|
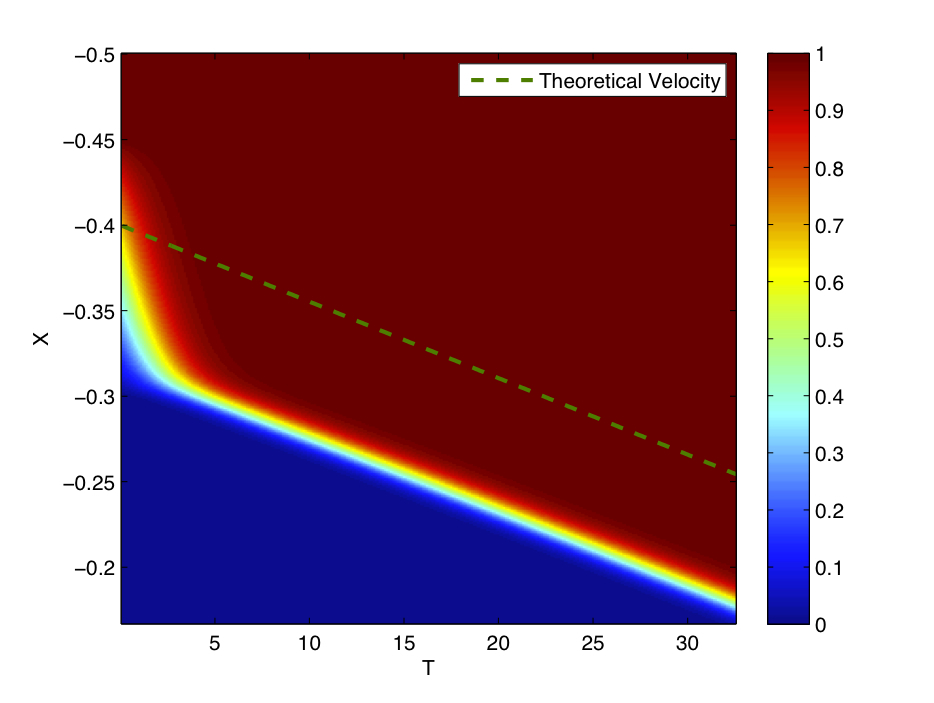
ZFK Equation
ZFK equation, abbreviation for Zeldovich–Frank-Kamenetskii equation, is a reaction–diffusion equation that models premixed flame propagation. The equation is named after Yakov Zeldovich and David A. Frank-Kamenetskii who derived the equation in 1938 and is also known as the Nagumo equation. The equation is analogous to KPP equation except that is contains an exponential behaviour for the reaction term and it differs fundamentally from KPP equation with regards to the propagation velocity of the traveling wave. In non-dimensional form, the equation reads :\frac = \frac + \omega(\theta) with a typical form for \omega given by :\omega =\frac \theta(1-\theta) e^ where \theta\in ,1/math> is the non-dimensional dependent variable (typically temperature) and \beta is the Zeldovich number. In the ZFK regime, \beta\gg 1. The equation reduces to Fisher's equation for \beta\ll 1 and thus \beta\ll 1 corresponds to KPP regime. The minimum propagation velocity U_ (which is usually the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction–diffusion System
Reaction–diffusion systems are mathematical models which correspond to several physical phenomena. The most common is the change in space and time of the concentration of one or more chemical substances: local chemical reactions in which the substances are transformed into each other, and diffusion which causes the substances to spread out over a surface in space. Reaction–diffusion systems are naturally applied in chemistry. However, the system can also describe dynamical processes of non-chemical nature. Examples are found in biology, geology and physics (neutron diffusion theory) and ecology. Mathematically, reaction–diffusion systems take the form of semi-linear parabolic partial differential equations. They can be represented in the general form :\partial_t \boldsymbol = \underline \,\nabla^2 \boldsymbol + \boldsymbol(\boldsymbol), where represents the unknown vector function, is a diagonal matrix of diffusion coefficients, and accounts for all local reactions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
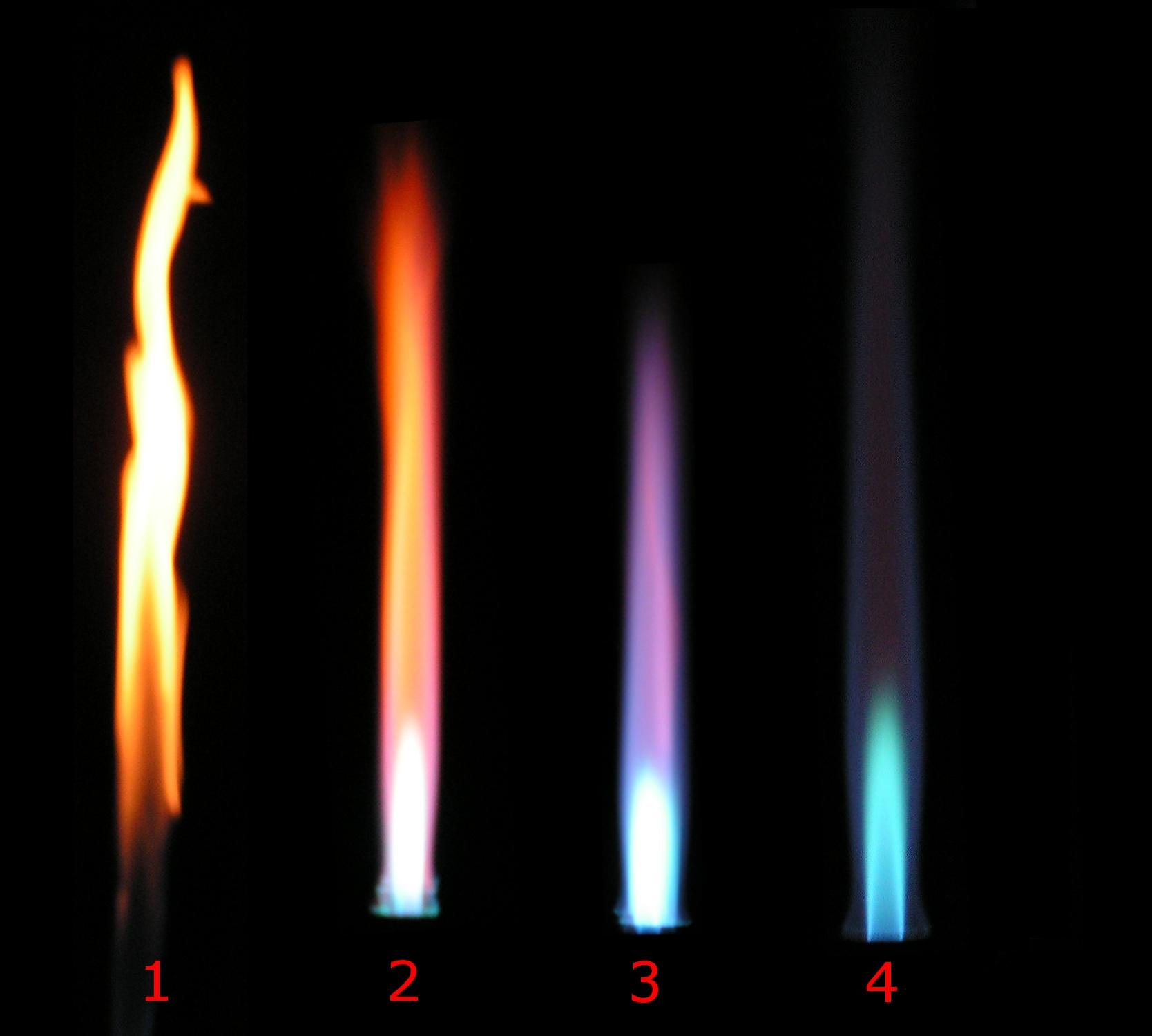
Premixed Flame
A premixed flame is a flame formed under certain conditions during the combustion of a premixed charge (also called pre-mixture) of fuel and oxidiser. Since the fuel and oxidiser—the key chemical reactants of combustion—are available throughout a homogeneous stoichiometric premixed charge, the combustion process once initiated sustains itself by way of its own heat release. The majority of the chemical transformation in such a combustion process occurs primarily in a thin interfacial region which separates the unburned and the burned gases. The premixed flame interface propagates through the mixture until the entire charge is depleted. The propagation speed of a premixed flame is known as the flame speed (or burning velocity) which depends on the convection-diffusion-reaction balance within the flame, i.e. on its inner chemical structure. The premixed flame is characterised as laminar or turbulent depending on the velocity distribution in the unburned pre-mixture (which provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Zeldovich
Yakov Borisovich Zeldovich ( be, Я́каў Бары́савіч Зяльдо́віч, russian: Я́ков Бори́сович Зельдо́вич; 8 March 1914 – 2 December 1987), also known as YaB, was a leading Soviet physicist of Belarusian origin, who is known for his prolific contributions in physical cosmology, physics of thermonuclear reactions, combustion, and hydrodynamical phenomena. From 1943, Zeldovich, a self-taught physicist, started his career by playing a crucial role in the development of the former Soviet program of nuclear weapons. In 1963, he returned to academia to embark on pioneering contributions on the fundamental understanding of the thermodynamics of black holes and expanding the scope of physical cosmology. Biography Early life and education Yakov Zeldovich was born into a Belarusian Jewish family in his grandfather's house in Minsk. However, in mid-1914, the Zeldovich family moved to Saint Petersburg. They resided there until August 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, Dav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KPP Equation
In mathematics, Fisher's equation (named after statistician and biologist Ronald Fisher) also known as the Kolmogorov–Petrovsky–Piskunov equation (named after Andrey Kolmogorov, Ivan Petrovsky, and Nikolai Piskunov), KPP equation or Fisher–KPP equation is the partial differential equation: : \frac - D \frac = r u(1-u).\, It is a kind of reaction–diffusion system that can be used to model population growth and wave propagation. Details Fisher's equation belongs to the class of reaction–diffusion equation: in fact, it is one of the simplest semilinear reaction-diffusion equations, the one which has the inhomogeneous term : f(u,x,t) = r u (1-u),\, which can exhibit traveling wave solutions that switch between equilibrium states given by f(u) = 0. Such equations occur, e.g., in ecology, physiology, combustion, crystallization, plasma physics, and in general phase transition problems. Fisher proposed this equation in his 1937 paper ''The wave of advance of advant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeldovich Number
The Zel'dovich number is a dimensionless number which provides a quantitative measure for the activation energy of a chemical reaction which appears in the Arrhenius exponent, named after the Russian scientist Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich, who along with David A. Frank-Kamenetskii, first introduced in their paper in 1938. In 1983 ICDERS meeting at Poitiers, it was decided to name after Zel'dovich.Clavin, P. (1985). Dynamic behavior of premixed flame fronts in laminar and turbulent flows. Progress in energy and combustion science, 11(1), 1-59. It is defined as :\beta = \frac \cdot \frac where *E_a is the activation energy of the reaction *R is the universal gas constant *T_b is the burnt gas temperature *T_u is the unburnt mixture temperature. In terms of heat release parameter \alpha, it is given by :\beta = \frac \alpha For typical combustion phenomena, the value for Zel'dovich number lies in the range \beta\approx 8-20. Activation energy asymptotics Activation energy asy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisher's Equation
In mathematics, Fisher's equation (named after statistician and biologist Ronald Fisher) also known as the Kolmogorov–Petrovsky–Piskunov equation (named after Andrey Kolmogorov, Ivan Petrovsky, and Nikolai Piskunov), KPP equation or Fisher–KPP equation is the partial differential equation: : \frac - D \frac = r u(1-u).\, It is a kind of reaction–diffusion system that can be used to model population growth and wave propagation. Details Fisher's equation belongs to the class of reaction–diffusion equation: in fact, it is one of the simplest semilinear reaction-diffusion equations, the one which has the inhomogeneous term : f(u,x,t) = r u (1-u),\, which can exhibit traveling wave solutions that switch between equilibrium states given by f(u) = 0. Such equations occur, e.g., in ecology, physiology, combustion, crystallization, plasma physics, and in general phase transition problems. Fisher proposed this equation in his 1937 paper ''The wave of advance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy Asymptotics
Activation energy asymptotics (AEA), also known as large activation energy asymptotics, is an asymptotic analysis used in the combustion field utilizing the fact that the reaction rate is extremely sensitive to temperature changes due to the large activation energy of the chemical reaction. History The techniques were pioneered by the Russian scientists Yakov Borisovich Zel'dovich, David A. Frank-Kamenetskii and co-workers in the 30s, in their study on premixed flames and thermal explosions (Frank-Kamenetskii theory), but not popular to western scientists until the 70s. In the early 70s, due to the pioneering work of Williams B. Bush, Francis E. Fendell, Forman A. Williams, Amable Liñán and John F. Clarke, it became popular in western community and since then it was widely used to explain more complicated problems in combustion. Method overview In combustion processes, the reaction rate \omega is dependent on temperature T in the following form ( Arrhenius law), :\omega(T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Clavin
Paul Clavin is a French scientist at Aix-Marseille University, working in the field of combustion and statistical mechanics. He is the founder of Institute for Research on Nonequilibrium Phenomena (IRPHE). Biography Clavin served as the chair of the Physical Mechanics at Institut Universitaire de France from 1993 to 2004. He received Ya.B. Zeldovich Gold Medal from The Combustion Institute in 2014 and a fellow of The Combustion Institute. A workshop titled ''Out-of-Equilibrium Dynamics'' was conducted in 2012 in honor of Clavin's 70th birthday. He is the recipient of Grand Prix award from French Academy of Sciences in 1998 and received Plumey award from Société Française de Physique in 1988. He was elected membre correspondant at the French Academy of sciences The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amable Liñán
Amable Liñán Martínez (born Noceda de Cabrera, Castrillo de Cabrera, León, Spain in 1934) is a Spanish aeronautical engineer considered a world authority in the field of combustion. Biography He holds a PhD in Aeronautical Engineering from the Technical University of Madrid, advised by :es:Gregorio Millán Barbany and Degree of Aeronautical Engineer from the Caltech advised by Frank E. Marble. He is currently Professor of Fluid Mechanics and professor emeritus at the Higher Technical School of Aeronautical Engineers of the Polytechnic University of Madrid (attached to the Department of Motorcycle and Thermofluidodynamics of said school). He has taught at universities in California, Michigan and Princeton University in the United States and in Marseilles in France, among others. Since 1997 he is an adjunct professor at Yale University. Research He has focused his research studies on the basic problems of combustion, both reactor and planetary probe dynamics, in the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Differential Equations
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function. The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to how is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like . However, it is usually impossible to write down explicit formulas for solutions of partial differential equations. There is, correspondingly, a vast amount of modern mathematical and scientific research on methods to numerically approximate solutions of certain partial differential equations using computers. Partial differential equations also occupy a large sector of pure mathematical research, in which the usual questions are, broadly speaking, on the identification of general qualitative features of solutions of various partial differential equations, such as existence, uniqueness, regularity, and stability. Among the many open questions are the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |