|
Yurammia
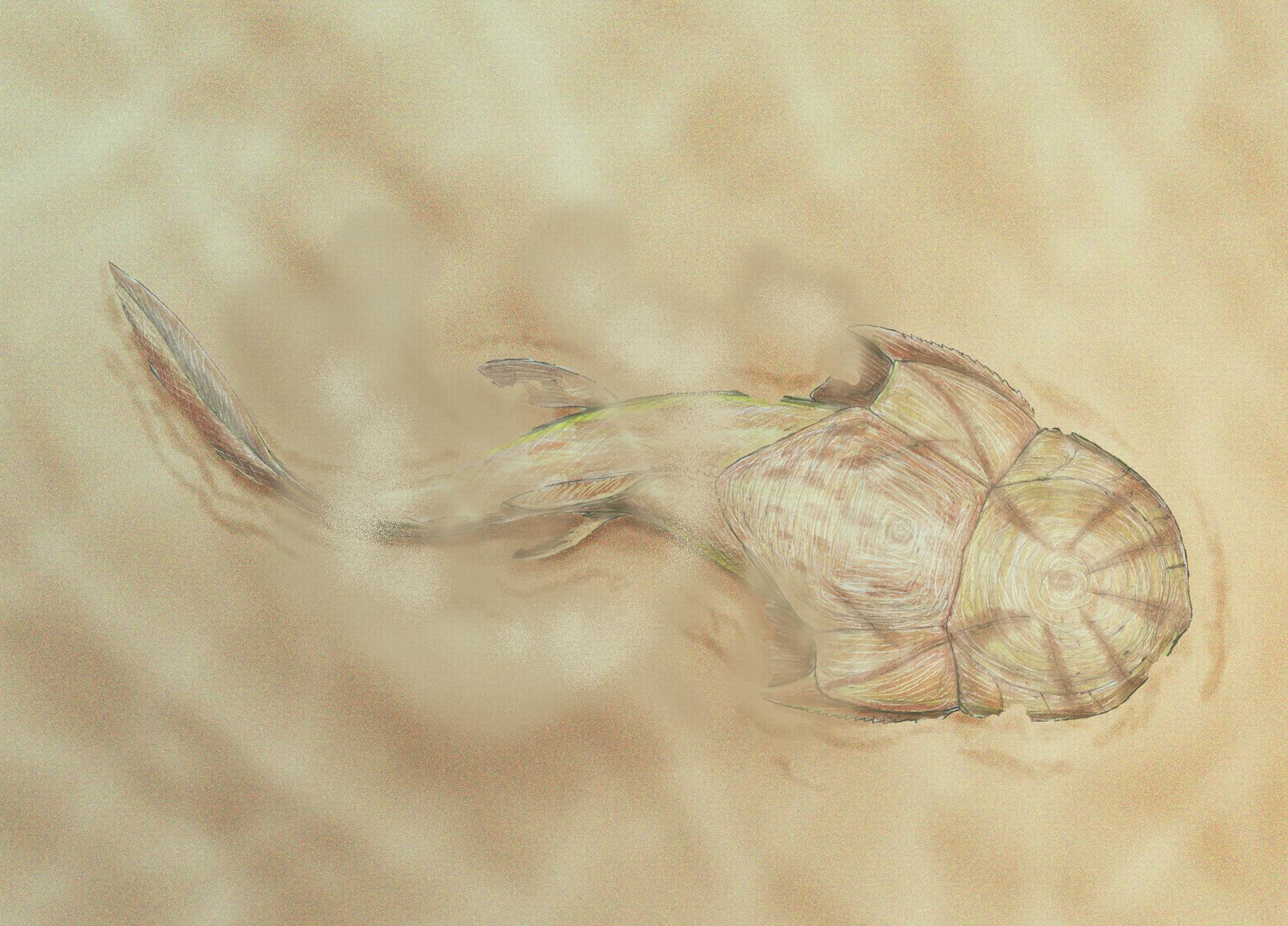
''Yurammia'' is a placoderm from what is now the Pambula River in New South Wales. Unlike all other known phyllolepids Phyllolepida ("leaf scales") is an extinct taxon of flattened placoderms found throughout the world, with fossils being found in Devonian strata. Like other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were bottom-dwelling predators that ambushed prey. ..., ''Yurammias plates had no external grooves. References Phyllolepids Placoderms of Antarctica {{placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllolepididae
Phyllolepididae is one of two families of phyllolepid placoderms. The family, as a whole, is believed to be descended from the Chinese placoderm, '' Gavinaspis ''(which forms the other, monotypic family, "Gavinaspididae"). All but two genera are, more or less, restricted to freshwater habitats of the Early to Middle Devonian of Australia. By the Frasnian, the genus '' Placolepis'' would spread throughout the world, with fossils being found in Australia, Turkey, Venezuela, and Antarctica, and by the start of the Famennian, phyllolepids would become extinct in Australia (then eastern Gondwana), with only species of '' Phyllolepis'' surviving in freshwater environments of Europe and North America. With the exception of '' Yurammia''. all phyllolepids have distinct ornamentation consisting primarily of concentric rings. Genera ''Phyllolepis'' The type genus is restricted to freshwater Famennian strata of Europe and North America. It is also the youngest genus of phyllolepid, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllolepididae
Phyllolepididae is one of two families of phyllolepid placoderms. The family, as a whole, is believed to be descended from the Chinese placoderm, '' Gavinaspis ''(which forms the other, monotypic family, "Gavinaspididae"). All but two genera are, more or less, restricted to freshwater habitats of the Early to Middle Devonian of Australia. By the Frasnian, the genus '' Placolepis'' would spread throughout the world, with fossils being found in Australia, Turkey, Venezuela, and Antarctica, and by the start of the Famennian, phyllolepids would become extinct in Australia (then eastern Gondwana), with only species of '' Phyllolepis'' surviving in freshwater environments of Europe and North America. With the exception of '' Yurammia''. all phyllolepids have distinct ornamentation consisting primarily of concentric rings. Genera ''Phyllolepis'' The type genus is restricted to freshwater Famennian strata of Europe and North America. It is also the youngest genus of phyllolepid, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
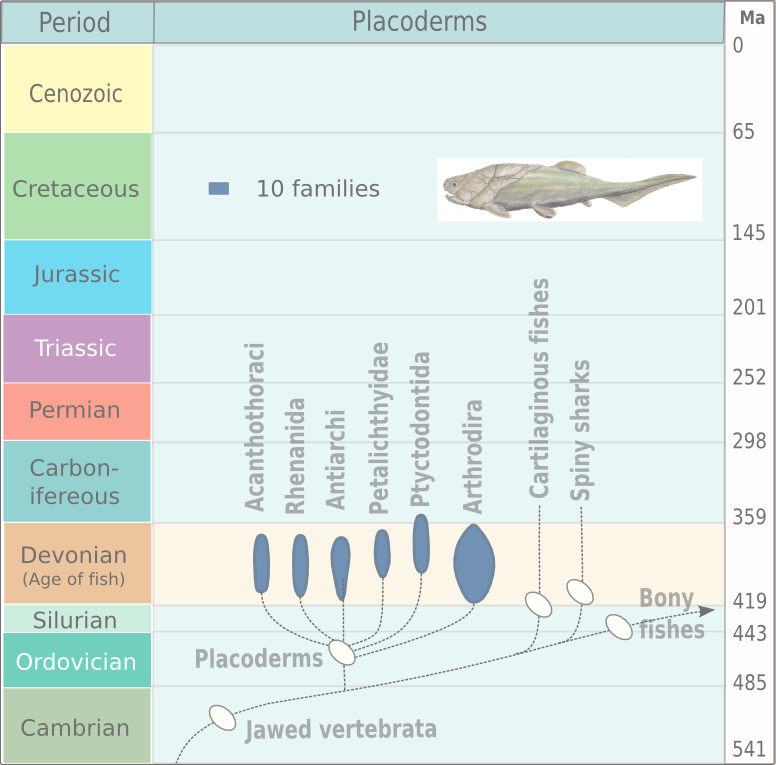
Placodermi
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate-skinned') is a Class (biology), class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their Fish jaw, jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyly, paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct Outgroup (cladistics), outgroups or sister taxon, sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed ''Rolfosteus'' measured just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllolepida
Phyllolepida ("leaf scales") is an extinct taxon of flattened placoderms found throughout the world, with fossils being found in Devonian strata. Like other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were bottom-dwelling predators that ambushed prey. Unlike other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were inhabitants of freshwater environments. Unlike the Rhenanida, the armor of the phyllolepids were made of whole plates, rather than numerous tubercles and scales, and unlike the Petalichthyida, the components of the comparatively wide mouth are known. The phyllolepids are considered to have been blind, as the orbits for the eyes are extremely small, so much so as to suggest that the eyes were vestigial, and that they were placed on the sides of the head, as opposed to visually-oriented bottom-dwelling predators, like, say stargazers or flatfish, which have the eyes placed high on top of the head. Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pambula River
Pambula River is an open semi-mature wave dominated barrier estuary or perennial river located in the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia. Course and features Pambula River rises in timbered highlands near the locality of Lochiel and flows generally east, flowing through Pambula Lake, before reaching its mouth into the Tasman Sea of the South Pacific Ocean near the locality of Pambula Beach. The river descends over its course. The catchment area of the river is with a volume of over a surface area of , at an average depth of . South of Pambula, the Princes Highway crosses the river. See also * Rivers of New South Wales * List of rivers of New South Wales (L–Z) * List of rivers of Australia This is a list of rivers of Australia. Rivers are ordered alphabetically, by state. The same river may be found in more than one state as many rivers cross state borders. Longest rivers nationally Longest river by state or territory Althoug ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet (Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Senat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllolepids
Phyllolepida ("leaf scales") is an extinct taxon of flattened placoderms found throughout the world, with fossils being found in Devonian strata. Like other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were bottom-dwelling predators that ambushed prey. Unlike other flattened placoderms, the phyllolepids were inhabitants of freshwater environments. Unlike the Rhenanida, the armor of the phyllolepids were made of whole plates, rather than numerous tubercles and scales, and unlike the Petalichthyida, the components of the comparatively wide mouth are known. The phyllolepids are considered to have been blind, as the orbits for the eyes are extremely small, so much so as to suggest that the eyes were vestigial, and that they were placed on the sides of the head, as opposed to visually-oriented bottom-dwelling predators, like, say stargazers or flatfish, which have the eyes placed high on top of the head. Despite having a relatively clear idea of the phyllolepids' lifestyle and anatomy, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |