|
Yalpana Vaipava Malai
Yalpana Vaipava Malai ( ta, Я«»Я«ЙЯ«┤Я»ЇЯ«фЯ»ЇЯ«фЯ«ЙЯ«Б Я«хЯ»ѕЯ«фЯ«хЯ««Я«ЙЯ«▓Я»ѕ) is a book written by a Tamil poet named Mayil Vaakaanar ( ta, Я««Я«»Я«┐Я«▓Я»Ї Я«хЯ«ЙЯ«ЋЯ«ЕЯ«ЙЯ«░Я»Ї) in 1736. This book contains historical facts of the early Tamil city of Jaffna. The book which may have been written around 1736 during the Governorship of Jan Maccara, the then Dutch Governor of Jaffna. It was translated from Tamil by C. Brito, and was first published in 1879. The work is looked upon as one of great authority among the Tamils of Jaffna. Sources The author says that he referred to the books '' Kailaya Malai'', '' Vaiyai Padal'' and '' Pararajasekaran Ula'' for his work. It is said that these books are composed not earlier than the fourteenth century, contain folklore, legends and myths mixed with historical anecdotes. Today, except the ''Kailaya Malai'' which has been printed, and a few manuscript copies of ''Vaiya Padal'', the other works are very rare and hardly procurable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaffna
Jaffna (, ) is the capital city of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jaffna District located on a peninsula of the same name. With a population of 88,138 in 2012, Jaffna is Sri Lanka's 12th most populous city. Jaffna is approximately from Kandarodai which served as an emporium in the Jaffna peninsula from classical antiquity. Jaffna's suburb Nallur served as the capital of the four-century-long medieval Jaffna Kingdom. Prior to the Sri Lankan Civil War, it was Sri Lanka's second most populous city after Colombo. The 1980s insurgent uprising led to extensive damage, expulsion of part of the population, and military occupation. Since the end of civil war in 2009, refugees and internally displaced people began returning to homes, while government and private sector reconstruction started taking place. Historically, Jaffna has been a contested city. It was made into a colonial port town during the Portuguese occupation of the J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35РђЊ37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (ЯцИЯц┐ЯцеЯЦЇЯцДЯЦЂ ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trincomalee
Trincomalee (; ta, Я«цЯ«┐Я«░Я»ЂЯ«ЋЯ»ІЯ«БЯ««Я«▓Я»ѕ, translit=Tiruk┼Їр╣Єamalai; si, ЯХГЯиіРђЇЯХ╗ЯињЯХџЯићЯХФЯиЈЯХИЯиЁЯХ║, translit= Trikuр╣Є─ЂmaрИиaya), also known as Gokanna and Gokarna, is the administrative headquarters of the Trincomalee District and major resort port city of Eastern Province, Sri Lanka. Located on the east coast of the island overlooking the Trincomalee Harbour, north-east of Colombo, south-east of Jaffna and miles north of Batticaloa, Trincomalee has been one of the main centres of Sri Lankan Tamil language speaking culture on the island for over two millennia. With a population of 99,135, the city is built on a peninsula of the same name, which divides its inner and outer harbours. People from Trincomalee are known as Trincomalians and the local authority is Trincomalee Urban Council. Trincomalee city is home to the famous Koneswaram temple from where it developed and earned its historic Tamil name ''Thirukonamalai''. The town is home to other hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manu Needhi Cholan
Ellalan ( ta, Я«јЯ«▓Я»ЇЯ«▓Я«ЙЯ«│Я«ЕЯ»Ї, translit=Ell─ЂрИиaр╣Ѕ; si, ЯХЉЯиЁЯиЈЯХ╗, translit=EрИи─Ђra) was a member of the Tamil Chola dynasty, also known as "Manu Needhi Cholan", who upon capturing the throne became king of the Anuradhapura Kingdom, in present-day Sri Lanka, from 205 BCE to 161 BCE. Ellalan is traditionally presented as being a just king even by the "'Sinhalese'". The Mahavamsa states that he ruled 'with even justice toward friend and foe, on occasions of disputes at law, and elaborates how he even ordered the execution of his son for killing a calf under his chariot wheels. Ellalan is a peculiar figure in the history of Sri Lanka and one with particular resonance given the past ethnic strife in the country. Although he was an invader, he is often regarded as one of Sri Lanka's wisest and most just monarchs, as highlighted in the ancient Sinhalese Pali chronicle, the '' Mahavamsa''. According to the chronicle, even Ellalan's nemesis Dutugamunu had a great respe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cholas
The Early Cholas were a Tamil kingdom of the pre and post Sangam period (600 BCEРђЊ300 CE). It was one of the three main kingdoms of South India. Their early capitals were Urayur or Tiruchirapalli and Kaveripattinam. Along with Pandyas and Cheras, Chola history goes back to the period when written records were scarce. Sources Ancient Tamil Nadu contained three monarchical states, headed by kings called ''Vendhar'' and several chieftaincies, headed by the chiefs called by the general denomination ''Vel'' or ''Velir''. Still lower at the local level there were clan chiefs called ''kizhar'' or ''mannar''. The Tamil area had an independent existence outside the control of these northern empires. The Tamil kings and chiefs were always in conflict with each other mostly over property. The royal courts were mostly places of social gathering rather than places of dispensation of authority; they were centres for distribution of resources. The names of the three dynasties, Cholas, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulakkottan
Kulakkottan ( ta, Я«ЋЯ»ЂЯ«│Я«ЋЯ»ЇЯ«ЋЯ»ІЯ«ЪЯ»ЇЯ«ЪЯ«ЕЯ»Ї) was an early Chola king and descendant of Manu Needhi Cholan who was mentioned in chronicles such as the ''Yalpana Vaipava Malai'' and stone inscriptions like Konesar Kalvettu. His name ''Kulakkottan'' means 'builder of tank and temple'. Kulakkottan was the son of Vararamatevan, said to have been ruler of Chola Nadu and Madurai. The historian and author, Mudaliyar Rasanayagam states that Vararamatevan and Kulakkottan arrived in Trincomalee during the reign of King Pandu of Anuradhapura. Vararamatevan found the Koneswaram temple destroyed by the Buddhist King Mahasena. He decided to restore it, a work which was later continued by his son. Kulakkottan was credited with the restoration of the ruined Koneswaram temple and for building Kantale Dam at Trincomalee in , and the Munneswaram temple of the west coast. He is known as the royal who settled ancient Vanniyars in the east of the island of Eelam. See also * List of Tam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Inscriptions In Sri Lanka
{{unreferenced, date=December 2014 The number of stone inscriptions that have been found in Sri Lanka to date is over 4000. But these inscriptions are of different types. Considering their locations and their appearances, for the ease of studying, they are classified as follows: 1. Cave Inscriptions 2. Rock Inscriptions (Giri lipi) 3. Slab Inscriptions (Puwaru lipi) 4. pile inscriptions (Tam lipi) From the name itself, it's easy to understand what type of these inscriptions are. Cave inscriptions can be found in Mihintale, Wessagiriya, Sithulpawwa, and Ritigala. Some examples for the rock inscriptions are the Galwala inscription, the bilingual inscription found in Gadaladeniya and the Alawala inscription. Polonnaruwa galpotha inscription, the Mihintale slab inscription, and the Thonigala inscription are examples for the slab inscriptions. Badulla inscription and the Katugahagalge inscription are classified under pillar inscriptions. Cave in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
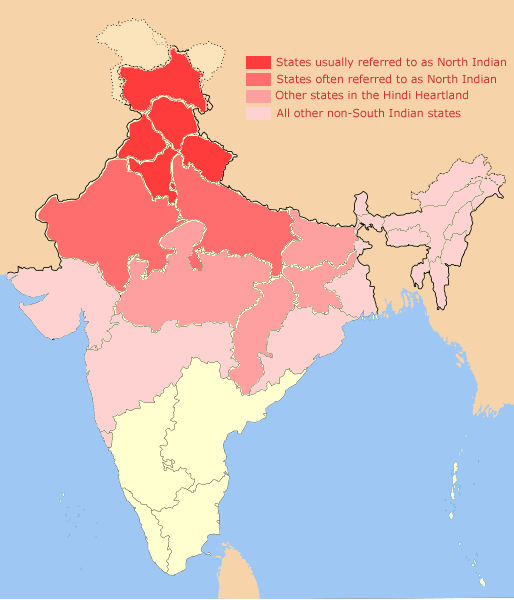
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panduvasdeva Of Upatissa Nuwara
Prince Panduvasudeva, (died 474 BC) was King of Upatissa Nuwara (in modern-day Sri Lanka) from 504 BC to 474 BC. He was the first monarch of the Kingdom of Upatissa Nuwara and succeeded Upatissa, who reigned as regent. Panduvasudeva had ten sons, including Abhaya and Tissa and one daughter, Unmada Chitra. He was a nephew of Prince Vijaya According to the ''Mah─Ђvaр╣Ѓsa'' chronicle, Prince Vijaya (c. 543РђЊ505 BCE) was the first Sinhalese monarchy, Sinhalese king. Legends and records from both Indian and Sri Lanka sources say that he along with several hundred followers came to .... Ancestors External links History of Sri Lankan KingsCodrington's Short History of Ceylon 474 BC deaths Year of birth unknown Monarch of Tambapanni Sinhalese kings House of Vijaya 6th-century BC Sinhalese monarchs 5th-century BC Sinhalese monarchs {{SriLanka-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Vijaya
According to the ''Mah─Ђvaр╣Ѓsa'' chronicle, Prince Vijaya (c. 543РђЊ505 BCE) was the first Sinhalese monarchy, Sinhalese king. Legends and records from both Indian and Sri Lanka sources say that he along with several hundred followers came to Sri Lanka, Sinhala after they were banished from Sinhapura. In Sri Lanka, Vijaya and his settlers defeated a yaksha near "Thammena" (Tambapaр╣Єр╣Є─Ф, believed to be in the central or western part of the island), eventually displacing the island's previous inhabitants from their city of Sirisavatthu. Vijaya's marriage to Kuveni, a daughter of a yaksha leader, may have cemented his ability to rule the kingdom of Tambapanni. However, Kuveni's renunciation of her people for love did not last long; Vijay betrayed her for a princess from India. Kuveni had two children by Vijaya, whose fates are unknown. Sources and variations Four versions of the legend explain the origin of the Sinhalese people. In all the versions, a prince comes to the isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)