|
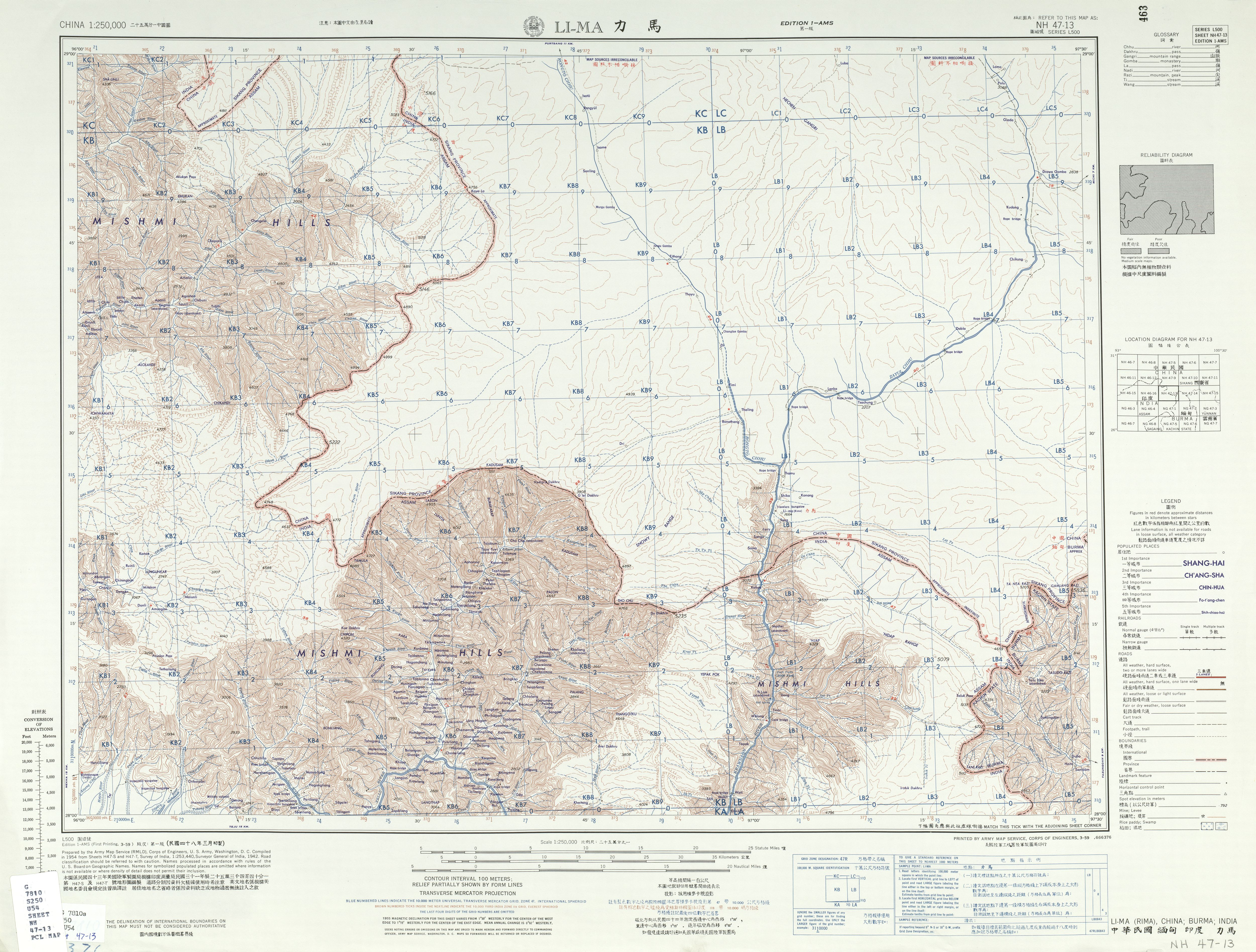
Lohit River
The Lohit River, also known as the Zayul Chu by the Tibetans and Tellu by the Mishmis, is a river in China and India, which joins the Brahmaputra River in the state of Assam. It is formed in the Zayul County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, through a merger of two rivers: the Kangri Karpo Chu (also called Rongto Chu and Zayul Ngu Chu), which originates in the Kangri Karpo range, and Zayul Chu (), which originates to its northeast. The two rivers merge below the town of Rima. The combined river descends through this mountainous region and surges through Arunachal Pradesh in India for before entering the plains of Assam where it is known as the Lohit River. Tempestuous and turbulent, and known as the river of blood partly attributable to the lateritic soil, it flows through the Mishmi Hills, to meet the Siang (Brahmaputra) at the head of the Brahmaputra valley. Course Thickly forested for the most part, alpine vegetation gives way to subtropical forests, and then to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zayul River
The Lohit River, also known as the Zayul Chu by the Tibetans and Tellu by the Mishmis, is a river in China and India, which joins the Brahmaputra River in the state of Assam. It is formed in the Zayul County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, through a merger of two rivers: the Kangri Karpo Chu (also called Rongto Chu and Zayul Ngu Chu), which originates in the Kangri Karpo range, and Zayul Chu (), which originates to its northeast. The two rivers merge below the town of Rima. The combined river descends through this mountainous region and surges through Arunachal Pradesh in India for before entering the plains of Assam where it is known as the Lohit River. Tempestuous and turbulent, and known as the river of blood partly attributable to the lateritic soil, it flows through the Mishmi Hills, to meet the Siang (Brahmaputra) at the head of the Brahmaputra valley. Course Thickly forested for the most part, alpine vegetation gives way to subtropical forests, and then to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
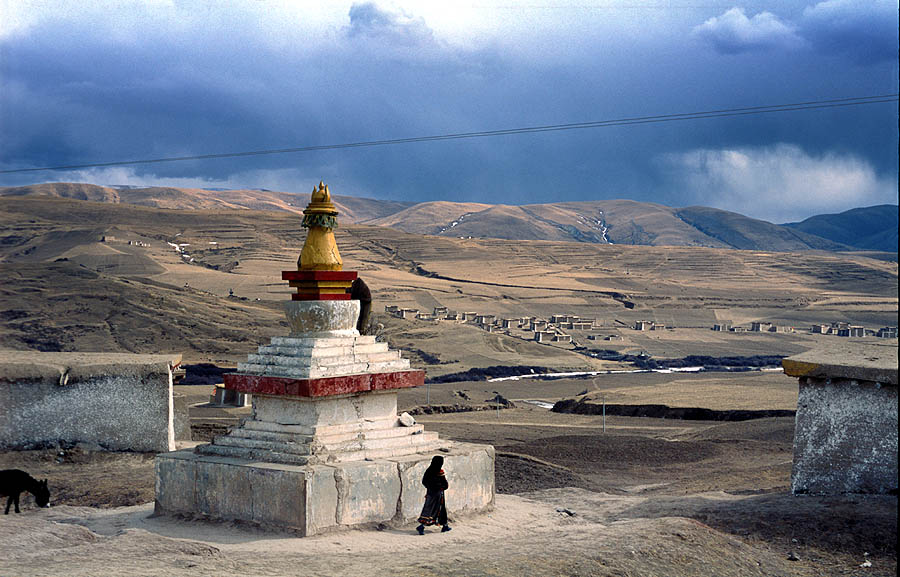
Rima, Tibet
__NOTOC__ Rima (; ) is the former capital of the Zayul in the southeastern Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It is on the border with India's Arunachal Pradesh at the confluence of the ''Rongto Chu'' and ''Zayul Chu'' rivers, which join to form the Zayul River The Lohit River, also known as the Zayul Chu by the Tibetans and Tellu by the Mishmis, is a river in China and India, which joins the Brahmaputra River in the state of Assam. It is formed in the Zayul County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, ... (or Lohit River) before it flows into Arunachal Pradesh. Rima was a notable border trading town, which the British contemplated as a location for a trade mart in the Lhasa Convention. References Bibliography * * * Populated places in Nyingchi {{Tibet-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangri Karpo
Kangri Karpo (), also spelt Gangri Garbo (), is a mountain range in eastern Tibet, located primarily in Nyingchi Prefecture as well as a portion of Qamdo Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. The mountain range lies to the east of the Himalayas and to the west of the Hengduan Mountains. The mountains are geographically a southern extension of the eastern Transhimalayas. Physical geography and climate The Kangri Karpo stretch for approximately from west to east. They lie at the eastern end of the Himalayan Range and were formed at the same time during the Indian subcontinent's collision with Eurasia. The Kangri Karpo are geologically related to the Himalayas, but are separated by the Yarlung Tsangpo's Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon, Grand Canyon. The eastern anchor of the Himalayas, Namcha Barwa, rises above the western Kangri Karpo just beyond the Yarlung Tsangpo. To the north, the Kangri Karpo are separated from the Nyenchen Tanglha by the Parlung Tsangpo River. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mêdog County
Mêdog, or Metok, or Motuo County (; ), also known as Pemako ( meaning "Lotus Array", ), is a county as well as a traditional region of the prefecture-level city of Nyingchi in the Tibet Autonomous Region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Pemako is considered famous as the Nyingma master Dudjom Rinpoche's birthplace, and as a prophesied refuge for Tibetan Buddhists by Padmasambhava. Geography Medog County is located in the southeast of the Tibet Autonomous Region and at the lower branch of Yarlung Tsangpo River. Medog County covers an area of . The average altitude of the county is above sea level. The county is located in the average altitude ranging from above sea level. It stretches from south of Kongpo and Bomê County through the lower Yarlung Tsangpo River to Arunachal Pradesh, surrounded by high mountains: the tallest is Namcha Barwa at ). Pemako has lush vegetation and many species of wild animals. Unlike other parts of Tibet, it receives plenty of rain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhimalayas
The Transhimalaya (also spelled Trans-Himalaya), or "Gangdise – Nyenchen Tanglha range" ( zh, s=冈底斯-念青唐古拉山脉, p=Gāngdǐsī-Niànqīngtánggǔlā Shānmài), is a mountain range in China, India and Nepal, extending in a west–east direction parallel to the main Himalayan range. Located north of Yarlung Tsangpo river on the southern edge of the Tibetan Plateau, the Transhimalaya is composed of the Gangdise range to the west and the Nyenchen Tanglha range to the east. The name ''Transhimalaya'' was introduced by the Swedish geographer Sven Hedin in early 20th century. The Transhimalaya was described by the ''Columbia Lippincott Gazetteer'' in 1952 as an "ill-defined mountain area" with "no marked crest line or central alignment and no division by rivers." On more-modern maps the Kailas Range (Gangdise or Kang-to-sé Shan) in the west is shown as distinct from the Nyenchen Tanglha range in the east. Geology The Transhimalayas are geologically distinct from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishmi Hills
The Mishmi Hills are located at the northeastern tip of India, in northeastern Arunachal Pradesh. On the Chinese side, they form the southern parts of Nyingchi Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region. These hills occur at the junction of Northeastern Himalaya and Indo-Burma ranges. The Himalayan arc takes a sharp turn and meets Indo-Burma ranges. The rocks of eastern lesser Himalaya and the central crystallines appear to be largely attenuated and truncated in Mishmi Hills. Geography Geomorphically, the Mishmi Hills are divided into 2 sections the flood plains of tributaries of Brahmaputra river and the Arunachal Himalayas consisting of snow-capped mountains, lower Himalayan ranges, and Shivalik ranges. The Hills reach heights above but have not been properly mapped. This hilly area is characterised by steeply sloping landform, sub-tropical evergreen forest and high rainfall. The central part of the Hills wrap around both sides of the Dibang Valley. The Mishmi Hills are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County (People's Republic Of China)
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces and Autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin Dynasty. The number of counties in China proper gradually increased from dynasty to dynasty. As Qin Shi Huang reorganized the counties after his unification, there were about 1,000. Under the Eastern Han Dynasty, the number of counties increased to above 1,000. About 1400 existed when the Sui dynasty abolish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawagarbo
Kawa Garbo or Khawa Karpo (; also transcribed as Kawadgarbo, Khawakarpo, Moirig Kawagarbo, Kawa Karpo or Kha-Kar-Po), as it is known by local residents and pilgrims, or Kawagebo Peak (), is the highest mountain in the Chinese province of Yunnan. It is located on the border between Dêqên County, Yunnan, and the counties of Zogang and Zayü of the Tibet Autonomous Region. It rises about west of Shengping (升平镇), the seat of Dêqên County, which lies on China National Highway 214. What is now Dêqên County has been part of Yunnan since the 1720s, when the current border with Tibet was established by the early Qing Dynasty. Kawagarbo is one of the most sacred peaks in the Tibetan world Keith Dowman. 1997. The Sacred Life of Tibet. San Francisco, California, USA: Thorsons. and is often referred to as Nyainqênkawagarbo to show its sacredness and avoid ambiguousness with the other Kawagarbo in the Anung-Derung-speaking Gongshan County. Geography Kawagarbo is the high poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of (about five times the size of Metropolitan France). With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World". The Tibetan Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |