|
ZNF837 Homology Unrooted Tree With Key
ZNF837 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF837 gene, is located at 19q13.431 with minus strand orientation. ZNF837 protein is characterized as a C2H2-type zinc finger protein. Homology and Evolution The human ZNF837 has homologs present in many mammals and seen more distantly. All homologs are chordates. All contain both COG5048 and Zf-C2H2_2 domains. The areas that these domains are found contain the highest conservation rates. In humans, 5 Zf-H2C2 double domains and 2 COG5048 domains are present. The protein sequence is fast evolving among these homologs. ZNF837 has numerous paralogs in humans, all of which are zinc finger proteins. Human ZNF837 In humans, there are no other aliases, and its neighboring genes are MIR4754, Alpha-1-B glycoprotein, A1BG, and 40S ribosomal protein S5, RPS5. ZNF837 mRNA that is made into function protein contains 1921 nucleotides, of which 222-1817 are translated to a protein containing 3 exons. The protein consists of 531 ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZNF837 Homology Unrooted Tree With Key
ZNF837 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF837 gene, is located at 19q13.431 with minus strand orientation. ZNF837 protein is characterized as a C2H2-type zinc finger protein. Homology and Evolution The human ZNF837 has homologs present in many mammals and seen more distantly. All homologs are chordates. All contain both COG5048 and Zf-C2H2_2 domains. The areas that these domains are found contain the highest conservation rates. In humans, 5 Zf-H2C2 double domains and 2 COG5048 domains are present. The protein sequence is fast evolving among these homologs. ZNF837 has numerous paralogs in humans, all of which are zinc finger proteins. Human ZNF837 In humans, there are no other aliases, and its neighboring genes are MIR4754, Alpha-1-B glycoprotein, A1BG, and 40S ribosomal protein S5, RPS5. ZNF837 mRNA that is made into function protein contains 1921 nucleotides, of which 222-1817 are translated to a protein containing 3 exons. The protein consists of 531 ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-1-B Glycoprotein
Alpha-1-B glycoprotein is a 54.3 kDa protein in humans that is encoded by the A1BG gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a plasma glycoprotein of unknown function. The protein shows sequence similarity to the variable regions of some immunoglobulin supergene family member proteins. Patients who have pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma show an overexpression of A1BG in pancreatic juice. Gene Neighborhood A1BG is located on the negative DNA strand of chromosome 19 from 58,858,172 – 58,864,865. Additionally, A1BG is located directly adjacent to the ZSCAN22 gene (58,838,385-58,853,712)) on the positive DNA strand, as well as the ZNF837 (58,878,990 - 58,892,389, complement) and ZNF497 (58865723 - 58,874,214, complement) genes on the negative strand. Expression A1BG is expressed at high levels in the adult and fetal liver. Additionally, the mammary gland shows roughly half as much expression as the liver. Trace amounts of A1BG expression can be found in the blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
40S Ribosomal Protein S5
40S ribosomal protein S5 is a ribosomal subunit of the Eukaryotic ribosome (80S) complex. In humans it is encoded by the ''RPS5'' gene. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, in ''eukaryotes'', consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit (whereas prokaryotic ribosomes are 70 Svedberg units, composed of 50S and 30S subunits). They are located in the cytoplasm. Together these subunits are composed of four RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the eukaryotic 40S subunit. The protein belongs to the S7P family of ribosomal proteins. Variable expression of this gene in colorectal cancers compared to adjacent normal tissues has been observed, although no correlation between the level of expression and the severity of the disease has been found. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes Pseudogenes are nonfunctio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectric Point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). However, pI is also used. For brevity, this article uses pI. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons (H+). Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface charge-determining ions are H+/HO−, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. The pI value can affect the solubility of a molecule at a given pH. Such molecules have minimum solubility in water or salt solutions at the pH that corresponds to their pI and often precipitate out of solution. Biological amphoteric molecules such as proteins contain both acidic and basic function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
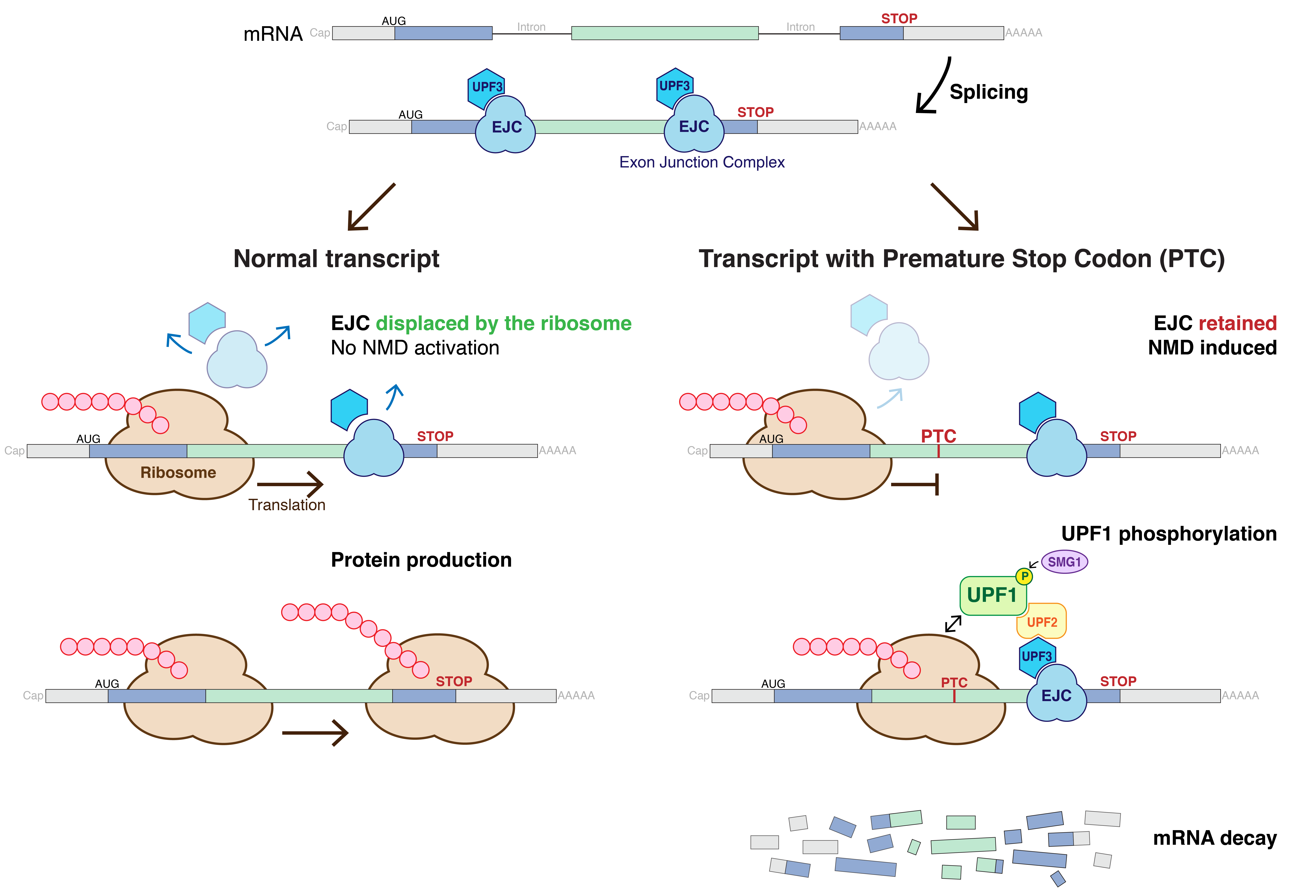
Nonsense-mediated Decay
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins. NMD was first described in human cells and in yeast almost simultaneously in 1979. This suggested broad phylogenetic conservation and an important biological role of this intriguing mechanism. NMD was discovered when it was realized that cells often contain unexpectedly low concentrations of mRNAs that are transcribed from alleles carrying nonsense mutations. Nonsense mutations code for a premature stop codon which causes the protein to be shortened. The truncated protein may or may not be functional, depending on the severity of what is not translated. In human genetics, NMD has the possibility to not only limit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyre2 Predicted Structure Of ZNF837
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as 'fire') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable accura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |