|
Zaden
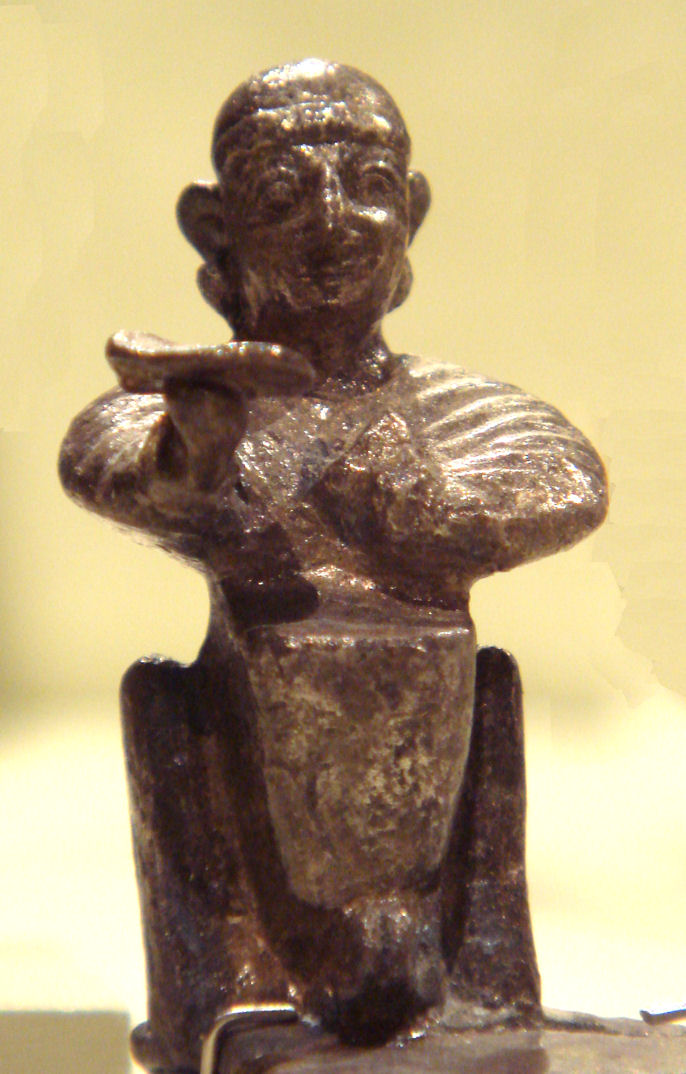
Zaden (; ka, ზადენი, tr) was, according to the medieval Georgian chronicles, the god of fruitfulness in a pre-Christian pantheon of the ancient Georgians of Kartli (Iberia of the Classical sources). King Parnajom of Iberia (109–90 BC) is reported to have built a fortress at Mount Zedazeni to house the colossus of Zadeni which, along with other pagan idols, are said to have been destroyed through the prayers of St. Nino, a 4th-century female baptizer of Georgians. Beyond the passages from the medieval annals and the surviving toponym of Zedazeni (from ''Zeda Zadeni'', i.e. "Upper Zaden"), we lack contemporary records and archaeological evidence about this cult, however. Zaden is surmised by several modern scholars to have been a Georgian version of the Luwian Santas or the Hittite Sandon, but the identification with Yazata of Zoroastrianism has also been suggested.Rapp, Stephen H. (2003), ''Studies In Medieval Georgian Historiography: Early Texts And Eurasian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
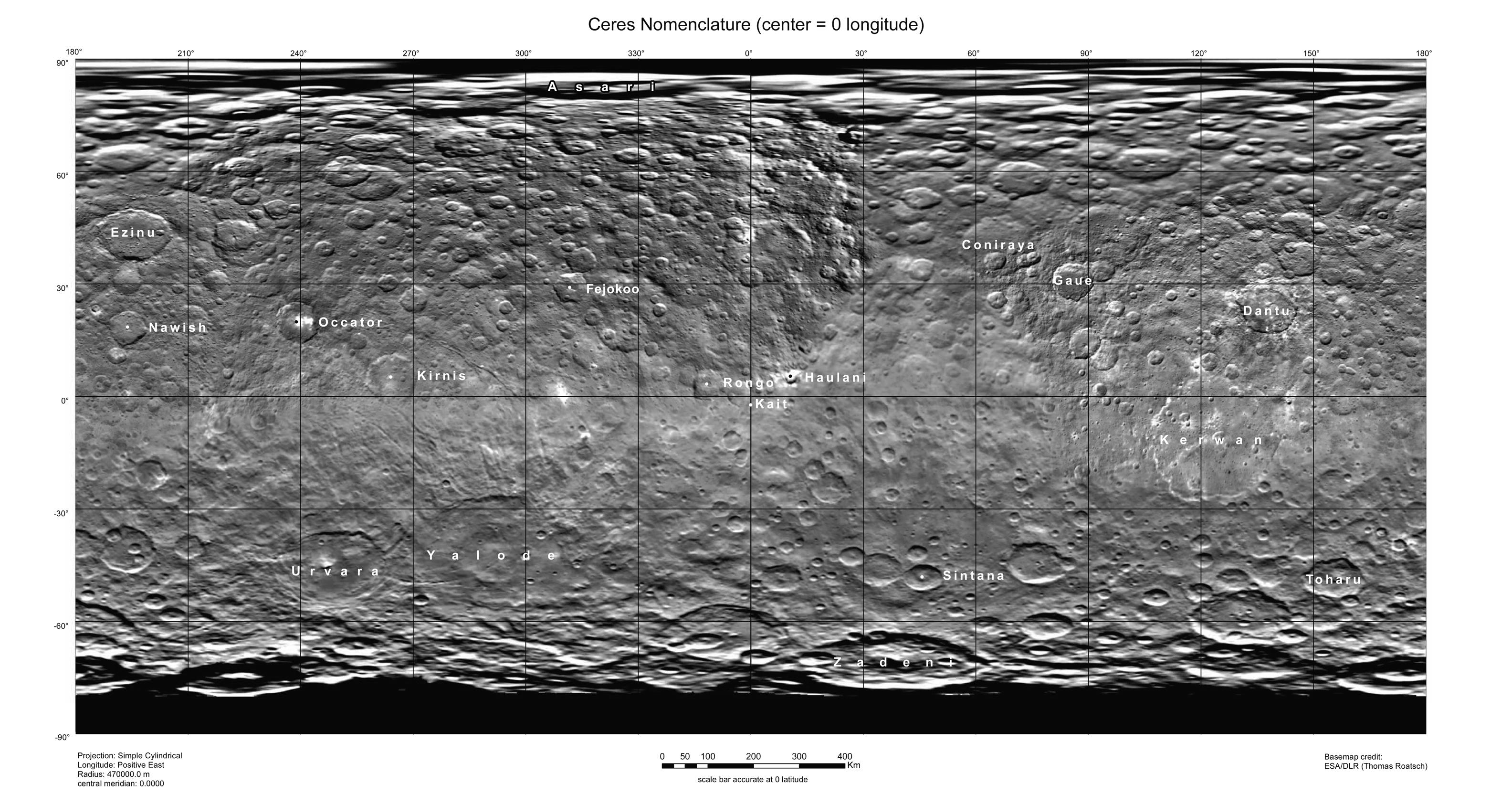
Zadeni (crater)
Ceres is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The IAU has adopted two themes for naming surface features on Ceres: agricultural deities for craters and agricultural festivals for everything else. As of 2020, the IAU has approved names for 151 geological features on Ceres: craters, montes, catenae, rupēs, plana, tholi, planitiae, fossae and sulci. In July 2018, NASA released a comparison of physical features found on Ceres with similar ones present on Earth. ''Piazzi'', named after Giuseppe Piazzi, the discoverer of Ceres, is a dark region southwest of Dantu crater in ground-based images that was named before ''Dawn'' arrived at Ceres. Overview of features Catenae Craters Ceres is saturated with impact crater An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Mythology
Georgian mythology ( ka, ქართული მითოლოგია, tr) refers to the mythology of pre-Christian Georgians ( /kʌrtˈvɛliənz/; Georgian: ქართველები, romanized: kartvelebi, pronounced ʰɑrtʰvɛlɛbi, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus.The mythology of the Kartvelian peoples is believed by many scholars to have formed part of the religions of the kingdoms of Diauehi, Colchis and Iberia. Later influences include the mythologies of the Ancient Greeks, Tuite, Kevin, ''The Meaning of Dæl, Symbolic and Spatial Associations of the South Caucasian Goddess of Game Animals'', Université de Montréal the Vainakh peoples and Iranians – the last-named comprising both the belief systems of the Northern Iranian nomad Scythians and Sarmatians (still preserved to some extent in the mythology of their descendants the Ossetians) and that of the Zoroastrian religion of the Ancient Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parnajom Of Iberia
P'arnajom or P'arnajob ( ka, ფარნაჯომი, ფარნაჯობი) (died 90 BC) was a king of Iberia from 109 to 90 BC, the fourth in the P'arnavaziani line. He is known exclusively from the royal list included in the medieval Georgian chronicles. He succeeded on death of his father, Mirian I in 109 BC. He is reported to have added another idol, that of the god Zaden, to the Iberian pagan pantheon, and to have built a fortress to house it. His policy of importing foreign religion is said to have caused a general uprising. The chronicle goes on to describe a great battle between P'arnajom and his nobles in which the king is defeated and killed, and the crown given to his son-in-law, Arshak/Artaxias, son of the king of Armenia, the rebels' ally. P'arnajom's son, Mirian (Mirvan), survives, however, to be taken and brought up at the Parthian court. References *Thomson, Robert W. (1996), ''Rewriting Caucasian History: The Medieval Armenian Adaptation of the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zedazeni
Zedazeni Monastery ( ka, ზედაზნის მონასტერი) is a Georgian Orthodox monastery, located on the Zedazeni mountain the hills of Saguramo, northeast to Mtskheta and to the east side of the Aragvi River. The monastery was founded by Saint John, one of the Holy Assyrian Fathers of Georgia whose mission was to strengthen Christianity in the region.David KhoshtariZedazeni Monastery Atinati 29.12.2020 History Saint John founded the monastery in the 540s (6th century) on Zedazeni mountain, where prior to Christianity used to be a cult of Zaden Zaden (; ka, ზადენი, tr) was, according to the medieval Georgian chronicles, the god of fruitfulness in a pre-Christian pantheon of the ancient Georgians of Kartli (Iberia of the Classical sources). King Parnajom of Iberia (109–90 ..., the idol of fruitfulness. References {{Georgian Churches Georgian Orthodox monasteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittite Mythology
Hittite mythology and Hittite religion were the religious beliefs and practices of the Hittites, who created an empire centered in what is now Turkey from . Most of the narratives embodying Hittite mythology are lost, and the elements that would give a balanced view of Hittite religion are lacking among the tablets recovered at the Hittite capital Hattusa and other Hittite sites. Thus, "there are no canonical scriptures, no theological disquisitions or discourses, no aids to private devotion". Some religious documents formed part of the corpus with which young scribes were trained, and have survived, most of them dating from the last several decades before the final burning of the sites. The scribes in the royal administration, some of whose archives survive, were a bureaucracy, organizing and maintaining royal responsibilities in areas that would be considered part of religion today: temple organization, cultic administration, reports of diviners, make up the main body of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (dwarf Planet)
Ceres (; minor-planet designation: 1 Ceres) is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first asteroid discovered, on 1 January 1801, by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planetthe only one always inside Neptune's orbit. Ceres's small size means that even at its brightest, it is too dim to be seen by the naked eye, except under extremely dark skies. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.7 to 9.3, peaking at opposition (when it is closest to Earth) once every 15- to 16-month synodic period. As a result, its surface features are barely visible even with the most powerful telescopes, and little was known about it until the robotic NASA spacecraft ''Dawn'' approached Ceres for its orbital mission in 2015. ''Dawn'' found Ceres's surface to be a mixture of water ice, and hydrated minerals such as carbonates and cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ontology and an eschatology which predicts the ultimate conquest of evil by good. Zoroastrianism exalts an uncreated and benevolent deity of wisdom known as ''Ahura Mazda'' () as its supreme being. Historically, the unique features of Zoroastrianism, such as its monotheism, messianism, belief in free will and judgement after death, conception of heaven, hell, angels, and demons, among other concepts, may have influenced other religious and philosophical systems, including the Abrahamic religions and Gnosticism, Northern Buddhism, and Greek philosophy. With possible roots dating back to the 2nd millennium BCE, Zoroastrianism enters recorded history around the middle of the 6th century BCE. It served as the state religion of the ancient Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazata
Yazata ( ae, 𐬫𐬀𐬰𐬀𐬙𐬀) is the Avestan word for a Zoroastrian concept with a wide range of meanings but generally signifying (or used as an epithet of) a divinity. The term literally means "worthy of worship or veneration",.. and is thus, in this more general sense, also applied to certain healing plants, primordial creatures, the '' fravashis'' of the dead, and to certain prayers that are themselves considered holy. The ''yazata''s collectively are "the good powers under Ahura Mazda", who is "the greatest of the ''yazata''s".. Etymology ''Yazata'' is an Avestan-language passive adjectival participle derived from ''yaz-''; "to worship, to honor, to venerate", from Proto-Indo-European ''*yeh₂ǵ-'' (“to worship, revere, sacrifice”). The word ''yasna'' or yagna– "worship, sacrifice, oblation, prayer" – comes from the same root. A ''yaza+ ta'' is accordingly "a being worthy of worship", "an object of worship" or "a holy being". As the stem form, ''yazat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandon (god)
Sandas (more commonly spelt as "Sandan") was the Anatolian ( Hittite) lion god during the Classical period. He used to be represented in association with a horned lion, and often resided inside a pyre surmounted by an eagle. Sandan was often associated to the Greek god Herakles, and sometimes to Marduk. In ceremonies, an image of the god was placed inside a pyre and was set on fire. Sandan appears in the coins of the Seleucids, as well as on other coins of Tarsus (Cilicia) during the time of the Roman emperors. In Tarsus, Sandon (sometimes spelled Sandes, Sandan, or Sanda) was visually represented as a mitre-wearing human form carrying a sword, a flower, or (commonly) an axe who stands on the back of a horned and winged lion. Associated primarily with war and weather, Sandon was the chief god in the Cilician pantheon from at least the beginning of the second millennium BC. The ancient Greeks and Romans equated Sandon with Herakles.Goldman, p. 544. A large monument to Sandon existe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia (, ; ) is a transcontinental country at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, by Russia to the north and northeast, by Turkey to the southwest, by Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of , and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital as well as its largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. In the early 4th century, ethnic Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of the early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. In the time of the Roman empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not '' milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were '' hellene'', '' gentile'', and ''heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Graeco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the " religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian religion, and the term presum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_p012_BAKU%2C_FIRE_TEMPLE_(cropped).jpg)
_b_016.jpg)