|
Zawyet El Aryan
Zawyet El Aryan () is a town in the Giza Governorate, located between Giza and Abusir. To the west of the town, just in the desert area, is a necropolis, referred to by the same name. Almost directly east across the Nile is Memphis. In Zawyet El Aryan, there are two pyramid complexes and five mastaba cemeteries. Pyramids Layer Pyramid The Layer Pyramid was built in the Third Dynasty, probably during the reign of Khaba. The pyramid was meant to be a step pyramid of possibly five to seven steps. No casing stones have been found, suggesting that the pyramid was never finished. The layout of the underground chambers resembles that of the Buried Pyramid. A corridor leading into the interior has thirty-two side chambers meant for storage of the burial equipment.Verner, Miroslav: ''The Pyramids: The Mystery, Culture, and Science of Egypt's Great Monuments''. Grove Press. 2001 (1997). , p. 270.Rainer Stadelmann: ''Die ägyptischen Pyramiden. Vom Ziegelbau zum Weltwunder'' (= ''K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Egypt
Egypt has a Centralisation, centralised system of local government officially called local administration as it is a branch of the Executive (government), Executive. The country is divided into twenty-seven governorates ( '; ; genitive case#Arabic, genitive case: ; plural: '), the top tier of local administration. A governorate is administered by a governor, who is appointed by the President of Egypt and serves at the president's discretion. Governors have the civilian rank of minister and report directly to the Prime Minister of Egypt, prime minister, who chairs the Board of Governors ''(majlis al-muhafzin)'' and meets with them on a regular basis. The Ministry of Local Development, Minister of Local Development coordinates the governors and their governorate's budgets. Overview Egypt generally has four tiers of local administration units: governorates, cities, counties ''(marakiz)'', districts (subdivisions of cities) and villages (subdivisions of counties). There is a tie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is documented. The Fourth Dynasty heralded the height of the pyramid-building age. The relative peace of the Third Dynasty allowed the Dynasty IV rulers the leisure to explore more artistic and cultural pursuits. King Sneferu's building experiments led to the evolution from the mastaba-styled step pyramids to the smooth sided “true” pyramids, such as those on the Giza Plateau. No other period in Egypt's history equaled Dynasty IV's architectural accomplishments.Egypt: Land and Lives of the Pharaohs Revealed, (2005), pp. 80–90, Global Book Publishing: Australia Each of the rulers of this dynasty (except for Shepseskaf, the last) commissioned at least one pyramid to serve as a tomb or cenotaph. The Fourth Dynasty was the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Base
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the military or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. A military base always provides accommodations for one or more units, but it may also be used as a command center, training ground or proving ground. In most cases, military bases rely on outside help to operate. However, certain complex bases are able to endure on their own for long periods because they are able to provide food, water and other necessities for their inhabitants while under siege. Bases for military aviation are called military air bases, or simply "air bases". Bases for military ships are called naval bases. The environmental impact of a given military base is dependent on its size and the manner of operation conducted at the base. Commonly, habitat destruction, reductions in soil quality, chemical contamination, and noise pollution are among the environmental damages ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serekh
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a serekh is a rectangular enclosure representing the niched or gated façade of a palace surmounted by (usually) the Horus falcon, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The serekh was the earliest convention used to set apart the royal name in ancient Egyptian iconography, predating the later and better known cartouche by four dynasties and five to seven hundred years. Appearance A serekh was an ornamental vignette combining a view of a palace façade and a plan (top view) of the royal courtyard. The term ''serekh'' derives from the Egyptian word for " facade". Different serekhs on different types of object display countless variations of the façade decor in its complexity and detail. It seems that no strict artistic rules for the design of the serekh itself existed.Jürgen von Beckerath: ''Handbuch der ägyptischen Königsnamen''. Münchner Ägyptologische Studien. Bd. 49. Philipp von Zabern, Mainz 1999, , p. 7-9.Rolf Gundlach: ''Horus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. Marble is commonly used for Marble sculpture, sculpture and as a building material. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shining stone", perhaps from the verb (), "to flash, sparkle, gleam"; Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that a "Pre-Greek origin is probable". This Stem (linguistics), stem is also the ancestor of the English language, English word "marmoreal," meaning "marble-like." While the English term "marble" resembles the French language, French , most other European languages (with words like "marmoreal") more closely resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba
A mastaba (, or ), also mastabah, mastabat or pr- djt (meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity" or "eternal house" in Ancient Egyptian), is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks. These edifices marked the burial sites of many eminent Egyptians during Egypt's Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. In the Old Kingdom epoch, local kings began to be buried in pyramids instead of in mastabas, although non-royal use of mastabas continued for over a thousand years. Egyptologists call these tombs ''mastaba'', from the Arabic word (maṣṭaba) "stone bench". History The afterlife was important in the religion of ancient Egyptians. Their architecture reflects this, most prominently by the enormous amounts of time and labour involved in building tombs. Ancient Egyptians believed the soul could live only if the body was fed and preserved from corruption and depredation. Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt (Roman Province)
, conventional_long_name = Roman Egypt , common_name = Egypt , subdivision = Roman province, Province , nation = the Roman Empire , era = Late antiquity , capital = Alexandria , title_leader = Praefectus Augustalis , image_map = Roman Empire - Aegyptus (125 AD).svg , image_map_caption = Province of Aegyptus in AD 125 , year_start = 30 BC , event_start = Conquest of Ptolemaic Kingdom , event1 = Formation of the Diocese of Egypt, Diocese , date_event1 = 390 , year_end = 641 , event_end = Muslim conquest of Egypt, Muslim conquest , life_span = 30 BC – 641 AD , stat_year1 = 1st century AD , stat_pop1 = . , today = Egypt , p1 = Ptolemaic Kingdom , flag_p1 = Ptolemaic-Empire 200bc.jpg , s1 = Sasanian Egypt , flag_s1 = Derafsh Kaviani flag of the late Sassanid Empire.svg , s2 = Rashidun Caliphate , flag_s2 = Mohammad adil-Rashidun-empire-at-its-peak-close.PNG , demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
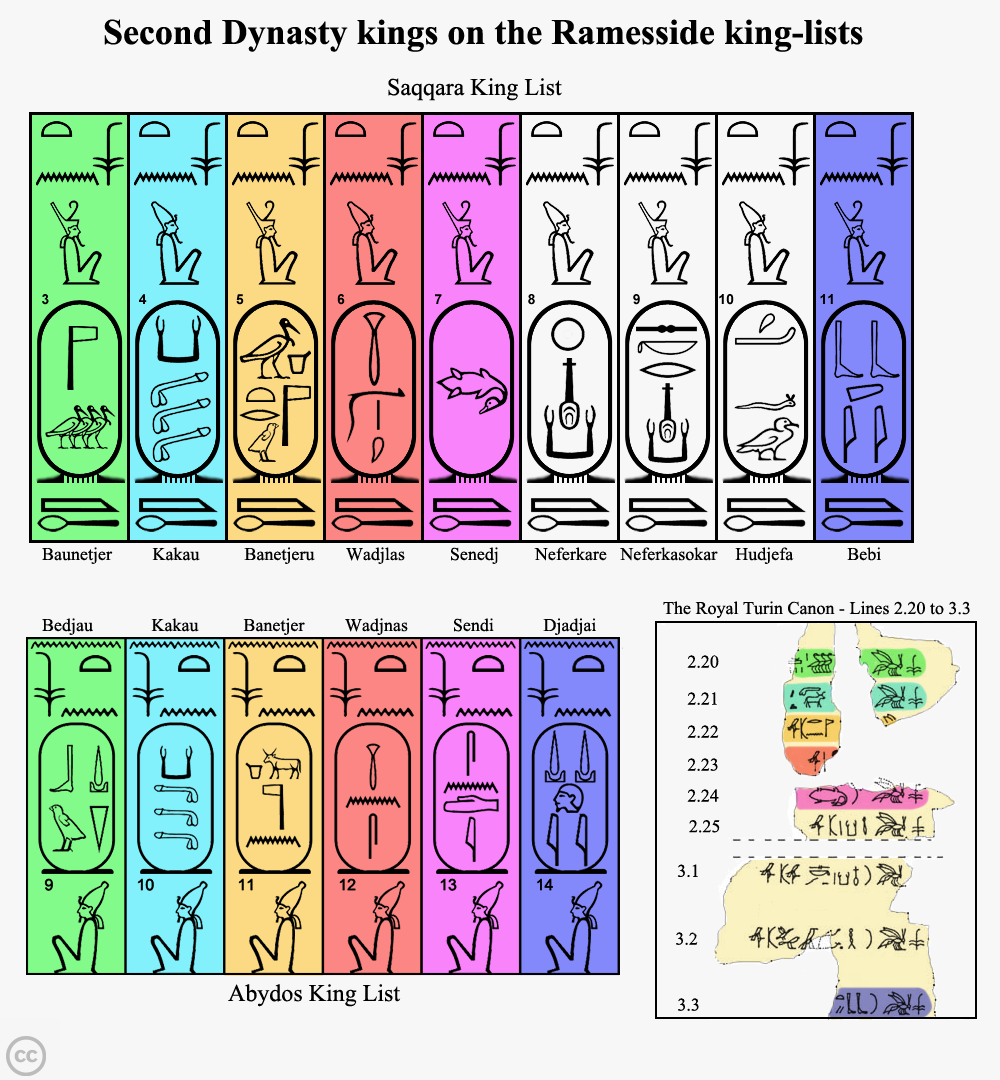
Second Dynasty Of Egypt
The Second Dynasty of ancient Egypt (or Dynasty II, c. 2890 – c. 2686 BC) is the latter of the two dynasties of the Egyptian Archaic Period, when the seat of government was centred at Thinis. It is most known for its last ruler, Khasekhemwy, but is otherwise one of the most obscure periods in Egyptian history. Though archaeological evidence of the time is very scant, contrasting data from the First and Third Dynasties indicates important institutional and economic developments during the Second Dynasty. Rulers For the first three pharaohs, sources are fairly close in agreement and the order is supported by an inscription on the statuette of Hetepdief, who served in the mortuary cults of these three kings. But the identity of the next few rulers is unclear. Surviving sources might be giving the Horus name or the Nebty name and the birth names of these rulers. They may also be entirely different individuals, or could be legendary names. This might never be resolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Dynasty Of Egypt
The First Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty I) covers the first series of Egyptian kings to rule over a unified Egypt. It immediately follows the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, possibly by Narmer, and marks the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, a time at which power was centered at Thinis. The date of this period is subject to scholarly debate about the Egyptian chronology. It falls within the early Bronze Age and is variously estimated to have begun anywhere between the 34th and the 30th centuriesBC. In a 2013 study based on radiocarbon dates, the beginning of the First Dynasty—the accession of Narmer (commonly known as Menes)—was placed at 3100BC give or take a century (3218–3035, with 95% confidence). The dynasty Information about this dynasty is derived from a few monuments and other objects bearing royal names, the most important being the Narmer Palette and Narmer Macehead, as well as Den and Qa'a king lists. No detailed records of the first two dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buried Pyramid
The Buried Pyramid (also called the Pyramid of Sekhemkhet) is an unfinished step pyramid constructed c. 2645 BC for Sekhemkhet Djoserty. He was the second pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, which reigned over Egypt circa 2686–2613 BC and is usually placed at the beginning of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Many historians believe that the third dynasty played an important role in the transition from Early Dynastic Period of Egypt to the Age of the Pyramids. The pyramid may be visited, but the public is not allowed access to the base and substructures. Sekhemkhet Djoserty was also the successor to the better-known pharaoh Djoser, who was buried in his famous step pyramid at Saqqara. The buried pyramid was originally modelled after Djoser's step pyramid and is located several hundred metres southwest. It is also arguable that the pyramid of Sekhemkhet was originally designed to surpass the step pyramid of Djoser but barely made it above ground level and hence was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giza Governorate
Giza Governorate ( ar, محافظة الجيزة ') is one of the governorates of Egypt. It is in the center of the country, situated on the west bank of the Nile River opposite Cairo. Its capital is the city of Giza. It includes a stretch of the left bank of the Nile Valley around Giza, and acquired a large stretch of Egypt's Western Desert, including Bahariya Oasis when the 6th of October Governorate was merged into it on 14 April 2011. The Giza Governorate is also home to the Great Sphinx and the Pyramids of Giza. Overview The rate of poverty is more than 60% in this governorate but recently some social safety networks have been provided in the form of financial assistance and job opportunities. The funding has been coordinated by the country's Ministry of Finance and with assistance from international organizations. Municipal divisions The governorate is divided into municipal divisions, with a total estimated population as of July 2017 of 8,666,090. In the case of Giz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)