|
Yuzhou City
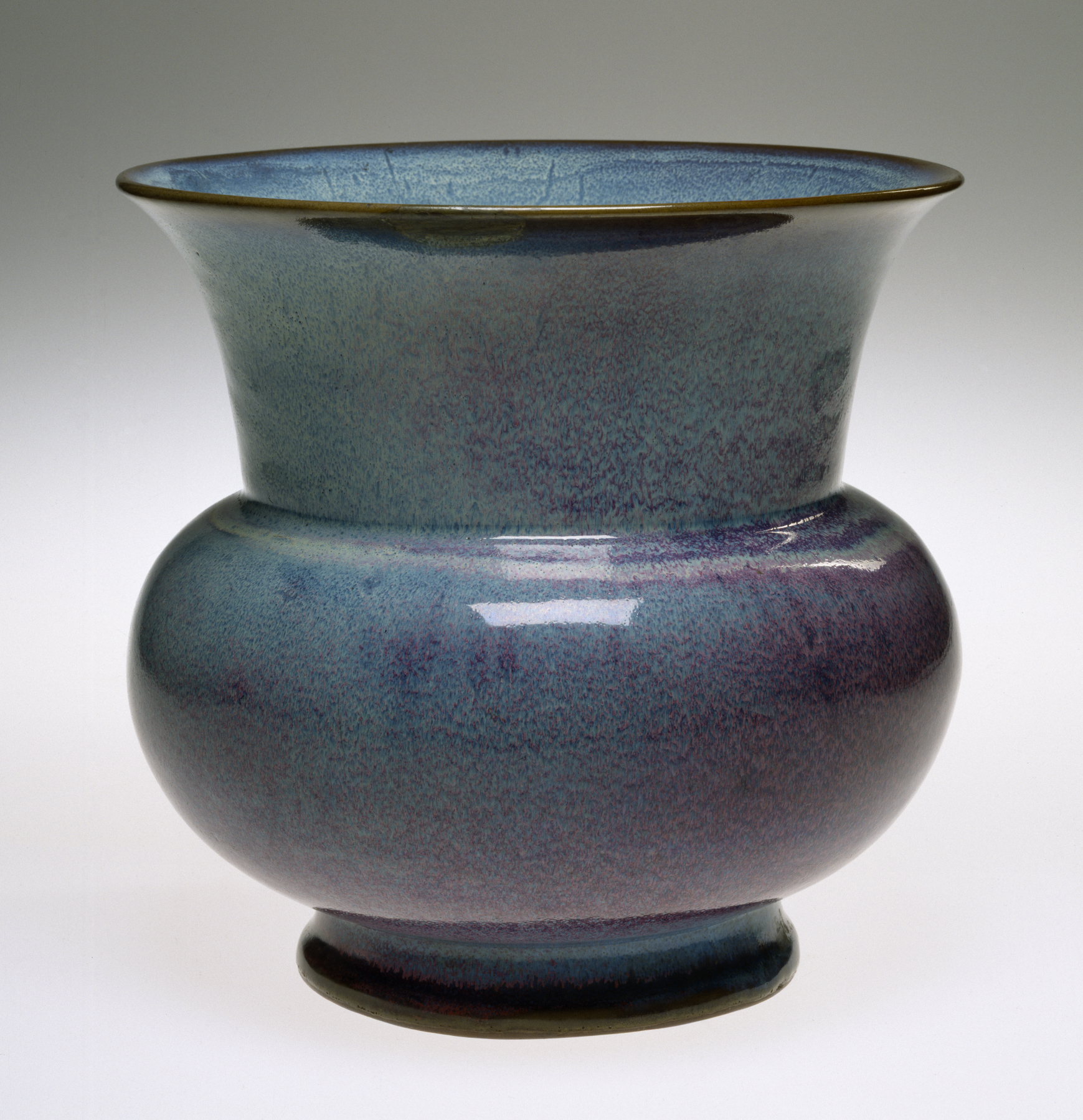
Yuzhou () is a county-level city in the central part of Henan, People's Republic of China. It occupies the northwest corner of the prefecture-level city of Xuchang. The city is named for Yu the Great, the founder of the Xia Dynasty, which the city's government claims was founded in present-day Yuzhou, and that the dynasty's capital was located in present-day Yuzhou. There is a statue of Yu the Great in Yuzhou, and he serves as a symbol of the city. The famous Jun ware () of porcelain originates in Yuzhou, specifically, in the town of (). Jun ware comprises one of the Five Great Kilns, a group of highly esteemed porcelain types from the Song dynasty. Yuzhou has historically served as a major center of traditional Chinese medicine, and the city's historic medicinal tradition has been recognized by the national government. Famous Chinese doctor Sun Simiao () had been a doctor in Yuzhou for a long period of time during the Tang dynasty. Nicknames for the city include "Summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level municipality (), county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city (1949–1970: ; 1970–1983: ), is a Administrative divisions of China#County level (3rd), county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity and a county which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Great Kilns
The Five Great Kilns (), also known as Five Famous Kilns, is a generic term for ceramic kilns or wares (in Chinese 窯 yáo can mean either) which produced Chinese ceramics during the Song dynasty (960–1279) that were later held in particularly high esteem. The group were only so called by much later writers, and of the five, only two (Ru and Guan) seem to have produced wares directly ordered by the Imperial court, though all can be of very high quality. All were imitated later, often with considerable success. All except Ding ware used celadon glazes, and in Western terms the celadon kilns are stoneware, as opposed to the Ding early porcelain. The celadons placed great emphasis on elegant forms and their ceramic glazes, and were otherwise lightly decorated, with no painting. The five kilns produced respectively: * Ru ware (汝) * Jun ware (钧) * Guan ware (官) * Ding ware (定) * Ge ware (哥) History of the term Although the group and name is generally said in books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service maintains 50 foreign news bureaus with more than 250 correspondents around the world. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, the BBC also has regional centres across England and national news c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, Anosmia, loss of smell, and Ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected Asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Lockdowns
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a number of non-pharmaceutical interventions colloquially known as lockdowns (encompassing stay-at-home orders, curfews, quarantines, and similar societal restrictions) have been implemented in numerous countries and territories around the world. These restrictions were established with the intention to reduce the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. By April 2020, about half of the world's population was under some form of lockdown, with more than 3.9 billion people in more than 90 countries or territories having been asked or ordered to stay at home by their governments. Although similar disease control measures have been used for hundreds of years, the scale of those implemented in the 2020s is thought to be unprecedented. Research and case studies have shown that lockdowns were generally effective at reducing the spread of COVID-19, therefore flattening the curve. The World Health Organization's recommendation on curfew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of China
Counties ( zh, t=縣, s=县, hp=Xiàn), formally county-level divisions, are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in Provinces and Autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and City districts. There are 1,355 counties in Mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xian'' have existed since the Warring States period and were set up nationwide by the Qin Dynasty. The number of counties in China proper gradually increased from dynasty to dynasty. As Qin Shi Huang reorganized the counties after his unification, there were about 1,000. Under the Eastern Han Dynasty, the number of counties increased to above 1,000. About 1400 existed when the Sui dynasty abolish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Shrine
An ancestral shrine, hall or temple ( or , vi, Nhà thờ họ; Chữ Hán: 家祠户), also called lineage temple, is a temple dedicated to deified ancestors and progenitors of surname lineages or families in the Chinese tradition. Ancestral temples are closely linked to Confucian philosophy and culture and the emphasis that it places on filial piety. A common central feature of the ancestral temples are the ancestral tablets that embody the ancestral spirits.Edward L. Davis (Editor), Encyclopedia of Contemporary Chinese Culture, Routledge, 2004 The ancestral tablets are typically arranged by seniority of the ancestors. Altars and other ritual objects such as incense burners are also common fixtures. Ancestors and gods can also be represented by statues. The temples are used for collective rituals and festivals in honor of the ancestors but also for other family- and community-related functions such as weddings and funerals. Sometimes, they serve wider community functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Archaeology, Chinese Academy Of Social Sciences
The Institute of Archaeology (IA; ) is a constituent institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS), based in Beijing, China. It was founded on 1 August 1950, as part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Its original 20 or so researchers came from the Beiping Research Academy and the Institute of History and Philology, Academia Sinica of the Republic of China. In 1977, the institute became part of the newly established CASS. Academic departments *Department of Prehistoric Archaeology, established 1953 *Department of Xia, Shang and Zhou Archaeology, established 1953 *Research Department of Han to Tang Archaeology, established 1953 *Research Center for Frontier Archaeology and Foreign Archaeology, established 2002 *Center for Scientific Archaeology, established 1995 *Archaeology Press, established 1955 *Center for Archaeological Data and Information, established 1996 In addition, the Research Center for Ancient Civilizations and the Conservation and Research Center of Cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longshan Culture
The Longshan (or Lung-shan) culture, also sometimes referred to as the Black Pottery Culture, was a late Neolithic culture in the middle and lower Yellow River valley areas of northern China from about 3000 to 1900 BC. The first archaeological find of this culture took place at the Chengziya Archaeological Site in 1928, with the first excavations in 1930 and 1931. The culture is named after the nearby modern town of Longshan (lit. "Dragon Mountain") in Zhangqiu, Shandong. The culture was noted for its highly polished black pottery (or egg-shell pottery). The population expanded dramatically during the 3rd millennium BC, with many settlements having rammed earth walls. It decreased in most areas around 2000 BC until the central area evolved into the Bronze Age Erlitou culture. The Longshan culture has been linked to the early Sinitic (of the Sino-Tibetan languages). According to the area and cultural type, the Longshan culture can be divided into two types: Shandong Longshan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Neolithic
In the archaeology of Southwest Asia, the Late Neolithic, also known as the Ceramic Neolithic or Pottery Neolithic, is the final part of the Neolithic period, following on from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic and preceding the Chalcolithic. It is sometimes further divided into Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) and Pottery Neolithic B (PNB) phases. The Late Neolithic began with the first experiments with pottery, around 7000 BCE, and lasted until the discovery of copper metallurgy and the start of the Chalcolithic around 4500 BCE. Southern Levant The Neolithic of the Southern Levant is divided into Pre-Pottery and Pottery or Late Neolithic phases, initially based on the sequence established by Kathleen Kenyon at Jericho. In the Mediterranean zone, the Pottery Neolithic is further subdivided into two subphases and several regional cultures, although the extent to which these represent real cultural phenomena is debated: * Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) or Late Neolithic 1 (LN1) ** Yar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |