|
Yeavering
Yeavering () is a hamlet in the north-east corner of the civil parish of Kirknewton in the English county of Northumberland. It is located on the River Glen at the northern edge of the Cheviot Hills. It is noteworthy as the site of a large Anglo-Saxon period settlement that archaeologists have interpreted as being one of the seats of royal power held by the kings of Bernicia in the 7th century CE. Evidence for human activity in the vicinity has been found from the Mesolithic, Neolithic and Bronze Age periods, although it would be in the Iron Age that significant settlement first occurred at Yeavering. In this period, a heavily inhabited hillfort was constructed on Yeavering Bell which appears to have been a major settlement centre at the time. According to Book 2 Chapter 14 of the ''Ecclesiastical History'' of the Venerable Bede (673–735), in the year 627 Bishop Paulinus of York accompanied the Northumbrian king Edwin and his queen Æthelburg to their royal vill (the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
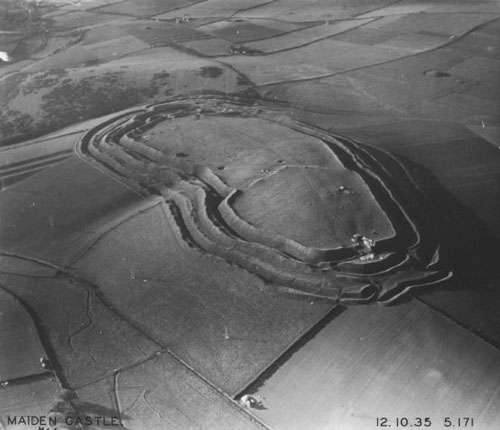
Yeavering Bell
Yeavering Bell is a twin-peaked hill near the River Glen in north Northumberland, England, to the west of Wooler, and forming part of the Cheviot Hills. The summit, 1158 feet (361 metres) above sea level, is encircled by the wall of a late-prehistoric hillfort, a tribal centre of the Votadini called in Brythonic and Old Welsh Din Gefron, from which the name stems (Old English *geafringa-). The hillfort encloses an area of approximately and is enclosed by a stone wall, upwards of thick, having four entrances, one of which is defended by a guard-house; and within this area is an inner fort, excavated out of the rock, of an oval form, measuring across at the widest part. On the sides of the hill, and in a high valley between the Bell and the next hill, called Whitelaw, there are many remains of stone huts rudely flagged, some in groups surrounded by rampiers (ramparts), and others isolated. Barrows, too, are numerous here. The hillfort enclosure was constructed in two phases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
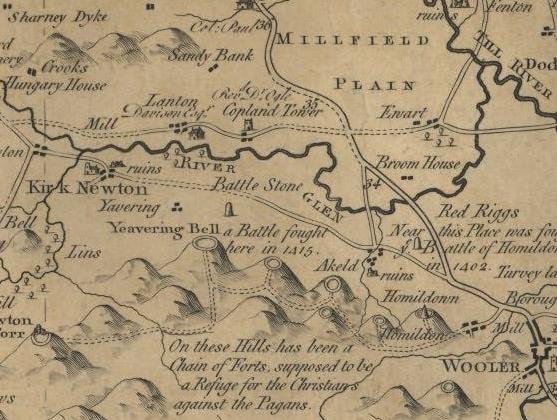
River Glen, Northumberland
The River Glen is a seven mile long tributary of the River Till flowing through Northumberland, England. The College Burn and Bowmont Water, both flowing out of the Cheviot Hills, meet near Kirknewton to form the River Glen. The Glen flows past the small settlements of Yeavering, Lanton, Coupland, Akeld and Ewart, before joining the Till. History The area around the Glen is rich in historical and archaeological interest. Iron Age hillforts on peaks to the south of the river overlook the Anglo-Saxon settlement and palace site at Yeavering, where St. Paulinus baptised new converts and, according to Bede, "washed them with the water of absolution in the river Glen, which is close by" (Tomlinson, 1888, p. 504). The area around the Glen was the setting for some of the bloodiest border warfare between Scotland and England. The Battle of Humbleton Hill was fought near the river in 1402, as was the Battle of Geteryne (Yeavering) in 1415. Arthurian myth A reference to a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirknewton, Northumberland
Kirknewton is a Northumbrian village in the north of the county of Northumberland, about from the town of Wooler and roughly the same distance to the Scottish Borders. The village lies in the valley of Glendale, which takes its name from the River Glen, whose source at the confluence of the Bowmont Water and the College Burn lies at the west end of the village. The population as taken at the 2011 Census was less than 100. Details are maintained in the parish of Akeld. Demography The parish of Kirknewton was one of the geographically largest in the United Kingdom, but one of the smallest in terms of population, with a count of 108 residents (56 female, 52 male) in the 2001 UK Census. Most residents live in the villages of Kirknewton, Westnewton and Hethpool, with the remainder scattered in remote farms and steadings, many of which are now holiday properties. Prior to the 2011 Census, the parish merged with neighbouring Akeld. Hethpool The name Hethpool derives from "P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin Of Northumbria
Edwin ( ang, Ēadwine; c. 586 – 12 October 632/633), also known as Eadwine or Æduinus, was the List of monarchs of Northumbria, King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from about 616 until his death. He converted to Christianity and was baptism, baptised in 627; after he fell at the Battle of Hatfield Chase, he was venerated as a saint. Edwin was the son of Ælla of Deira, Ælle, the first known king of Deira, and seems to have had at least two siblings. His sister Acha of Deira, Acha was married to Æthelfrith of Bernicia, Æthelfrith, king of neighbouring Bernicia. An otherwise unknown sibling fathered Hereric, who in turn fathered Abbess Hilda of Whitby and Hereswith, wife to Æthelric, the brother of king Anna of East Anglia. Early life and exile The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reported that on Ælle's death a certain "Aethelric of Deira, Æthelric" assumed power. The exact identity of Æthelric is uncertain. He may have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheviot Hills
The Cheviot Hills (), or sometimes The Cheviots, are a range of uplands straddling the Anglo-Scottish border between Northumberland and the Scottish Borders. The English section is within the Northumberland National Park. The range includes The Cheviot (the highest hill), plus Hedgehope Hill to the east, Windy Gyle to the west, and Cushat Law and Bloodybush Edge to the south. The hills are sometimes considered a part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland as they adjoin the uplands to the north. Since the Pennine Way runs through the region, the hills are also considered a part of the northern Pennines although they are separated from the Cheviot Hills by the Tyne Gap, part of which lies within the southern extent of the Northumberland National Park. The Cheviot Hills are primarily associated with geological activity from approximately 480 to 360 million years ago, when the continents of Avalonia and Laurentia collided, resulting in extensive volcanic activity (the Caledonian o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey. It is bordered by land on three sides; by the Scottish Borders region to the north, County Durham and Tyne and Wear to the south, and Cumbria to the west. The fourth side is the North Sea, with a stretch of coastline to the east. A predominantly rural county with a landscape of moorland and farmland, a large area is part of Northumberland National Park. The area has been the site of a number of historic battles with Scotland. Name The name of Northumberland is recorded as ''norð hẏmbra land'' in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, meaning "the land north of the Humber". The name of the kingdom of ''Northumbria'' derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the people south of the Humber Estuary. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Vill
A royal vill, royal ''tun'' or ''villa regalis'' ( ang, cyneliċ tūn) was the central settlement of a rural territory in Anglo Saxon England, which would be visited by the King and members of the royal household on regular circuits of their kingdoms. The royal vill was the centre for the administration of a subdivision of a kingdom, and the location where the subdivision would support the royal household through the provision of food rent. Royal vills have been identified as the centres of the ''regiones'' of the early Anglo-Saxon period, and of the smaller multiple estates into which ''regiones'' were gradually divided by the 8th century. The British Isles during the early Middle Ages lacked the sophisticated long-distance trade in essential foodstuffs required to support agriculturally unproductive households in a single location. Kings and their entourages could therefore only support themselves by constantly moving between territories with an obligation to support them, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paulinus Of York
Paulinus (died 10 October 644) was a Roman missionary and the first Bishop of York. A member of the Gregorian mission sent in 601 by Pope Gregory I to Christianize the Anglo-Saxons from their native Anglo-Saxon paganism, Paulinus arrived in England by 604 with the second missionary group. Little is known of Paulinus's activities in the following two decades. After some years spent in Kent, perhaps in 625, Paulinus was consecrated a bishop. He accompanied Æthelburg of Kent, sister of King Eadbald of Kent, on her journey to Northumbria to marry King Edwin of Northumbria, and eventually succeeded in converting Edwin to Christianity. Paulinus also converted many of Edwin's subjects and built some churches. One of the women Paulinus baptised was a future saint, Hilda of Whitby. Following Edwin's death in 633, Paulinus and Æthelburg fled Northumbria, leaving behind a member of Paulinus's clergy, James the Deacon. Paulinus returned to Kent, where he became Bishop of Rocheste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Brittonic people of the Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending from the Firth of Forth and around modern Stirling to the River Tyne, including at its peak what are now the Falkirk, Lothian and Borders regions and Northumberland. This area was briefly part of the Roman province of ''Britannia''. The earliest known capital of the Votadini appears to have been the Traprain Law hill fort in East Lothian, until that was abandoned in the early 5th century. They afterwards moved to Din Eidyn (Edinburgh). The name is recorded as ''Votadini'' in classical sources, and as ''Otodini'' on old maps of ancient Roman Britain. Their descendants were the early medieval kingdom known in Old Welsh as '' Guotodin'', and in later Welsh as ''Gododdin'' . One of the oldest known pieces of British literature is a poem called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
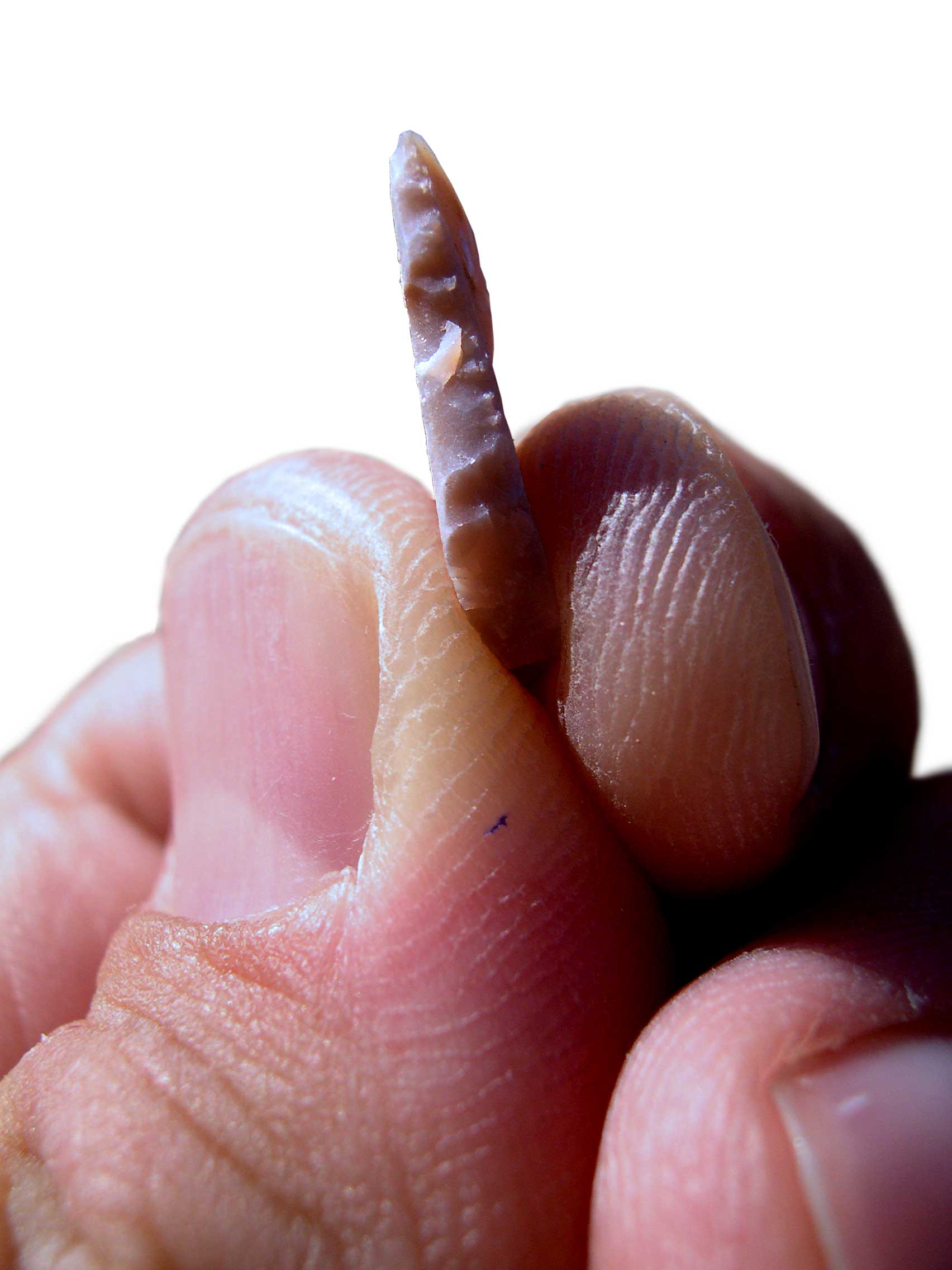
Microliths
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric microlit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. Hillforts developed in the Late Bronze and Early Iron Age, roughly the start of the first millennium BC, and were used in many Celtic areas of central and western Europe until the Roman conquest. Nomenclature The spellings "hill fort", "hill-fort" and "hillfort" are all used in the archaeological literature. The ''Monument Type Thesaurus'' published by the Forum on Information Standards in Heritage lists ''hillfort'' as the preferred term. They all refer to an elevated site with one or more ramparts made of earth, stone and/or wood, with an external ditch. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Scale
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale. History The scale was devised in 1805 by the Irish hydrographer Francis Beaufort (later Rear Admiral), a Royal Navy officer, while serving on . The scale that carries Beaufort's name had a long and complex evolution from the previous work of others (including Daniel Defoe the century before) to when Beaufort was Hydrographer of the Navy in the 1830s, when it was adopted officially and first used during the voyage of HMS ''Beagle'' under Captain Robert FitzRoy, who was later to set up the first Meteorological Office (Met Office) in Britain giving regular weather forecasts. In the 18th century, naval officers made regular weather observations, but there was no standard scale and so they could be very subjective – one man's "stiff breeze" might be another's "soft breeze". Beaufort succeeded in standardising the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |