|
Zacpetén
Zacpeten is a pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site in the northern Petén Department of Guatemala. It is notable as one of the few Maya communities that maintained their independence through the early phases of Spanish control over Mesoamerica. History The site of Zacpeten occupies a peninsula on Lake Salpeten in the Petén Department of northern Guatemala. The site was sporadically inhabited by the Maya since its initial settlement during the Middle Preclassic (1000 – 300 BC). After abandonment during Late Preclassic and Early Classic, the site was resettled from the Late to Terminal Classic (AD 600 – 950). Abandoned again, it was reoccupied in the Late Postclassic by the Maya peoples who survived the Classic Maya collapse and migrated from Mayapan in Yucatán (now in Mexico) after the collapse of the city in the fifteenth century. These people, the Kowoj Maya, brought their distinctive pottery and constructed typical Mayapan temple assemblages with a raised shrine lying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
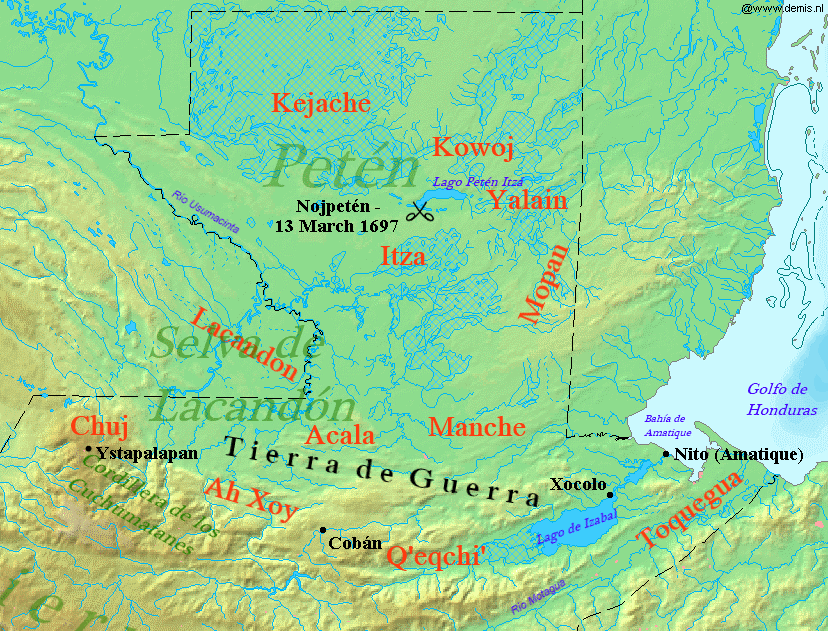
Spanish Conquest Of Petén
The Spanish conquest of Petén was the last stage of the Spanish conquest of Guatemala, conquest of Guatemala, a prolonged conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas. A wide lowland plain covered with dense rainforest, Petén contains a central drainage basin with a series of lakes and areas of savannah. It is crossed by several ranges of low karstic hills and rises to the south as it nears the Guatemalan Highlands. The conquest of Petén Basin, Petén, a region now incorporated into the modern republic of Guatemala, climaxed in 1697 with the capture of Nojpetén, the island capital of the Itza people, Itza kingdom, by Martín de Ursúa, Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi. With the defeat of the Itza, the last independent and unconquered native kingdom in the Americas fell to European colonisers. Sizeable Maya peoples, Maya populations existed in Petén before the conquest, particularly around the central lakes and along the rivers. Petén was divided into different M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kowoj
The Kowoj [koʔwox] (also recorded as ''Ko'woh'', ''Couoh'', ''Coguo'', ''Cohuo'', ''Kob'ow'' and ''Kob'ox'', and ''Kowo'') was a Maya civilization, Maya group and polity, from the Late Postclassic period (ca. 1250–1697) of Mesoamerican chronology. The Kowoj claimed to have migrated from Mayapan sometime after the city's collapse in 1441 AD. Indigenous documents also describe Kowoj in Mayapan and linguistic data indicate migrations between the Yucatán Peninsula and the Petén Basin, Petén region. A specific variant of temple assemblage, in a C-shaped plaza, defines the location of the Kowoj in both Mayapan and Petén Basin, Petén. These assemblages were the exemplary centers of the Ko'woj. The temple assemblages also communicated a prestigious connection with Mayapan and differentiated the Kowoj from their Itza people, Itzá neighbors in the Petén Basin region. Temple assemblage with raised shrine lies at a right angle to a western facing temple rather than facing into it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoxte
Topoxte () (or Topoxté in Spanish orthography) is a pre-Columbian Maya civilization, Maya archaeological site in the Petén Basin in northern Guatemala with a long occupational history dating as far back as the Mesoamerican chronology, Middle Preclassic.Pinto & Noriega 1995, pp.576–7. As the capital of the Kowoj, Kowoj Maya, it was the largest of the few Mesoamerican chronology, Postclassic Mesoamerican sites in the area. Topoxte is located on an island on Laguna Yaxhá, Yaxha Lake across from the important Classic period center of Yaxha.Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.617. Topoxte was named by Teobert Maler in 1904;Chase 1976, p.155. the name means "seed of the Ramón tree." There is no record of the name Topoxte prior to this. The Ramón tree, commonly known as breadnut, was an important component of the ancient Maya diet and subsistence, Maya diet. Prior to this the site was known as ''Islapag'', as noted in 1831 by Juan Galindo in his report to the Society of Antiquaries of London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin-pyramid Complex
A twin-pyramid complex or twin-pyramid group was an architectural innovation of the Maya civilization of ancient Mesoamerica. Twin-pyramid complexes were regularly built at the great city of Tikal in the central Petén Basin of Guatemala to celebrate the end of the 20-year '' kʼatun'' cycle of the Maya Long Count Calendar. A twin-pyramid complex has been identified at Yaxha, a large city that was to the southeast of Tikal. Another has been mapped at Ixlu,Martin and Grube 2000, p.51. and Zacpeten appears also to possess at least one twin-pyramid complex and possibly two. These examples outside of Tikal itself indicate that their cities were closely linked to Tikal politically. The basic layout of a twin-pyramid complex consists of identical pyramids on the east and west sides of a small plaza, with a walled enclosure to the north housing a sculpted stela-altar pair and a range building to the south. Plain monuments were generally raised at the foot of the east pyramid. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of Guatemala
In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya peoples, Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their Maya civilization, civilization.Jones 2000, p. 356. The first contact between the Maya and European colonization of the Americas, European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spain, Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Hispaniola, Santo Domingo (Hispaniola) was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492. This era encompasses the history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous cultures prior to significant European influence, which in some cases did not occur until decades or even centuries after Columbus's arrival. During the pre-Columbian era, many civilizations developed permanent settlements, cities, agricultural practices, civic and monumental architecture, major Earthworks (archaeology), earthworks, and Complex society, complex societal hierarchies. Some of these civilizations had declined by the time of the establishment of the first permanent European colonies, around the late 16th to early 17th centuries, and are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petén Basin
The Petén Basin is a geographical subregion of the Maya Lowlands, primarily located in northern Guatemala within the Department of El Petén, and into the state of Campeche in southeastern Mexico. During the Late Preclassic and Classic periods of pre-Columbian Mesoamerican chronology many major centers of the Maya civilization flourished, such as Tikal and Calakmul. A distinctive Petén-style of Maya architecture and inscriptions arose. The archaeological sites La Sufricaya and Holmul are also located in this region. History By the first half of the 1st millennium BCE, the Petén and Mirador Basin of this region were already well-established with a number of monumental sites and cities of the Maya civilization. Significant Maya sites of this Preclassic era of Mesoamerican chronology include Nakbé, El Mirador, Naachtun, San Bartolo and Cival in the Mirador Basin. Classic Period Later, Petén became the heartland of the Maya Classic Period (c. 200 – 900 CE). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itza People
The Itza are a Maya ethnic group descendants of the Chanes Maya, Chanes from the Chontal Maya, Chontal region of Tabasco from where they made a historic migration arriving at Bacalar and northern Yucatán during the 10th century, then they arrived at Champotón, Campeche, Champotón and finally in the 15th century they settled around Lake Petén Itzá where they remained independent until 1697. During the Spanish colonial era and later by the Guatemalan government, the Itza were victims of repressive policies that accelerated the extinction of the Itza culture and language, leading to the loss of much of their ethnic identity. They are one of the smallest Maya groups and have the lowest population; the few Itza descendants are settled in the town of San José, Petén, San José, north of Lake Petén Itzá in the department of Petén Department, Petén, Guatemala, and are considered highly acculturated to mestizo society, with only 36 elderly people remaining as native speakers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Grube
Nikolai Grube is a German epigrapher. He was born in Bonn in 1962.Houston et al 2001, p.486. Grube entered the University of Hamburg in 1982 and graduated in 1985. His doctoral thesis was published at the same university in 1990. After he received his doctorate, Grube moved to the University of Bonn.Interdisciplinary Latin America Center at the University of Bonn (1) n.d. Nikolai Grube has been heavily involved in the decipherment of the Maya hieroglyphic script. Biography He has served as professor of anthropology and art history at both the University of Texas at Austin and the University of Bonn., inside back cover. At the University of Bonn he has worked in the Seminar for Ethnology. He has worked with several archaeological projects in the Maya region, including those at Caracol in Belize and Yaxha in the Petén Department of Guatemala. He has also occupied a position at the University of Hamburg. He is fluent in the Yucatec language of the modern Maya inhabitants of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assemblage (archaeology)
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames & Hudson
Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, and popular culture. Headquartered in London, it has a sister company in New York City, and subsidiaries in Melbourne, Singapore, and Hong Kong. In Paris it has a sister company, Éditions Thames & Hudson, and a subsidiary called Interart which distributes English-language books. The Thames & Hudson group currently employs approximately 150 staff in London and approximately 65 more around the world. The publishing company was founded in 1949 by Walter and Eva Neurath, who aimed to make the world of art and the research of top scholars available to a wider public. The company's name reflects its international presence, particularly in London and New York. It remains an independent, family-owned company, and is one of the largest publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |