|
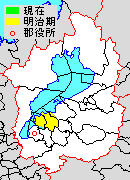
Yamakami Domain
was a '' Fudai'' feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan. It was located in southeastern Ōmi Province, in the Kansai region of central Honshu. The domain was centered at Yamakami ''jin'ya'', located in what is now the Yamakami neighborhood of the city of Higashiōmi in Shiga Prefecture. History Yamakami was located in a strategically important location on a road connecting Ōmi with Ise Province and the area was hotly contested by various warlords in the Sengoku period. Yamakami Domain was created for Inagaki Shigetada, a ''hatamoto'' in the service of Shogun Tokugawa Ietsuna who rose through the ranks of the Shogunate bureaucracy, including serving as a ''wakadoshiyori''. He gained additional fiefs with his promotions, eventually meeting the required ''kokudaka'' to be allowed to establish a cadet branch of the Inagaki clan. Inagaki Shigetada constructed a ''jin'ya'' and ''jōkamachi'', but the domain's financial situation became critical during the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han System
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokudaka
refers to a system for determining land value for taxation purposes under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo-period Japan, and expressing this value in terms of ''koku'' of rice. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Koku"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 549. One 'koku' (roughly equivalent to five bushels) was generally viewed as the equivalent of enough rice to feed one person for a year. The actual revenue or income derived holding varied from region to region, and depended on the amount of actual control the fief holder held over the territory in question, but averaged around 40 percent of the theoretical ''kokudaka''. pp. 14–15. The amount taxation was not based on the actual quantity of rice harvested, but was an estimate based on the total economic yield of the land in question, with the value of other crops and produce converted to their equivalent value in terms of rice. The ranking of precedence of the ''daimyō'', or feudal rulers, was determined in part by the ''kokudaka'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamō District, Shiga
is a district located in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. As of September 1, 2011, the district has an estimated population of 35,629 and a density of 220 persons per km2. The total area is 162.15 km2. Towns *Hino *Ryūō Merger *On January 1, 2006 the town of Gamō merged into the city of Higashiōmi. *On March 21, 2010 the town of Azuchi merged into the city of Ōmihachiman 260px, City Hall 260px, Traditional buildings Preservation Area is a city located in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 82,233 in 34747 households and a population density of 570 persons per km². The total area .... Transition Light blue autonomies are Gamō District's towns, deep blue autonomies are Gamō District's villages, and gray autonomies are others. Districts in Shiga Prefecture {{Shiga-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōka District, Shiga
was a district located in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. As of 2003, the district had an estimated population of 147,928 and a density of 267.90 persons per km2. The total area was 552.18 km2. Towns and villages Before the dissolution in 2004, the district had seven towns as listed below. Each municipality is now a part of the city noted in the parentheses. * Ishibe ( Konan) * Kōsei (Konan) * Kōka (Kōka) * Kōnan (Kōka) * Minakuchi (Kōka) * Shigaraki (Kōka) * Tsuchiyama (Kōka) Mergers *On October 1, 2004: ** the towns of Kōsei and Ishibe were merged to create the city of Konan. ** the former town of Kōka absorbed the towns of Kōnan, Minakuchi, Shigaraki and Tsuchiyama to create the city of Kōka was a after ''Tenpō'' and before ''Kaei.'' This period spanned the years from December 1844 through February 1848. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * December 2, 1844 (): The new era name of ''Kōka'', meaning "Becoming Wide .... Kōka Distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasu District, Shiga
was a district located in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. On October 1, 2004, the former town of Yasu absorbed the town of Chūzu, effectively turning Yasu District into Yasu City. Therefore, Yasu District was dissolved as a result of this merger. As of 2003, the district had an estimated population of 49,155 and a density Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ... of 799.92 persons per km2. The total area was 61.45 km2. Former Towns and villages * Chūzu * Yasu Transition Light blue autonomies are Yasu District's town, deep blue autonomies are Yasu District's village, and gray autonomies are others. {{coord missing, Shiga Prefecture Former districts of Shiga Prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Mass
Jeffrey Paul Mass (June 29, 1940 – March 30, 2001) was an American academic, historian, author and Japanologist. He was Yamato Ichihashi Professor of Japanese History at Stanford University.Sanford, John "Jeffrey Mass, a leading authority on Japanese medieval history, dead at 60,"Stanford News Service. April 9, 2001; retrieved 2012-11-9. Early life Mass was born in New York City in 1940. He earned a bachelor's degree in history from Hamilton College in 1961, a master's degree in history from New York University in 1965, and he received his doctorate in history from Yale in 1971.Hamilton College "Hamilton College Honorary Degree Presented in memoriam to Jeffrey P. Mass ’62" retrieved 2012-11-9. Career Mass joined the Stanford University faculty in 1973. He was made a full professor in 1981. After 1987, he spent the late spring and summer of each year teaching at Oxford University. During many years, his research was supported by a Fulbright Research Fellowship, a Mellon Fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadastral
A cadastre or cadaster is a comprehensive recording of the real estate or real property's metes-and-bounds of a country.Jo Henssen, ''Basic Principles of the Main Cadastral Systems in the World,'/ref> Often it is represented graphically in a cadastral map. In most countries, legal systems have developed around the original administrative systems and use the cadastre to define the dimensions and location of land parcels described in legal documentation. A land parcel or cadastral parcel is defined as "a continuous area, or more appropriately volume, that is identified by a unique set of homogeneous property rights". Cadastral surveys document the Boundary (real estate), boundaries of land ownership, by the production of documents, diagrams, sketches, plans (''plats'' in the US), charts, and maps. They were originally used to ensure reliable facts for land valuation and taxation. An example from early England is the Domesday Book in 1086. Napoleon established a comprehensive c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han System
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abolition Of The Han System
The in the Empire of Japan and its replacement by a system of prefectures in 1871 was the culmination of the Meiji Restoration begun in 1868, the starting year of the Meiji period. Under the reform, all daimyos (, ''daimyō'', feudal lords) were required to return their authority to the Emperor Meiji and his house. The process was accomplished in several stages, resulting in a new centralized government of Meiji Japan and the replacement of the old feudal system with a new oligarchy. Boshin War After the defeat of forces loyal to the Tokugawa shogunate during the Boshin War in 1868, the new Meiji government confiscated all lands formerly under direct control of the Shogunate (''tenryō'') and lands controlled by daimyos who remained loyal to the Tokugawa cause. These lands accounted for approximately a quarter of the land area of Japan and were reorganized into prefectures with governors appointed directly by the central government. Return of the domains The second pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boshin War
The , sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a clique seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court. The war stemmed from dissatisfaction among many nobles and young samurai with the shogunate's handling of foreigners following the opening of Japan during the prior decade. Increasing Western influence in the economy led to a decline similar to that of other Asian countries at the time. An alliance of western samurai, particularly the domains of Chōshū, Satsuma, and Tosa, and court officials secured control of the Imperial Court and influenced the young Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Yoshinobu, the sitting ''shōgun'', realizing the futility of his situation, abdicated and handed over political power to the emperor. Yoshinobu had hoped that by doing this the House of Tokugawa could be preserved and participate in the future gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakumatsu Period
was the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate ended. Between 1853 and 1867, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a feudal Tokugawa shogunate to the modern empire of the Meiji government. The major ideological-political divide during this period was between the pro-imperial nationalists called and the shogunate forces, which included the elite swordsmen. Although these two groups were the most visible powers, many other factions attempted to use the chaos of to seize personal power.Hillsborough, ''page # needed'' Furthermore, there were two other main driving forces for dissent: first, growing resentment on the part of the (or outside lords), and second, growing anti-Western sentiment following the arrival of Matthew C. Perry. The first related to those lords whose predecessors had fought against Tokugawa forces at the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, after which they had been permanently excluded from all powerfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sōshaban
were officials of the Tokugawa shogunate in Edo period Japan. Conventional interpretations have construed this Japanese title as "master of ceremonies" Created in 1632, this ''bakufu'' title identified an official selected from the ranks of the ''daimyōs'' whose responsibility was to formally introduce ''hatamoto'' and other ''daimyōs'' to the ''shōgun'' during audiences, to read aloud the list of presents received by the ''shōgun'' from the various domains during New Year's and other ceremonial occasions, and in general to regulate the details of these ceremonies. The title was initially assigned to two ''daimyōs'', but was subsequently increased to up to twenty-four, who performed their duties in rotation. The ''Sōshaban'' were also responsible for managing the guard of Edo Castle at night. After 1658, the four ''Jisha-bugyō'' came to be selected from the ranks of the ''Sōshaban'', who continued to hold their original title concurrently; the title was also restricted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |