|
Yantra Mandir
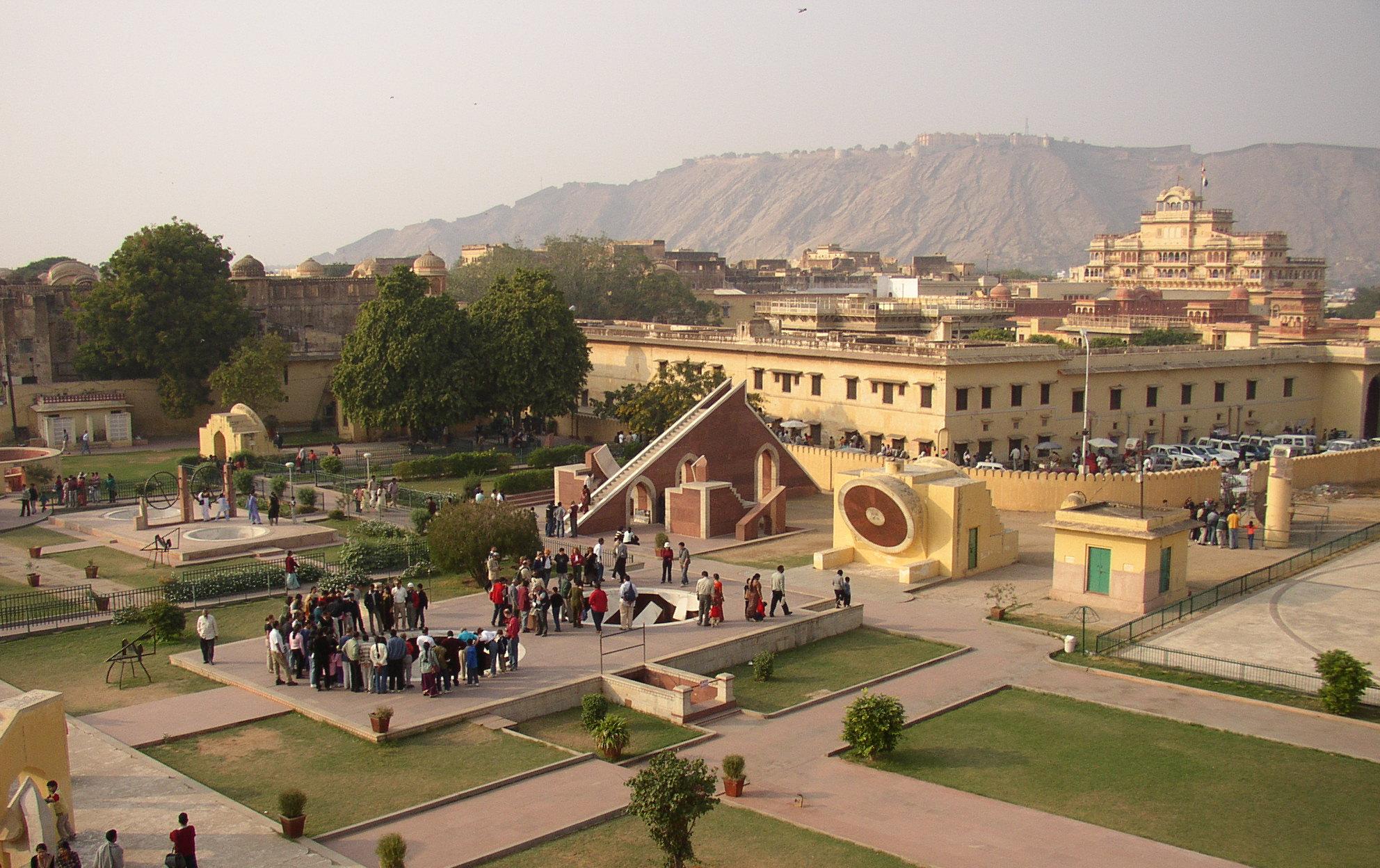
A Jantar Mantar ( Hindustani pronunciation: ͡ʒən̪t̪ər mən̪t̪ər is an assembly of stone-built astronomical instruments, designed to be used with the naked eye. There were five Jantar Mantars in India, all of them built at the command of the Rajah Jai Singh II, who had a keen interest in mathematics, architecture and astronomy; The largest example is the equinoctial sundial belonging to Jaipur's assembly of instruments, consisting of a gigantic triangular gnomon with the hypotenuse parallel to the Earth's axis. On either side of the gnomon is a quadrant of a circle, parallel to the plane of the equator. The instrument can be used with an accuracy of about 2 seconds by a "skilled observer" to measure the time of day, and the declination of the Sun and the other heavenly bodies. It is the world's largest stone sundial, known as the Vrihat Samrat Yantra. The Jaipur Jantar Mantar is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jantar Mantar At Jaipur
Jantar may refer to: *Jantar, Poland, a village in Poland *Anna Jantar (1950 – 1980), a Polish singer *SZD-38 Jantar 1, a glider designed and produced in Poland from 1971 **SZD-41 Jantar Standard, Standard Class glider **SZD-42 Jantar 2, Open Class competition glider **SZD-48 Jantar Standard 2/3, a Standard Class glider produced in Poland from 1977 * Amber (russian: янтарь, jantárʹ, links=no), fossilized tree resin See also *Jandar (other) *Yantar (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend foward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and right ascension is like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedh Shala
Jantar Mantar or Vedh Shala is located in the holy city of New Ujjain. It is an observatory built by Maharaja Jai Singh II in 1725 which consists of 13 architectural astronomy instruments. The observatory is one of the five observatories built by Maharaja Jai Singh II when he was governor of Ujjain. Vedh Shala was constructed with the aim of measuring local time, altitude (of the place) and also to measure declination of the Sun, stars and planets and to determine eclipses. Motion, speed and properties of stars and planets were also recorded using several special instruments. Jai Singh II was also an astronomer and had deep interest in science and astronomy. In early 18th century, he sent his scholars to several countries to study design, construction and technology of the observatories and also the prevalent technology. The scholars returned with their observations and many manuals on astronomy. Subsequently between 1724 and 1737, Jai Singh II had five observatories constructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jantar Mantar, Jaipur
The Jantar Mantar, Jaipur is a collection of 19 astronomical instruments built by the Rajput king Sawai Jai Singh II, the founder of Jaipur, Rajasthan. The monument was completed in 1734.The Jantar Mantar at Jaipur, India Portal to the Heritage of Astronomy, in partnership with UNESCO World Heritage Site It features the world's largest stone , and is a World Heritage site. It is near [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yantra
Yantra () (literally "machine, contraption") is a geometrical diagram, mainly from the Tantric traditions of the Indian religions. Yantras are used for the worship of deities in temples or at home; as an aid in meditation; used for the benefits given by their supposed occult powers based on Hindu astrology and tantric texts. They are also used for adornment of temple floors, due mainly to their aesthetic and symmetric qualities. Specific yantras are traditionally associated with specific deities and/or certain types of energies used for accomplishment of certain tasks, vows, that may be materialistic or spiritual in nature. It becomes a prime tool in certain sadhanas performed by the sadhaka the spiritual seeker. Yantras hold great importance in Hinduism, Jainism, and Buddhism. Representations of the yantra in India have been considered to date back to 11,000–10,000 years BCE. The Baghor stone, found in an upper-paleolithic context in the Son River valley, is considered the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The Solar System has at least eight planets: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets each rotate around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole. All of them possess an atmosphere, although that of Mercury is tenuous, and some share such features as ice caps, seasons, volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. Apart from Venus and Mars, the Solar System planets generate magnetic fields, and all except Venus and Mercury have natural satellites. The giant planets bear ring syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jantar Mantar, Varanasi
Jantar Mantar is an observatory built in Varanasi in the year 1737 by Maharaja Jai Singh II of kingdom of Amber (later called Jaipur). The observatory is one of the five built by Maharaja Jai Singh II. - - History Maharaja Jai Singh II was also an astronomer and had a deep interest in science and astronomy. In the early 18th century, he sent his scholars to several countries to study design, construction and technology of the observatories and also the prevalent technology. The scholars returned with their observations and many manuals on astronomy. Subsequently, between 1724 and 1737, Maharaja Jai Singh II had five observatories constructed in Jaipur, Mathura, New Delhi, Ujjain and in Varanasi. There is another evidence of the observatory being built at least two centuries before 1772. According to the ''Collected writing of Dharampal'', Sir Robert Barker, in 1772, wrote that the observatory was built about 200 years before by Raja Mawnsing, son of Jaysing. He states, "Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathura, Uttar Pradesh
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. In ancient times, Mathura was an economic hub, located at the junction of important caravan routes. The 2011 Census of India estimated the population of Mathura at 441,894. In Hinduism, Mathura is birthplace of Krishna, which is located at the Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex. It is one of the Sapta Puri, the seven cities considered holy by Hindus, also called Mokshyadayni Tirth. The Kesava Deo Temple was built in ancient times on the site of Krishna's birthplace (an underground prison). Mathura was the capital of the kingdom of Surasena, ruled by Kansa, the maternal uncle of Krishna. Mathura is part of the Lord Krishna circuit (Mathura,Vrindavan, Barsana, Govardhan, Kurukshetra, Dwarka and Bhalka). Janmashtami is grandly celebrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, [ʊd͡ːʒɛːn]) is a city in Ujjain district of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the public administration, administrative centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the ''Kumbh Mela'' held there every 12 years. The famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city. An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti (India), Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas. During the 18th century, the city briefly became the capital of Scindia state of the Maratha Empire, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jantar Mantar, New Delhi
Jantar Mantar is located in the modern city of New Delhi. “Jantar Mantar” literally means “instruments for measuring the harmony of the heavens”. It consists of 13 architectural astronomy instruments. The site is one of five built by Maharaja Jai Singh II of Jaipur, from 1723 onwards, revising the calendar and astronomical tables. Jai Singh, born in 1688 into a royal Rajput family that ruled the regional kingdom, was born into an era of education that maintained a keen interest in astronomy. There is a plaque fixed on one of the structures in the Jantar Mantar observatory in New Delhi that was placed there in 1910 mistakenly dating the construction of the complex to the year 1710. Later research, though, suggests 1724 as the actual year of construction. Its height is . The primary purpose of the observatory was to compile astronomical tables, and to predict the times and movements of the sun, moon and planets. Some of these purposes nowadays would be classified as ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |