag of Europe, European flag, created for the Council of Europe in 1955, as well as the Anthem of Europe, European anthem. No country has ever joined the EU without first belonging to the Council of Europe. The Council of Europe is an official United Nations General Assembly observers, United Nations Observer. Being an international organization, the Council of Europe cannot make laws, but it does have the ability to push for the enf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamar Of Georgia
Tamar the Great ( ka, თამარ მეფე, tr, lit. "King Tamar") ( 1160 – 18 January 1213) reigned as the Queen of Georgia from 1184 to 1213, presiding over the apex of the Georgian Golden Age. A member of the Bagrationi dynasty, her position as the first woman to rule Georgia in her own right was emphasized by the title ''mepe'' ("king"), afforded to Tamar in the medieval Georgian sources. Tamar was proclaimed heir and co-ruler by her reigning father George III in 1178, but she faced significant opposition from the aristocracy upon her ascension to full ruling powers after George's death. Tamar was successful in neutralizing this opposition and embarked on an energetic foreign policy aided by the decline of the hostile Seljuq Turks. Relying on a powerful military elite, Tamar was able to build on the successes of her predecessors to consolidate an empire which dominated the Caucasus until its collapse under the Mongol attacks within two decades after Tamar's dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Description Of The Kingdom Of Georgia
''Description of Kingdom of Georgia'' was written by Vakhushti Bagrationi. The full name of the work is "''Description of Kingdom of Georgia, its habits and canons''" ( ka, აღწერა სამეფოსა საქართველოსა, ზნენი და ჩვეულებანი საქართველოსანი). The work was completed on 20 October 1745 in Moscow. The work thoroughly describes the geography of Georgia, its regions and peoples, and narrates the history of Georgia from its origin to the first half of the 18th century. The work was inscribed on UNESCO's Memory of the World Register Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ... in 2013. References Historiography of Georgia (country) 18th-century history books Memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
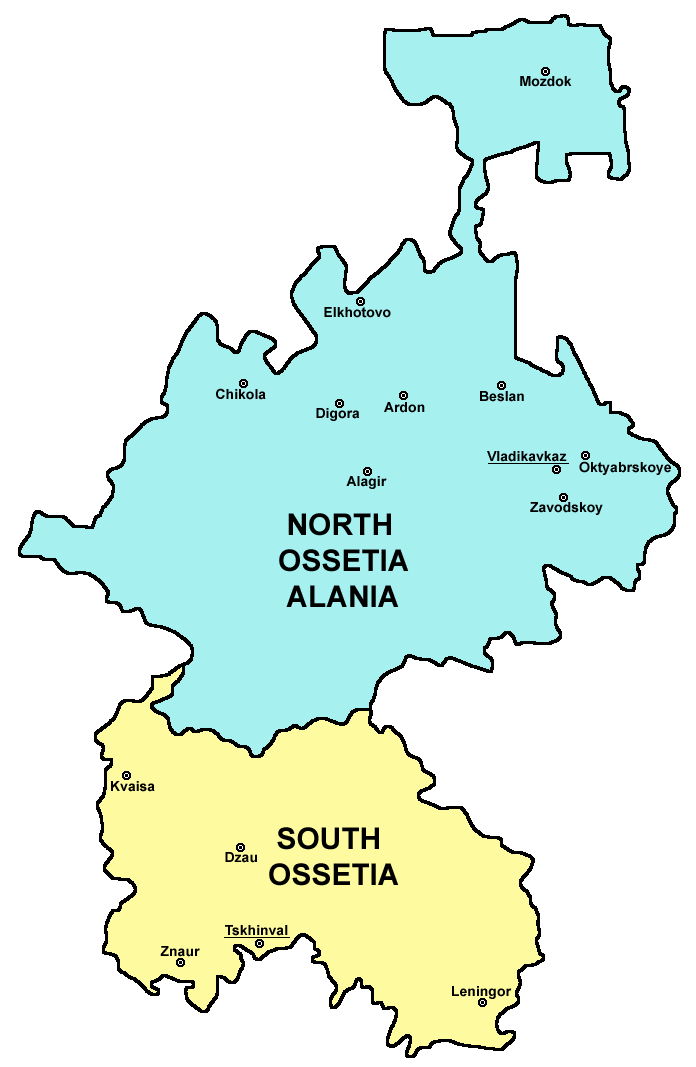
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774 — North Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire. * 1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian SFSR, South Ossetia remains a part of Georgian SSR. * 20 September 1990 — South Osse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvals
The Dvals ( ka, დვალები, ''Dvalebi''; os, Туалтæ, ''Twaltæ'') were a ethnographic group of Georgians, their lands lying on both sides of the central Greater Caucasus mountains, somewhere between the Darial and Mamison gorges. This historic territory mostly covers the north of Kartli, parts of the Racha and Khevi regions in Georgia and south of Ossetia in Russia. Etymology The name of the ''Dvals'' ( ka, დვალნი, ) is found in old Georgian annals. Their land was called Dvaleti (დვალეთი. ''Dvalet`i'') after them. The ethnonym survived to modern times as ''"Twal"'' and ''"Urs-Twal"'' ( os, Урстуалтæ meaning "white Twals"). The Georgian surname ''Dvali'' (დვალი), ''Dvalishvili'' (დვალიშვილი), Dvalidze(დვალიძე) and Ossetian ''Tuallagov/Twallægtæ'' also come from the name Dvals. History When the Mongols destroyed the Alanian kingdom in the Northern Caucasus in the 13th–14th centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)