|
ZEVS (transmitter)
ZEVS is a facility of the Russian Navy to transmit messages to submerged submarines in deep water using ELF waves. It is located near Murmansk on the Kola Peninsula. As ZEVS works on 82 hertz, it can be only used for very rudimentary transmissions. Due to its extreme low frequency the techniques used by ZEVS are quite different from those of standard transmitters. The antenna used by ZEVS is a ground dipole. This is simply an arrangement of two widely separated electrodes, through which the transmission current is fed into the ground. As ZEVS is a location of high strategic importance, nearly no official information of the facility is available. Nearly all of the following information was obtained from satellite imagery, which can be seen on Wikimapia. ZEVS consists of 2 units, situated at and at . They are supplied by Kolenergo with electricity and have there the designation PS-373 (Cyrillic: ПС-373) and PS-393 (Cyrillic: ПС-393). These Kolenergo substations are designed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication With Submarines
Communication with submarines is a field within military communications that presents technical challenges and requires specialized technology. Because radio waves do not travel well through good electrical conductors like salt water, submerged submarines are cut off from radio communication with their command authorities at ordinary radio frequencies. Submarines can surface and raise an antenna above the sea level, or float a tethered buoy carrying an antenna, then use ordinary radio transmissions, however this makes them vulnerable to detection by anti-submarine warfare forces. Early submarines during World War II mostly traveled on the surface because of their limited underwater speed and endurance, and dove mainly to evade immediate threats or for stealthy approach to their targets. During the Cold War, however, nuclear-powered submarines were developed that could stay submerged for months. In the event of a nuclear war, submerged ballistic missile submarines have to be order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
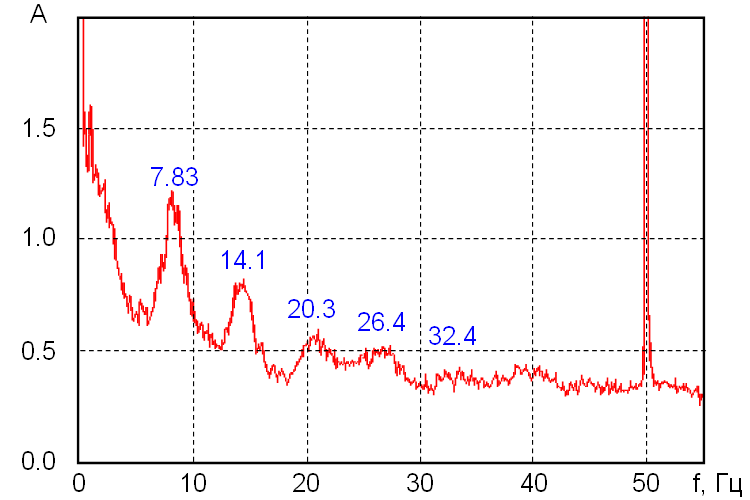
Extremely Low Frequency
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation ( radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric science, an alternative definition is usually given, from 3 Hz to 3 kHz.Liemohn, Michael W. and A. A. CHAN,Unraveling the Causes of Radiation Belt Enhancements". EOS, TRANSACTIONS, AMERICAN GEOPHYSICAL UNION, Volume 88, Number 42, 16 October 2007, pages 427-440. Republished by NASA and accessed online, 8 February 2010. Adobe File, page 2. In the related magnetosphere science, the lower frequency electromagnetic oscillations (pulsations occurring below ~3 Hz) are considered to lie in the ULF range, which is thus also defined differently from the ITU radio bands. ELF radio waves are generated by lightning and natural disturbances in Earth's magnetic field, so they are a subject of research by atmospheric scientists. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murmansk
Murmansk (Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. "Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ'') is a port city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast in the far northwest part of Russia. It sits on both slopes and banks of a modest ria or fjord, Kola Bay, an estuarine inlet of the Barents Sea. Its bulk is on the east bank of the inlet. It is in the north of the rounded Kola Peninsula which covers most of the oblast. The city is from the border with Norway and from the Finnish border. The city is named for the Murman Coast, which is in turn derived from an archaic term in Russian for "Norwegian". Benefiting from the North Atlantic Current, Murmansk resembles cities of its size across western Russia, with highway and railway access to the rest of Europe, and the northernmost trolleybus system on Earth. It lies over 2° n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kola Peninsula
sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк , image_name= Kola peninsula.png , image_caption= Kola Peninsula as a part of Murmansk Oblast , image_size= 300px , image_alt= , map_image= Murmansk in Russia.svg , map_caption = Location of Murmansk Oblast within Russia , location= Northwest Russia , coordinates= , area_km2= 100000 , length_km= 370 , width_km= 244 , highest_mount= Yudychvumchorr , elevation_m= 1201 , waterbody = * Barents Sea * White Sea , country= Russia , country_admin_divisions_title= Oblast , country_admin_divisions= Murmansk Oblast , density_km2= , demonym= , population= , citizenships= The Kola Peninsula (russian: Кольский полуостров, Kolsky poluostrov; sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely inside the Arctic Circle and is bordered by the Barents Sea to the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Dipole
In radio communication, a ground dipole, also referred to as an earth dipole antenna, transmission line antenna, and in technical literature as a horizontal electric dipole (HED), is a huge, specialized type of radio antenna that radiates extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic waves. It is the only type of transmitting antenna that can radiate practical amounts of power in the frequency range of 3 Hz to 3 kHz, commonly called ELF waves. A ground dipole consists of two ground electrodes buried in the earth, separated by tens to hundreds of kilometers, linked by overhead transmission lines to a power plant transmitter located between them. Alternating current electricity flows in a giant loop between the electrodes through the ground, radiating ELF waves, so the ground is part of the antenna. To be most effective, ground dipoles must be located over certain types of underground rock formations. The idea was proposed by U.S. Dept. of Defense physicist Nicholas Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TGC-1
TGC-1 (also referred as TGK-1; full name: Territorial generating company number 1; , ''Territorial’naya generiruyushchaya kompaniya No 1''; traded as ) is a regional power company operating in North-West Russia. The company has its headquarters in Saint Petersburg with branches in Karelia and Kola. History The company was created in 2005 by the merger of Lenenergo, Kolenergo and Karelenergogeneratsiya power companies. Formation of the new company was announced on 1 March 2005 by Lenenergo, Kolenergo and RAO UES. The company was officially registered on 25 March 2005 and began to operate on 1 October 2005. The integration of predecessor companies was completed on 1 November 2006. The majority shareholder of this time was RAO UES. Operations The company operates 52 thermal, hydro and co-generation stations in Saint Petersburg, Leningrad Oblast, Murmansk Oblast and Karelia. It has an installed generation capacity of 6,92 GW of electric power. In addition, TGC-1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Sanguine
Project Sanguine was a U.S. Navy project, proposed in 1968 for communication with submerged submarines using extremely low frequency (ELF) radio waves. The originally proposed system, hardened to survive a nuclear attack, would have required a giant antenna covering two fifths of the state of Wisconsin. Because of protests and potential environmental impact, the proposed system was never implemented. A smaller, less hardened system called Project ELF consisting of two linked ELF transmitters located at Clam Lake, Wisconsin and Republic, Michigan was built beginning in 1982 and operated from 1989 until 2004. The system transmitted at a frequency of 76 Hz. At ELF frequencies the bandwidth of the transmission is very small, so the system could only send short coded text messages at a very low data rate. These signals were used to summon specific vessels to the surface to receive longer operational orders by ordinary radio or satellite communication. Proposed system The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INS Kattabomman
INS Kattabomman is the designation of the VLF-transmission facility of the Indian Navy situated at Vijayanarayanam near Tirunelveli in Tamil Nadu. The facility spread over 3,000 acres has 13 masts, which are arranged in two rings around the central mast. The centre mast has a height of 301 metres, the masts on the inner ring measure 276.4 metres, that on the outer ring measure 227.4 metres. Two further masts of the station carrying an umbrella antenna, the INS Kattabomman is 471 metres tall and the tallest structure in India. They are also the tallest military structure in the world. The facility opened an ELF transmission facility in 2014. History Development and construction of INS Kattabomman started in 1984 as Project Skylark and costed . It was commissioned into service by Indian President Ramaswamy Venkataraman on 20 October 1990. It is named after king Veera Pandya Kattabomman, who died during the Indian independence movement. After operationalising the base, India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Radio Systems
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Electronics Of Russia
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |