|
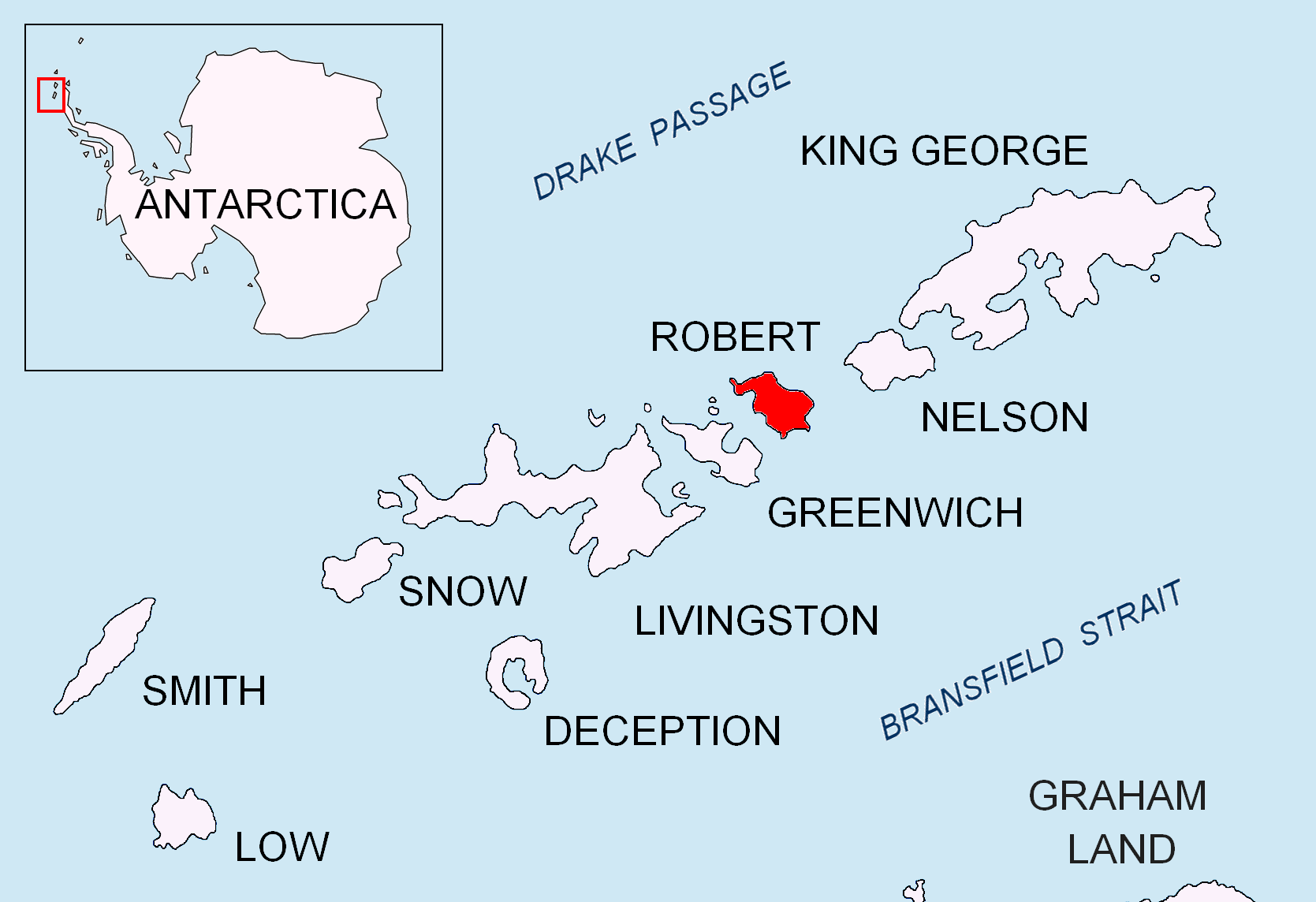
Yundola Cove
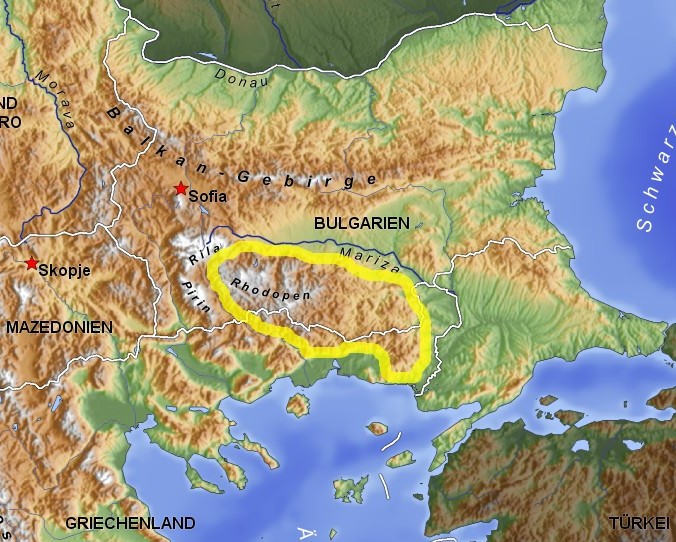
Yundola Cove ( bg, залив Юндола, zaliv Yundola, ) is a 1.34 km wide cove indenting for 670 m the north coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica west of Lavrenov Point. The feature is named after Yundola Saddle between Rila Mountain and the Rhodope Mountains in southern Bulgaria. Location The cove is located at (Bulgarian mapping in 2009). Map * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Yundola Cove.SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in .... (details in Bulgarianbasic datain English) External links Yundo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Island (South Shetland Islands)
Robert Island or Mitchells Island or Polotsk Island or Roberts Island is an island long and wide, situated between Nelson Island and Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Robert Island is located at . Surface area . The name "Robert Island" dates back to around 1821 and is now established in international usage. Much of the Coppermine Peninsula in the west of the island is made up by a perched strandflat surface that was in past at sea level. Captain Richard Fildes may have named Robert Island for his brig . Fildes was sealing in the South Shetlands in 1821–1822 until ice destroyed his vessel in March 1822. Fildes Strait is named for him. See also * List of lighthouses in Antarctica * Clothier Harbor * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavrenov Point
Lavrenov Point ( bg, Лавренов нос, ‘Lavrenov Nos’ \la-'vre-nov 'nos\) is a point on the north coast of Robert Island, South Shetland Islands forming the east side of the entrance to Yundola Cove. Situated 2.7 km west of Newell Point and 2.6 km southeast of Catharina Point. Bulgarian early mapping in 2008. Named after the Bulgarian painter Tsanko Lavrenov (1896–1978). Map * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated. References Lavrenov Point.SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rila
Rila ( bg, Рила, ) is the highest mountain range of Bulgaria, the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula and Southeast Europe. It is situated in southwestern Bulgaria and forms part of the Rila–Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope Massif. The highest summit is Musala at an elevation of 2,925 m which makes Rila the sixth highest mountain range in Europe after the Caucasus, the Alps, Sierra Nevada (Spain), Sierra Nevada, the Pyrenees and Mount Etna, and the highest one between the Alps and the Caucasus. It spans a territory of 2,629 km2 with an average elevation of 1487 m. The mountain is believed to have been named after the Rilska River, river of the same name, which comes from the Old Bulgarian language, Old Bulgarian verb "рыти" meaning "to grub". Rila has abundant water resources. Some of the Balkans' longest and deepest rivers originate from Rila, including the Maritsa, Iskar (river), Iskar and Nestos (river), Mesta rivers. Bulgaria's main water divide separating the Black Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gazett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coves Of Robert Island
A cove is a small type of bay or coastal inlet. Coves usually have narrow, restricted entrances, are often circular or oval, and are often situated within a larger bay. Small, narrow, sheltered bays, inlets, creeks, or recesses in a coast are often considered coves. Colloquially, the term can be used to describe a sheltered bay. Geomorphology describes coves as precipitously-walled and rounded cirque-like openings as in a valley extending into or down a mountainside, or in a hollow or nook of a cliff or steep mountainside. A cove can also refer to a corner, nook, or cranny, either in a river, road, or wall, especially where the wall meets the floor. A notable example is Lulworth Cove on the Jurassic Coast in Dorset, England. To its west, a second cove, Stair Hole, is forming. Formation Coves are formed by differential erosion Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |