|
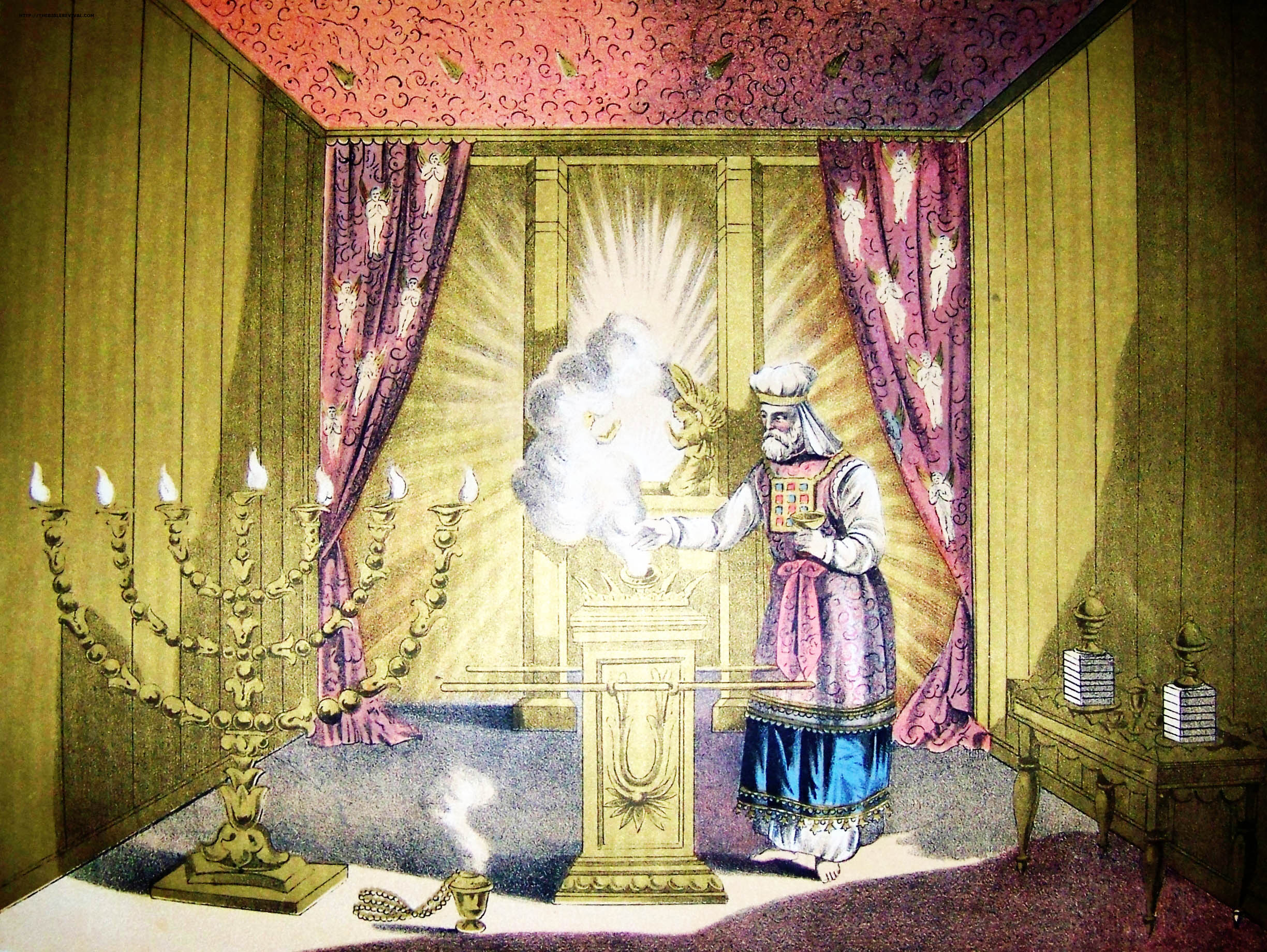
Zadok
Zadok (), also spelled Ṣadok, Ṣadoc, Zadoq, Tzadok or Tsadoq (; lit. 'righteous, justified'), was a Kohen (priest), biblically recorded to be a descendant of Eleazar the son of Aaron. He was the High Priest of Israel during the reigns of David and Solomon as kings of Israel. He aided King David during the revolt of his son Absalom, was subsequently instrumental in bringing Solomon to the throne, and officiated at Solomon's coronation. After Solomon's building of the First Temple in Jerusalem, Zadok was the first High Priest to serve there. The prophet Ezekiel extols the sons of Zadok as staunch opponents of paganism during the era of pagan worship, and indicates their birthright to unique duties and privileges in the future temple. Hebrew Bible The Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) states that Zadok was a patrilineal descendant of Eleazar the son of Aaron the high priest. The lineage of Zadok is presented in the genealogy of Ezra (his descendant) as being of ninth generation of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sons Of Zadok
The Sons of Zadok () or Zadokites is a lineage of priests (kohen, kohanim) descended from Zadok that is described in the prophecies of Ezekiel. Zadok himself was the first High Priest of Israel, high priest in Solomon's Temple (10th century BCE). His descendants were high priests in that temple until Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), its destruction in 587 BCE. Ezekiel's prophecy came several decades after that destruction and describes the Zadokite family's loyalty to God while the rest of the nation rebelled against God. The sons of Zadok are mentioned four times in the Hebrew Bible as part of the Third Temple prophecy in the final chapters of the Book of Ezekiel (chapters 40:46, 43:19, 44:15, and 48:11). They are a theme in Jewish and Christian interpretation of these chapters. Hebrew Bible Ezekiel 44:5-15 describes the "rebellion" of the Israelite people and of the Levites. The sins involved in this rebellion include idol worship in verses 10 and 12 and the offering of sacrific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Priest Of Israel
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahimaaz
Ahimaaz ( ''ʾĂḥīmaʿaṣ'', "My Brother Is Counselor") was son of the high priest Zadok. Ahimaaz first appears in the reign of King David (reigned c. 1000-962 BCE). During Absalom's revolt he remained faithful to David, and, along with Jonathan, son of Abiathar, assisted him by giving him news about the proceedings of Absalom in Jerusalem ( 2 Samuel 15:24–37; 17:15–21). He was a swift runner, and was the first to bring David news of the defeat of Absalom, although he refrained from mentioning his death (2 Samuel 18:19–33). Under King Solomon (c. 970–930 BCE), Ahimaaz's father Zadok became high priest. When Zadok died, Ahimaaz succeeded him in that position ( 1 Chronicles 6:8, 53). He may have been the same Ahimaaz who took as wife Basemath, one of Solomon's daughters ( 1 Kings 4:15). Subsequent kings of Israel, Ahaz Ahaz (; ''Akhaz''; ) an abbreviation of Jehoahaz II (of Judah), "Yahweh has held" (; ''Ya'úḫazi'' 'ia-ú-ḫa-zi'' Hayim Tadmor and Shigeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abiathar
Abiathar ( ''ʾEḇyāṯār'', "father (of) abundance"/"abundant father"), in the Hebrew Bible, is a son of Ahimelech or Ahijah, Kohen Gadol, High Priest at Nob, Israel, Nob, the fourth in descent from Eli (Bible), Eli and the last of Eli's House to be a High Priest. Bible account 1 Samuel and 2 Samuel mention Abiathar several times. According to these books, Abiathar was the only one of the priests to escape from Saul's (reigned c. 1020–1000 BCE) massacre in Nob, Israel, Nob, when his father and the priests of Nob were slain on the command of Saul. He fled to David (reigned c. 1003–970 BCE) at Keilah, taking with him the ephod and other priestly regalia. In rabbinical literature that links the later extermination of David's male descendants with that of the priests of Nob, the survival of David's descendant Jehoash of Judah, Joash is connected to that of Abiathar. The Biblical account says Abiathar joined David, who was then in the cave of Adullam. He remained with David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ruler of all Twelve Tribes of Israel under an amalgamated History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. The hypothesized dates of Solomon's reign are from 970 to 931 BCE. According to the biblical narrative, after Solomon's death, his son and successor Rehoboam adopted harsh policies towards the northern Israelites, who then rejected the reign of the Davidic line, House of David and sought Jeroboam as their king. In the aftermath of Jeroboam's Revolt, the Israelites were split between the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel in the north (Samaria) and the Kingdom of Judah in the south (Judea); the Bible depicts Rehoboam and the rest of Solomon's Patrilineality#In the Bible, patrilineal descendants ruling over independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phinehas
According to the Hebrew Bible, Phinehas (also spelled Phineas, ; , ''Phinees'', ) was a priest during the Exodus. The grandson of Aaron and son of Eleazar, the High Priests (), he distinguished himself as a youth at Shittim with his zeal against the heresy of Peor. Displeased with the immorality with which the Moabites and Midianites had successfully tempted the Israelites () to inter-marry and to worship Baal-peor, Phinehas personally executed an Israelite man and a Midianite woman while they were together in the man's tent, running a javelin or spear through the man and the belly of the woman, bringing to an end the plague sent by Yahweh to punish the Israelites for sexually intermingling with the Midianites. Phinehas is commended by Yahweh in Numbers 25:10–13, as well as King David in Psalm 106 () for having stopped Israel's fall into idolatrous practices brought in by Midianite women, as well as for stopping the desecration of Yahweh's sanctuary. After the entry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan (son Of Abiathar)
Jonathan is a character in the Hebrew Bible, appearing in 2 Samuel and 1 Kings. He is introduced as the son of Abiathar the High Priest in 2 Samuel 15:27. He was also a companion of Ahimaaz, son of Zadok: together they work as messengers for David during Absalom's rebellion (2 Sam 15:36). 2 Samuel 17 describes an incident in which they hide from Abasalom's men in a well in Bahurim. In 1 Kings 1, during Adonijah's conspiracy, Jonathan tells Adonijah that David had made Solomon king (1 Kgs 1:43). Jonathan is not mentioned again, and misses out on becoming high priest, since his father is replaced by Zadok. Keith Bodner calls him an "under-rated (yet intriguing) character", and notes that he is "used in a larger discussion about succession", which Bodner argues is ironic, "since he himself is banished into obscurity by the succession of a rival house." Jonathan was the 9th Samaritan High Priest The Samaritan High Priest (in Samaritan Hebrew: ''haKa’en haGadol''; ) is the High P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaron
According to the Old Testament of the Bible, Aaron ( or ) was an Israelite prophet, a high priest, and the elder brother of Moses. Information about Aaron comes exclusively from religious texts, such as the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament ( Luke, Acts, and Hebrews), and the Quran. The Hebrew Bible relates that, unlike Moses, who grew up in the Egyptian royal court, Aaron and his elder sister Miriam remained with their kinsmen in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. When Moses first confronted the Egyptian king about the enslavement of the Israelites, Aaron served as his brother's spokesman to the Pharaoh. Part of the Law given to Moses at Sinai granted Aaron the priesthood for himself and his male descendants, and he became the first High Priest of the Israelites. Levitical priests or '' kohanim'' are traditionally believed and halakhically required to be of direct patrilineal descent from Aaron. According to the Book of Numbers, Aaron died at 123 years of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, ''Sefer (Hebrew), Sēfer Malik, Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of ancient Israel also including the books of Book of Joshua, Joshua, Book of Judges, Judges, and Books of Samuel, Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings mixes legends, folktales, miracle stories and "fictional constructions" in with the annals for the purpose of providing a Theology, theological explanation for the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BC and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark Of The Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant, also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, was a religious storage chest and relic held to be the most sacred object by the Israelites. Religious tradition describes it as a wooden storage chest decorated in solid gold accompanied by an ornamental lid known as the mercy seat, Seat of Mercy. According to the Book of Exodus and Books of Kings, First Book of Kings in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, the Ark contained the Tablets of Stone, Tablets of the Law, by which Yahweh, God delivered the Ten Commandments to Moses at Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai. According to the Book of Exodus, the Book of Numbers, and the Epistle to the Hebrews in the New Testament, it also contained Aaron's rod and a pot of manna. The biblical account relates that approximately one year after the Israelites' The Exodus, exodus from Egypt, the Ark was created according to the pattern that God gave to Moses when the Israelites were encamped at the foot of Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (), was a biblical Temple in Jerusalem believed to have existed between the 10th and 6th centuries Common Era, BCE. Its description is largely based on narratives in the Hebrew Bible, in which it was commissioned by biblical king Solomon before being destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), Siege of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in 587 BCE. No excavations are allowed on the Temple Mount, and no positively identified remains of the destroyed temple have been found. Most modern scholars agree that the First Temple existed on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem by the time of the Babylonian siege, and there is significant debate among scholars over the date of its construction and the identity of its builder. The Hebrew Bible, specifically within the Books of Kings, Book of Kings, includes a detailed narrative about the construction's ordering by Solomon, the penultimate ruler of the Kingdom of Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |