|
Zahnradbahn Stuttgart
The Stuttgart Rack Railway (German: ''Zahnradbahn Stuttgart'') is an electric rack railway in Stuttgart, Germany. It is the only urban rack railway in Germany, and one of only four rack railways operating in Germany, along with the Bavarian Zugspitze Railway, the Drachenfels Railway and the Wendelstein Railway. Overview Affectionately called ''Zacke'' (''spike'') by the residents of Stuttgart, the line was opened on 23 August 1884. It connects the urban districts of Stuttgart South (Marienplatz) and Degerloch (Albplatz). The route runs along the ''Alte Weinsteige'', which was historically the main route to the ''Filder'' towns until the ''Neue Weinsteige'' was built in 1826. Over its route the line climbs a height of (from AMSL). The maximum grade on the route is 17.5% (7 in 40) (between Liststrasse and Pfaffenweg). On the branch line to the depot of the (old) rack railway yard, the maximum is 20.0% (1 in 5). Between the stops at Pfaffenweg and Wielandshöhe there is a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riggenbach Rack System
A rack railway (also rack-and-pinion railway, cog railway, or cogwheel railway) is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with this rack rail. This allows the trains to operate on steep grades above 10%, which is the maximum for friction-based rail. Most rack railways are mountain railways, although a few are transit railways or tramways built to overcome a steep gradient in an urban environment. The first cog railway was the Middleton Railway between Middleton and Leeds in West Yorkshire, England, United Kingdom, where the first commercially successful steam locomotive, ''Salamanca'', ran in 1812. This used a rack and pinion system designed and patented in 1811 by John Blenkinsop. The first mountain cog railway was the Mount Washington Cog Railway in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, which carried its first fare-paying passengers in 1868. The track was comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verkehrs- Und Tarifverbund Stuttgart
The ''Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund Stuttgart GmbH'' (VVS; en, Stuttgart Transport and Tariff Association LLC) is a transport association that coordinates the local public transport in Stuttgart, the capital of Baden-Württemberg, as well as in the neighbouring districts of Böblingen, Esslingen, Ludwigsburg and Rems-Murr, and parts of Göppingen and Ostalbkreis. The network ensures uniform conditions of carriage and fare regulations as well as a coordinated timetable. It cooperates with the administrative districts and municipalities as well as the Verband Region Stuttgart. History The ''VVS-Gemeinschaftsstarif'' was introduced on 1 October 1978 when the ''Stuttgarter Vorortverkehr'' was replaced by the S-Bahn Stuttgart. Initially, it was a tariff community between Deutsche Bundesbahns (express trains, local trains, S-Bahn and train buses), the german post and almost all means of transport of Stuttgart trams (SSB). At the same time, SSB gave up its own fare; only on the airp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is usually, though not necessarily, steel bars ( rebar) and is usually embedded passively in the concrete before the concrete sets. However, post-tensioning is also employed as a technique to reinforce the concrete. In terms of volume used annually, it is one of the most common engineering materials. In corrosion engineering terms, when designed correctly, the alkalinity of the concrete protects the steel rebar from corrosion. Description Reinforcing schemes are generally designed to resist tensile stresses in particular regions of the concrete that might cause unacceptable cracking and/or structural failure. Modern reinforced concrete can contain varied reinforcing materials made of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
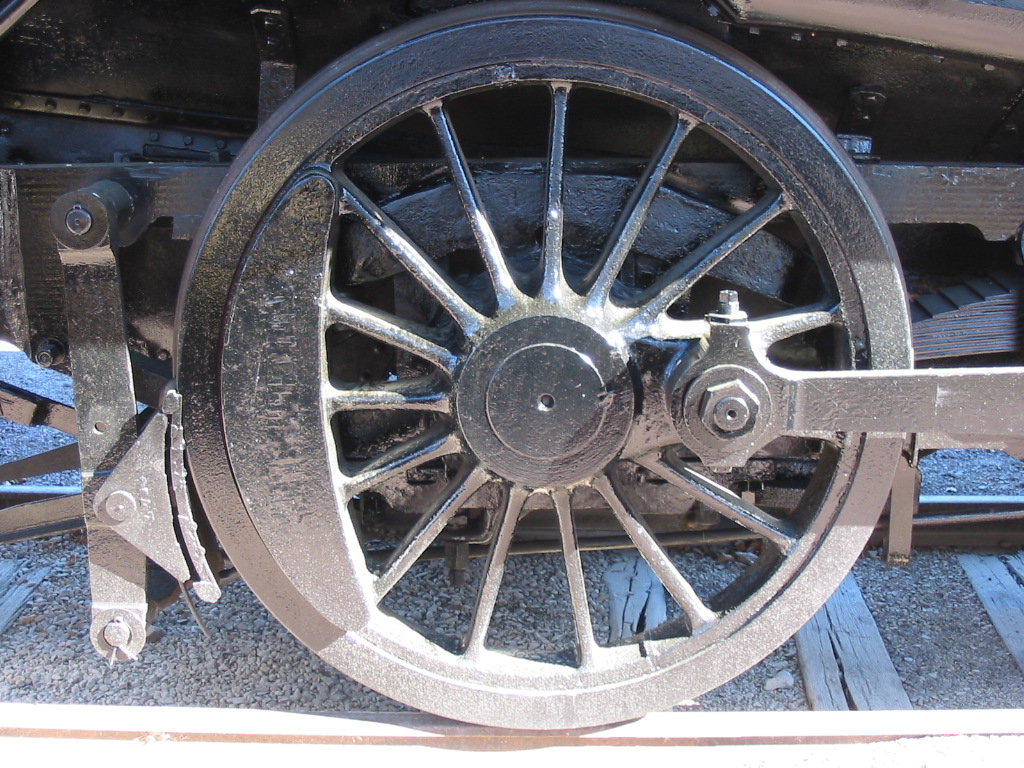
Maschinenfabrik Esslingen
Maschinenfabrik Esslingen (ME), was a German engineering firm that manufactured locomotives, tramways, railway wagons, roll-blocks, technical equipment for the railways, (turntables and traversers), bridges, steel structures, pumps and boilers. Founding It was founded by Emil Kessler on 11 March 1846 in Stuttgart, as a result of an initiative of the Kingdom of Württemberg to create a railway industry that was not dependent on foreign manufacturers. Emil Kessler brought vital experience from his time with the engineering works in Karlsruhe, where he had been a member of the board since 1837 and the sole director since 1842. The foundation stone of the new factory was laid at Esslingen am Neckar on 4 May 1846. One year later, in October 1847, the first locomotive ordered by the Royal Württemberg State Railways (''Königlich Württembergische Staats-Eisenbahnen'') or ''K.W.St. E.'' was delivered. History After the death of Emil Kessler in 1867 his 26-year-old son, Emil Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railcar
A railcar (not to be confused with a railway car) is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach (carriage, car), with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors" (or "rail motors"). Self-propelled passenger vehicles also capable of hauling a train are, in technical rail usage, more usually called "rail motor coaches" or "motor cars" (not to be confused with the motor cars, otherwise known as automobiles, that operate on roads). The term is sometimes also used as an alternative name for the small types of multiple unit which consist of more than one coach. That is the general usage nowadays in Ireland when referring to any diesel multiple unit (DMU), or in some cases electric multiple unit (EMU). In North America the term "railcar" has a much broader sense and can be used (as an abbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livery
A livery is an identifying design, such as a uniform, ornament, symbol or insignia that designates ownership or affiliation, often found on an individual or vehicle. Livery will often have elements of the heraldry relating to the individual or corporate body feature in the livery. Alternatively, some kind of a personal emblem or badge, or a distinctive colour, is featured. The word itself derives from the French ''livrée'', meaning ''dispensed, handed over''. Most often it would indicate that the wearer of the livery was a servant, dependant, follower or friend of the owner of the livery, or, in the case of objects, that the object belonged to them. In the late medieval phenomenon of bastard feudalism, livery badges worn by the "retainers" of great lords, sometimes in effect private armies, became a great political concern in England. Etymology "In the ''Black'' Book of 1483, it was laid down that each person should receive "... for his Livery at night, half a chet loaf, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passenger Car (rail)
A passenger railroad car or passenger car (United States), also called a passenger carriage, passenger coach (United Kingdom and International Union of Railways), or passenger bogie (India) is a railroad car that is designed to carry passengers. The term ''passenger car'' can also be associated with a sleeping car, a baggage car, a dining car, railway post office and prisoner transport cars. The first passenger cars were built in the early 1800s with the advent of the first railroads, and were small and little more than converted freight cars. Early passenger cars were constructed from wood; in the 1900s construction shifted to steel and later aluminum for improved strength. Passenger cars have increased greatly in size from their earliest versions, with modern bi-level passenger cars capable of carrying over 100 passengers. Amenities for passengers have also improved over time, with developments such as lighting, heating, and air conditioning added for improved passenger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passing Loop
A passing loop (UK usage) or passing siding (North America) (also called a crossing loop, crossing place, refuge loop or, colloquially, a hole) is a place on a single line railway or tramway, often located at or near a station, where trains or trams travelling in opposite directions can pass each other. Trains/trams going in the same direction can also overtake, provided that the signalling arrangement allows it. A passing loop is double-ended and connected to the main track at both ends, though a dead end siding known as a refuge siding, which is much less convenient, can be used. A similar arrangement is used on the gauntlet track of cable railways and funiculars, and in passing places on single-track roads. Ideally, the loop should be longer than all trains needing to cross at that point. Unless the loop is of sufficient length to be dynamic, the first train to arrive must stop or move very slowly, while the second to arrive may pass at speed. If one train is too long for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Adhesion
An adhesion railway relies on adhesion traction to move the train. Adhesion traction is the friction between the drive wheels and the steel rail. The term "adhesion railway" is used only when it is necessary to distinguish adhesion railways from railways moved by other means, such as by a stationary engine pulling on a cable attached to the cars or by railways that are moved by a pinion meshing with a rack. The friction between the wheels and rails occurs in the wheel-rail interface or contact patch. The traction force, the braking forces and the centering forces, all contribute to stable running. However, running friction increases costs by requiring higher fuel consumption and by increasing the maintenance needed to address fatigue (material) damage, wear on rail heads and on the wheel rims and rail movement from traction and braking forces. Variation of friction coefficient Traction or friction is reduced when the top of the rail is wet or frosty or contaminated with grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)