|
YME1L1
ATP-dependent metalloprotease YME1L1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''YME1L1'' gene. YME1L1 belongs to the AAA proteins, AAA family of ATPases and mainly functions in the maintenance of mitochondrial morphology. Mutations in this gene would cause infantile-onset mitochondriopathy. Structure Gene The ''YME1L1'' gene is located at chromosome 10p14, consisting of 20 exons. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Protein YME1L1 consists of 716 amino acids and is highly similar to all mitochondrial AAA proteases and in particular to yeast Yme1p. Three different domains are identified via sequence analysis, including an AAA consensus sequence between amino acids 317 and 502, an ATP/GTP binding motif, and a HEXXH motif typical of a zinc-dependent binding Protein domain, domain. Function YME1L1 is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and is more abundant in tissues with a high content of mitochondria such as human adul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMA1
Metalloendopeptidase OMA1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''OMA1'' gene. OMA1 is a Zinc, Zn2+-dependent metalloendopeptidase in the inner membrane of Mitochondrion, mitochondria. The OMA1 acronym was derived from overlapping proteolytic activity with m-AAA protease 1. The OMA1 protease acts at the intersection of a mitochondrial quality control system and energy metabolism, whereby its activation correlates with Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, outer membrane permeabilization and cytochrome c release in the context of apoptosis. Mammalian OMA1 can cleave the inner-membrane shaping protein Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, OPA1 and the signaling peptide DELE1 in a context-dependent manner. Gene The human ''OMA1'' gene spans with 9 exons 66 kb of the reverse strand of the short arm of chromosome 1 (1p32.2-p32.1). ''OMA1'' is conserved and Sequence homology, homologues have been identified in model organisms, such as Laboratory mouse, mice an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of cells, and disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself. In medical practice, hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are said to have ''trophic'' effects. A diminished muscular trophic condition is designated as ''atrophy''. Atrophy is reduction in size of cell, organ or tissue, after attaining its normal mature growth. In contrast, hypoplasia is the reduction in the cellular numbers of an organ, or tissue that has not attained normal maturity. Atrophy is the general physiological process of reabsorption and breakdown of tissues, involving apoptosis. When it occurs as a result of disease or loss of trophic support because of other diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite the fact that these terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
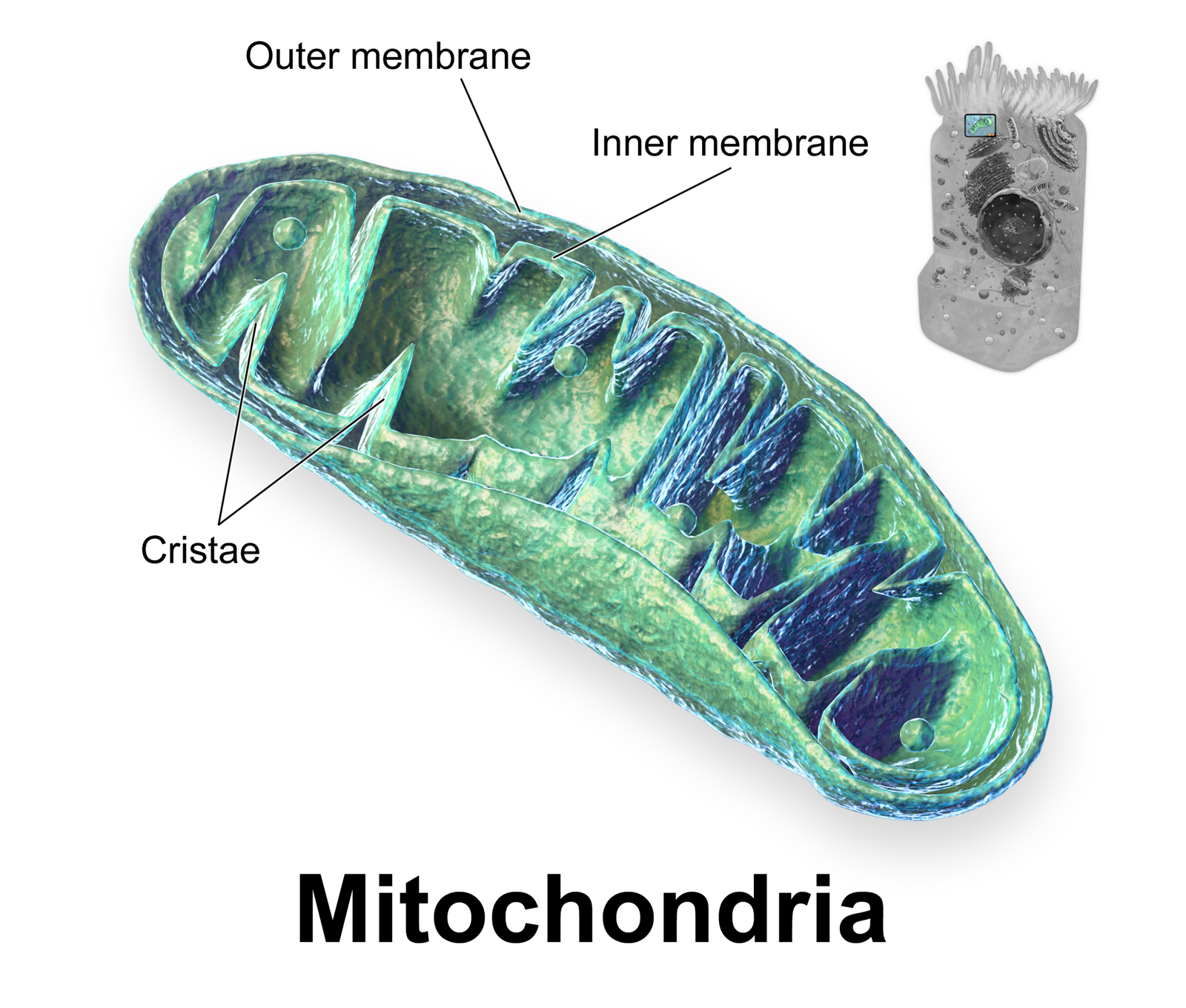
Cristae Morphogenesis
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptotic
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. The electrons that transferred from NADH and FADH2 to the ETC involves 4 multi-subunit large enzymes complexes and 2 mobile electron carriers. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are membrane-bound. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial Fission
Mitochondrial fission is the process where mitochondria divide or segregate into two separate mitochondrial organelles. Mitochondrial fission is counteracted by the process of mitochondrial fusion, whereby two separate mitochondria can fuse together to form a large one. Mitochondrial fusion in turn can result in elongated mitochondrial networks. Both mitochondrial fission and fusion are balanced in the cell, and mutations interfering with either processes are associated with a variety of diseases. Mitochondria can divide by prokaryotic binary fission and since they require mitochondrial DNA for their function, fission is coordinated with DNA replication. Some of the proteins that are involved in mitochondrial fission have been identified and some of them are associated with mitochondrial diseases. Mitochondrial fission has significant implications in stress response and apoptosis. Mechanism FtsZ Localization The FtsZ protein (a homologue to eukaryotic tubulin), found in many bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPA1
Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPA1'' gene. This protein regulates mitochondrial fusion and cristae structure in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and contributes to ATP synthesis and apoptosis, and small, round mitochondria. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in dominant optic atrophy (DOA), leading to loss in vision, hearing, muscle contraction, and related dysfunctions. Structure Eight transcript variants encoding different isoforms, resulting from alternative splicing of exon 4 and two novel exons named 4b and 5b, have been reported for this gene. They fall under two types of isoforms: long isoforms (L-OPA1), which attach to the IMM, and short isoforms (S-OPA1), which localize to the intermembrane space (IMS) near the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). S-OPA1 is formed by proteolysis of L-OPA1 at the cleavage sites S1 and S2, removing the transmembrane domain. Function This gene product is a nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translocase Of The Inner Membrane
The translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) is a complex of proteins found in the inner mitochondrial membrane of the mitochondria. Components of the TIM complex facilitate the translocation of proteins across the inner membrane and into the mitochondrial matrix. They also facilitate the insertion of proteins into the inner mitochondrial membrane, where they must reside in order to function, these mainly include members of the mitochondrial carrier family of proteins. The TIM23 complex The TIM23 complex facilitates translocation of matrix-targeted proteins into the mitochondrial matrix. These proteins contain a cleavable presequence. The TIM23 complex is made up of the subunits Tim17, Tim21 and Tim23, which are thought to contribute to the structural formation of the translocation channel that spans the inner membrane, and Tim44, which is a peripheral membrane protein. Tim44 is only weakly associated with Tim23 and is located on the matrix side of the inner membrane. At the openin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |