|
Yoshitoshi Tokugawa
200px, Lieutenant General Baron Tokugawa Yoshitoshi Baron was a lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army and one of the pioneers of military aviation in Japan. He is credited with having made the first flight in a powered aircraft in Japan in 1910. Biography Family and early career Tokugawa Yoshitoshi was born in Tokyo and was the son of Count Tokugawa Atsumori (1856–1924) (head of the Shimizu Tokugawa clan). Through his father, he was the grandnephew of the last Shōgun, Tokugawa Yoshinobu. Although his father had been created a count in the ''kazoku'' peerage in 1884, he had relinquished the title in 1899, so Yoshitoshi did not inherit his title. Tokugawa graduated from the 15th class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1903, after having specialized in military engineering. In 1909, he was sent as a military attaché to France, specifically to study aeronautical engineering and military applications for the use of aircraft in combat. On orders of the Imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army General Staff
The , also called the Army General Staff, was one of the two principal agencies charged with overseeing the Imperial Japanese Army. Role The was created in April 1872, along with the Navy Ministry, to replace the Ministry of Military Affairs (''Hyōbushō'') of the early Meiji government. Initially, the Army Ministry was in charge of both administration and operational command of the Imperial Japanese Army however, from December 1878, the Imperial Army General Staff Office took over all operational control of the Army, leaving the Army Ministry only with administrative functions. The Imperial Army General Staff was thus responsible for the preparation of war plans; the military training and employment of combined arms military intelligence; the direction of troop maneuvers; troop deployments; and the compilation of field service military regulations, military histories, and cartography. The Chief of the Army General Staff was the senior ranking uniformed officer in the Imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
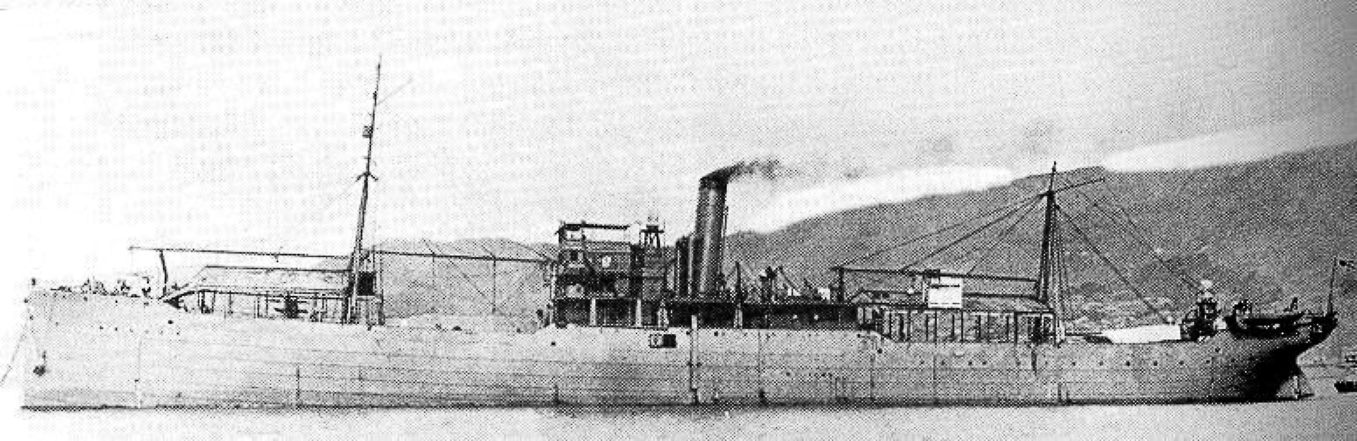
Japanese Seaplane Carrier Wakamiya
''Wakamiya'' ( ja, 若宮丸, later 若宮艦) was a seaplane carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy and the first Japanese aircraft carrier. She was converted from a transport ship into a seaplane carrier and commissioned in August 1914. She was equipped with four Japanese-built French Maurice Farman seaplanes (powered by Renault engines). In September 1914, she conducted the world's first naval-launched air raids. Early career ''Wakamiya'' was initially the Russian freighter ''Lethington'', built by Duncan in Port Glasgow, United Kingdom, laid down in 1900 and launched 21 September 1900. She was captured on a voyage from Cardiff to Vladivostok during the Russo-Japanese War near Okinoshima in 1905 by the Japanese torpedo boat ''TB No. 72''. She was acquired by the Japanese government, renamed ''Takasaki-Maru'' until given the official name of ''Wakamiya-Maru'' on 1 September, and from 1907 was managed as a transport ship by NYK. In 1913 she was transferred to the Imperial J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiautschou Bay Concession
The Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory was a German leased territory in Imperial and Early Republican China from 1898 to 1914. Covering an area of , it centered on Jiaozhou ("Kiautschou") Bay on the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula (german: Schantung Halbinsel). ''Jiaozhou'' became romanized as Kiaochow, Kiauchau or Kiao-Chau in English and as Kiautschou or Kiaochau in German. The administrative center was at Tsingtau (Pinyin ''Qingdao''). It was operated by the East Asia Squadron of the Imperial German Navy. The Russian Empire resented the German move as an infringement on Russian ambitions in the region. Background of German expansion in China Germany was a relative latecomer to the imperialistic scramble for colonies across the globe. A German colony in China was envisioned as a two-fold enterprise: as a coaling station to support a global naval presence, and because it was felt that a German colonial empire would support the economy in the mother country. Densely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army Air Service
The Imperial Japanese Army Air Service (IJAAS) or Imperial Japanese Army Air Force (IJAAF; ja, 大日本帝國陸軍航空部隊, Dainippon Teikoku Rikugun Kōkūbutai, lit=Greater Japan Empire Army Air Corps) was the aviation force of the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA). Just as the IJA in general was modeled mainly on the German Army, the IJAAS initially developed along similar lines to the Imperial German Army Aviation; its primary mission was to provide tactical close air support for ground forces, as well as a limited air interdiction capability. The IJAAS also provided aerial reconnaissance to other branches of the IJA. While the IJAAS engaged in strategic bombing of cities such as Shanghai, Nanking, Canton, Chongqing, Rangoon, and Mandalay, this was not the primary mission of the IJAAS, and it lacked a heavy bomber force. It did not usually control artillery spotter/observer aircraft; artillery battalions controlled the light aircraft and balloons that operated in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugaki Kazushige
was a Japanese general in the Imperial Japanese Army and cabinet minister before World War II, the 5th principal of Takushoku University, and twice Governor-General of Korea. Nicknamed Ugaki Issei, he served as Foreign Minister of Japan in the Konoe cabinet in 1938. Biography Military career Ugaki was the fifth son of an impoverished farming family in Ochi village, Bizen Province (currently the town of Seto, Okayama). He excelled in all studies, and passed a teacher recruitment examination. He worked as an elementary school teacher in his teens, moved to Tokyo, and managed to secure a position at the first class of the reformed Imperial Japanese Army Academy. He graduated in 1891 ranked 11th out of a class of 150. In 1900, he graduated from the Army Staff College, ranked 3rd out of a class of 39 and was awarded a sword of merit. He became a protege of General Kawakami Soroku as a captain and was sent as military attaché to Germany from 1902 to 1904, and again from 1906 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hino Kumazo
Hino may refer to: Places Estonia * Hino, Põlva County * Hino, Võru County ** Lake Hino Japan * Hino, Shiga * Hino, Tokyo * Hino, Tottori ** Hino District, Tottori ** Hino River Transportation * Hino Motors, a Japanese truck manufacturer owned by Toyota ** Hino Pakistan * Hino Station (other), railway stations in Japan: ** Hino Station (Nagano), a railway station Susuka, Nagano, operated by Nagano Electric Railway ** Hino Station (Shiga) is a passenger railway station in located in the town of Hino, Shiga Prefecture, Japan, operated by the private railway operator Ohmi Railway. Lines Hino Station is served by the Ohmi Railway Main Line, and is located 37.8 rail kilometers from ..., a railway station operated by Ohmi Railway ** Hino Station (Tokyo), a railway station operated by East Japan Railway Company Other uses * Hino (surname), a Japanese surname * Hé-no, also called Hino, an Iroquois thunder spirit See also * Heino (other) {{disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
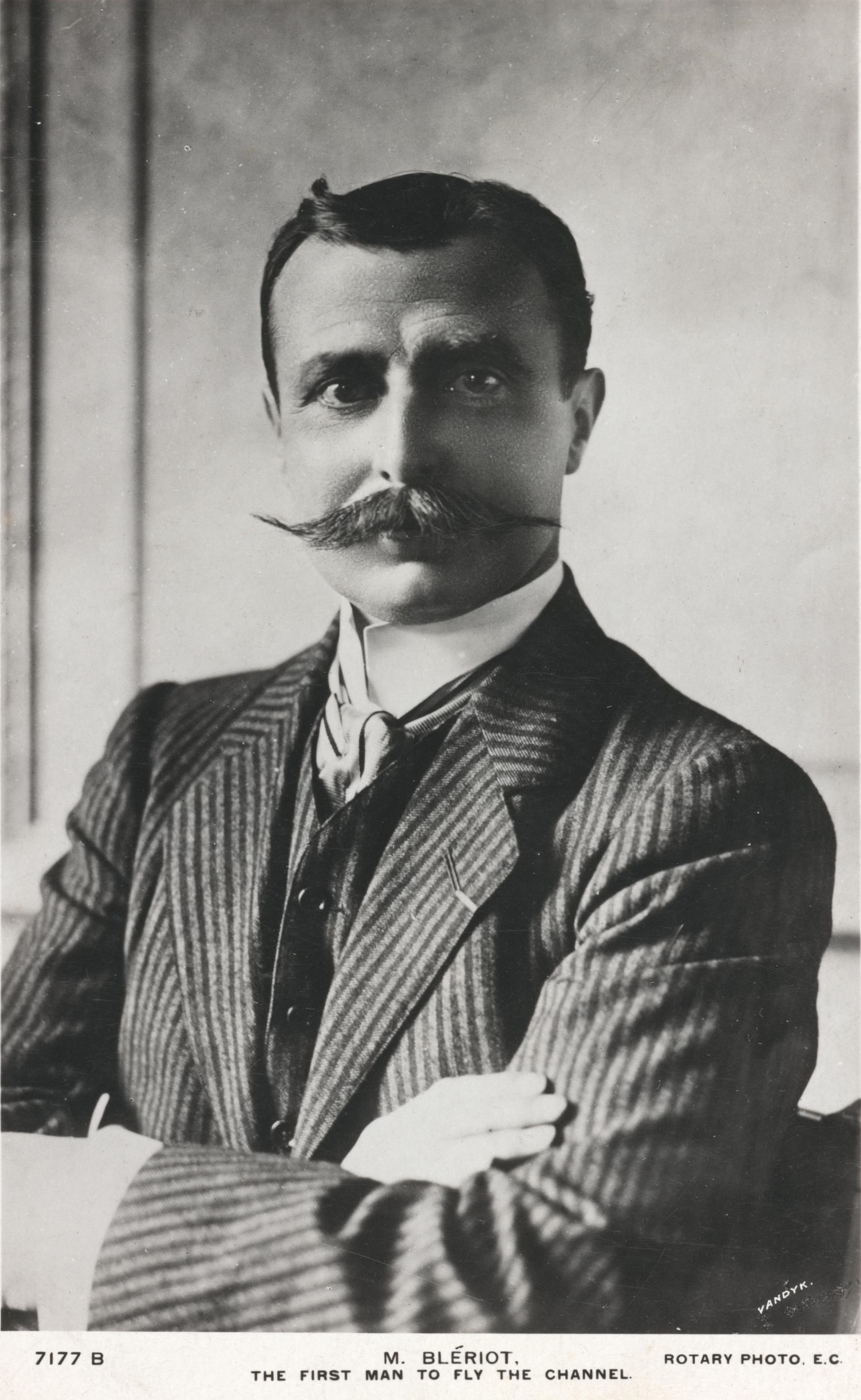
Blériot Aéronautique
Blériot Aéronautique was a French aircraft manufacturer founded by Louis Blériot. It also made a few motorcycles between 1921 and 1922 and cyclecars during the 1920s. Background Louis Blériot was an engineer who had developed the first practical headlamp for cars and had established a successful business marketing them. In 1901 he had built a small unmanned ornithopter, but his serious involvement with aviation began in April 1905 when he witnessed Gabriel Voisin's first experiments with a floatplane glider towed behind a motorboat on the river Seine. A brief partnership with Voisin followed, but after the failure of the Blériot III and its modified version, the Blériot IV, the partnership was dissolved and Blériot set up his own company, "Recherches Aéronautique Louis Blériot" (Louis Blériot Aeronautical Research) at Courbevoie in March 1909. Blériot's early experiments File:Bleriot V.jpg, Blériot V File:Bleriot VI.jpg, Blériot VI File:Bleriot VII.jpg, Blér ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerial Photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography. Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs or "drones"), balloons, blimps and dirigibles, rockets, pigeons, kites, or using action cameras while skydiving or wingsuiting. Handheld cameras may be manually operated by the photographer, while mounted cameras are usually remotely operated or triggered automatically. Aerial photography typically refers specifically to bird's-eye view images that focus on landscapes and surface objects, and should not be confused with air-to-air photography, where one or more aircraft are used as chase planes that "chase" and photograph other aircraft in flight. Elevated photography can also produce bird's-eye images closely resembling aerial photography (despite not actually being aerial shots) when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokorozawa Aviation Museum
The is a museum located in the city of Tokorozawa, Saitama dedicated to the history of aviation in Japan. It contains aircraft and other displays (many of which are interactive) and an IMAX theatre. Located on the site of Japan's first airfield which started operations in 1911 with a flight by Yoshitoshi Tokugawa, the original single runway is still visible and has been incorporated into a larger multifunction park adjacent to the museum. It is located in the Tokorozawa Aviation Memorial Park. Aircraft in collection At any given time the aircraft on display will vary. The NAMC YS-11 and the Curtiss EC-46 Commando are on permanent display in the park, but the collection visible in the museum itself changes. The collection is as follows: * ''91-1143'' Curtiss EC-46A Commando (outside)Tokor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |