|
Yeldham Railway Station
Yeldham railway station was located in Great Yeldham, Essex Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G .... It was from London Liverpool Street via Marks Tey. It closed in 1962. References External links Yeldham station on navigable 1946 O. S. map* Disused railway stations in Essex Former Colne Valley and Halstead Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1862 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1962 1862 establishments in England {{EastEngland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Yeldham
Great Yeldham is a village in north Essex, England, about from the Suffolk border. Great Yeldham is situated along the busy main A1017 road (formerly A604) between Braintree and Haverhill. The village is where the infant River Colne is joined by a stream from near Stambourne and another that has flowed via Toppesfield. The river flows via Colchester on its 39-mile journey to the sea. Great Yeldham contains the "Great Oak", an old preserved oak tree in the centre of the village, which is claimed to have been recorded in William the Conqueror's Domesday Book of 1086. In 1967 Great Yeldham elected a Communist councillor, June Cohen, to the surprise of many in the area. Agriculture From the 1950s to the 1970s Great Yelham was home to the Whitlock Bros, manufacturers and exporters of Dinkum Diggers (tractors with backhoes and fronthoes, often known these days as 'JCB's). In 1972 Whitlock Bros. was taken over by Hymac, and production subsequently moved to Rhymney in Wales. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braintree District
Braintree is a local government district in the English county of Essex, with a population (2011 census) of 147,084. Its main town is Braintree. The three towns of the district are Braintree, Halstead and Witham. The district was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of the urban districts of Braintree and Bocking, Halstead, and Witham and (for list of parishes) Braintree Rural District and Halstead Rural District. Council The council is controlled by the Conservatives who hold 34 of the 49 seats. The council is based at Causeway House on Bocking End in Braintree. The building was purpose-built for the council and opened in 1981. Wards There are 26 wards: * Bocking Blackwater *Bocking North *Bocking South * Braintree Central and Beckers Green *Braintree South *Braintree West *Bumpstead *Coggeshall *Gosfield & Greenstead Green *Great Notley & Black Notley *Halstead St Andrews *Halstead Trinity *Hatfield Peverel and Terling *Hedingham *Kelvedon and Feering * Rayne *Silver End ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
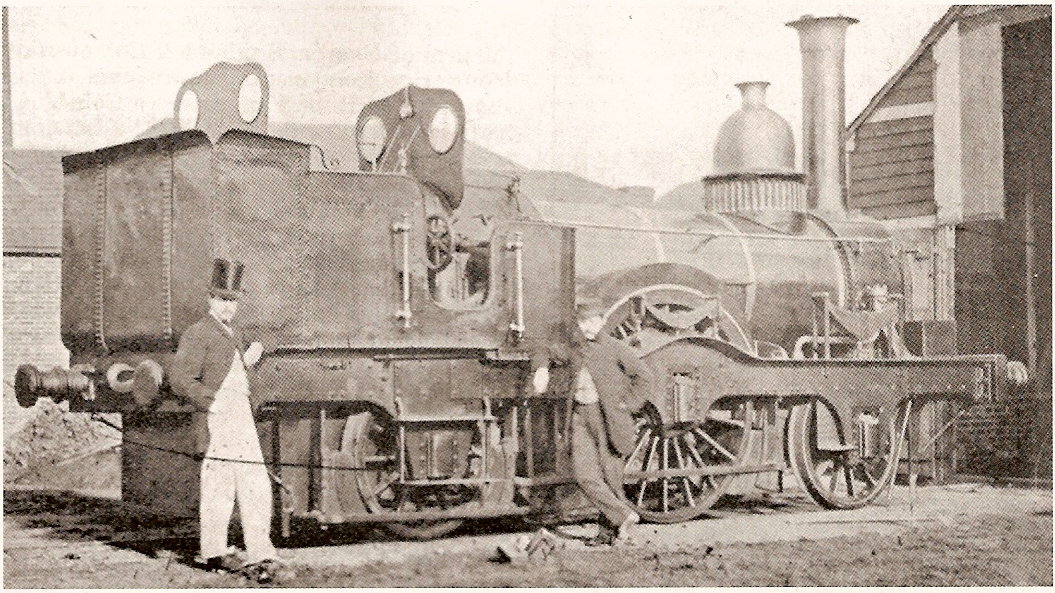
Colne Valley And Halstead Railway
The Colne Valley and Halstead Railway (CVHR) is a closed railway between Haverhill, Suffolk and Chappel and Wakes Colne, Essex, in England. History A railway in the Colne Valley was first proposed in 1846 when the Colchester, Stour Valley, Sudbury and Halstead Railway Company was incorporated to build a line from Marks Tey on the Eastern Counties Railway to Sudbury, with a branch to Halstead and a line from Colchester to Hythe. A later extension to Bury St. Edmunds and Clare was also approved, however a shortage of funds resulted in only the Stour Valley Railway to Sudbury and the line to Hythe being built. In 1856, the Colne Valley and Halstead Railway Company was formed by local people to build a branch line from Chappel and Wakes Colne railway station to Halstead. It was authorised on 30 June 1856, and opened on 16 April 1860 between Chappel (north of Marks Tey) and Halstead, a distance of .Railway Magazine December 1958 p. 890 A extension was authorised on 13 Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the " Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At that time, it was divided into the new British Railways' Eastern Region, North Eastern Region, and partially the Scottish Region. History The company was the second largest created by the Railways Act 1921. The principal constituents of the LNER were: * Great Eastern Railway * Great Central Railway * Great Northern Railway * Great North of Scotland Railway * Hull and Barnsley Railway * North British Railway * North Eastern Railway The total route mileage was . The North Eastern Railway had the largest route mileage of , whilst the Hull and Barnsley Railway was . It covered the area north and east of London. It included the East Coast Main Line from London to Edinburgh via York and Newcastle upon Tyne and the routes from Edinburgh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and Greater London to the south and south-west. There are three cities in Essex: Southend, Colchester and Chelmsford, in order of population. For the purposes of government statistics, Essex is placed in the East of England region. There are four definitions of the extent of Essex, the widest being the ancient county. Next, the largest is the former postal county, followed by the ceremonial county, with the smallest being the administrative county—the area administered by the County Council, which excludes the two unitary authorities of Thurrock and Southend-on-Sea. The ceremonial county occupies the eastern part of what was, during the Early Middle Ages, the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex. As well as rural areas and urban areas, it forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sible And Castle Hedingham Railway Station
Sible and Castle Hedingham railway station was a station in Sible Hedingham, Essex Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and G .... It was from London Liverpool Street via Marks Tey. It closed for passengers in 1962. References External links Sible and Castle Hedingham station on navigable 1946 O. S. map* Disused railway stations in Essex Former Colne Valley and Halstead Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1861 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1962 1861 establishments in England {{EastEngland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Colne Valley And Halstead Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1862
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1962
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |