|
Yujiulü Dengshuzi
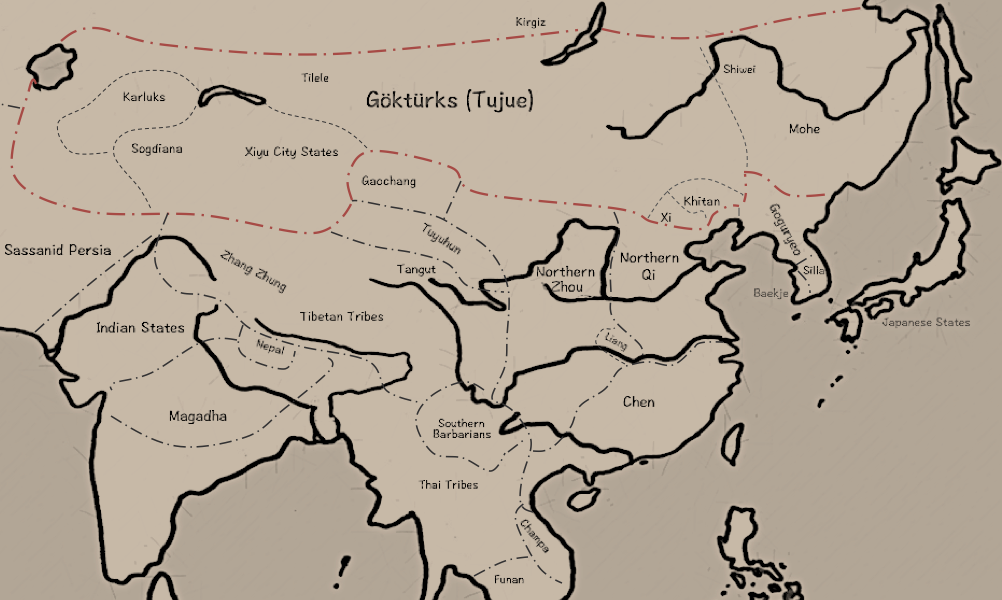
Yujiulü Dengshuzi (; pinyin: Yùjiǔlǘ Dèngshūzǐ) (?–555) was the last western khagan of the Rouran. He was a cousin of Anagui. Reign He was enthroned in March 553 by remnants of Rouran and support of Western Wei in Woye (modern northern part of Ulansuhai Nur, Urad, Inner Mongolia). In 555, the Tujue invaded and occupied the Rouran and Dengshuzi led 3000 soldiers in retreat to Western Wei. He was later delivered to Turks by Emperor Gong with his soldiers under pressure from Muqan Qaghan Muqan Qaghan (Old Turkic: 𐰢𐰆𐰴𐰣𐰴𐰍𐰣 Muqan qaγan, Chinese:木桿可汗/木杆可汗, Pinyin: mùgǎn kěhàn, Wade-Giles: mu-kan k'o-han or 木汗可汗, mùhàn kěhàn, mu-han k'o-han, personal name: 阿史那燕都, āshǐn .... References Mongol khans Rouran rulers 555 deaths {{Rouran rulers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouran Khaganate
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organization of the Zhou Polity" ''Early China''. p. 20 The Rouran supreme rulers are noted for being the first to use the title of "khagan", having borrowed this popular title from the Xianbei.Vovin, Alexander (2007). "Once again on the etymology of the title ''qaγan''". ''Studia Etymologica Cracoviensia'', vol. 12online resource The Rouran Khaganate lasted from the late 4th century until the middle 6th century, when they were defeated by a Göktürk rebellion which subsequently led to the rise of the Turks in world history. Their Khaganate overthrown, some Rouran remnants possibly became TatarsXu Elina-Qian''Historical Development of the Pre-Dynastic Khitan'' University of Helsinki, 2005. pp. 179–180 while others possibly migrated west and beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulansuhai Nur
Ulansuhai Nur or Wuliangsuhai()is a freshwater lake in China, it is located in southwest of Inner Mongolia, situated in the north bank of the middle reaches of Yellow River The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at th .... The lake is 233 km 2, with a drainage area of 11,800 km 2, an elevation of 1018.79 m, length 35.4 km and mean width 6.6 km (max 12.7 km). The lake is rich in fish. Ulansuhai Nur is a rare big multi-functional lake in this desolate and drought-stricken grassland. The area of bulrush is 150 square kilometers and there are nearly 200 species of birds and over 20 kinds of fish in the lake area. Notes {{Authority control Lakes of Inner Mongolia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Khans
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, Khorchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muqan Qaghan
Muqan Qaghan (Old Turkic: 𐰢𐰆𐰴𐰣𐰴𐰍𐰣 Muqan qaγan, Chinese:木桿可汗/木杆可汗, Pinyin: mùgǎn kěhàn, Wade-Giles: mu-kan k'o-han or 木汗可汗, mùhàn kěhàn, mu-han k'o-han, personal name: 阿史那燕都, āshǐnà yàndōu, a-shih-na yen-to, Sogdian: ''mwx’n x’γ’n'', Ruanruan: ''Muɣan Qaɣan'') was the second son of Bumin Qaghan and the third khagan of the Göktürks who expanded their khaganate and secured the borders against the Hephthalites. Reign His accession to power was followed by finishing off remnants of Rouran. Around the new year 554, after defeat of Yujiulü Kangdi at the hands of Göktürks, the remnants of Rouran, which by that point was near its end, surrendered to Northern Qi to seek protection from Gökturks attacks. Emperor Wenxuan personally attacked Muqan Qaghan, fighting his army off and then created Yujiulü Anluochen as the new khagan of Rouran, settling the Rouran people within Northern Qi territory, at Mayi ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gong Of Western Wei
Emperor Gong of Western Wei ((西)魏恭帝) (537 – April 557Volume 167 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' indicated that Emperor Gong was killed between the ''jiawu'' day of the 2nd month and the ''gengzi'' day of the 3rd month of the 1st year of the ''Yongding'' era of Chen Baxian's reign; the dates corresponds to 9 and 15 Apr 557 in the Julian calendar.), personal name né Yuan Kuo (元廓), later changed to Tuoba Kuo (拓拔廓), was the last emperor of the Western Wei — a rump state of and successor to Northern Wei. He was made emperor in 554 after his older brother Emperor Fei was deposed by the paramount general Yuwen Tai. He carried little actual power, and in 556, after Yuwen Tai's death, Yuwen Tai's nephew Yuwen Hu, serving as guardian to Yuwen Tai's son Yuwen Jue, forced Emperor Gong to yield the throne to Yuwen Jue, ending Western Wei and starting Northern Zhou. The former emperor was killed in 557. Because Northern Wei's other branch successor state, Eastern Wei, had fallen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inner Mongolia is geographically divided into eastern and western divisions. The eastern division is often included in Northeastern China (Dongbei) with major cities including Tongliao, Chifeng, Hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urad Front Banner
Urad Qianqi ( mn, Урадын Өмнөд Хошуу ; ) is a banner of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, People's Republic of China. It is located in the west of the region, situated on the northern (left) bank of the Yellow River, on the Ordos Loop, and in between the cities of Bayan Nur and Baotou Baotou (; mn, Buɣutu qota, Бугат хот) is the largest city by urban population in Inner Mongolia, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, as of the 2020 census, its built-up (''or metro'') area made up of its 5 urban districts is h .... Administratively, it is part of Bayan Nur City, and has a total area of and in 2020 had 257,826 inhabitants. Its seat is the town of Mona-uul (). Other towns include Dashetai (Tashetai) (). Climate References Banners of Inner Mongolia Bayannur {{InnerMongolia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouran
The Rouran Khaganate, also Juan-Juan Khaganate (), was a tribal confederation and later state founded by a people of Proto-Mongolic Donghu origin.*Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (2000)"Ji 姬 and Jiang 姜: The Role of Exogamic Clans in the Organization of the Zhou Polity" ''Early China''. p. 20 The Rouran supreme rulers are noted for being the first to use the title of "khagan", having borrowed this popular title from the Xianbei.Vovin, Alexander (2007). "Once again on the etymology of the title ''qaγan''". ''Studia Etymologica Cracoviensia'', vol. 12online resource The Rouran Khaganate lasted from the late 4th century until the middle 6th century, when they were defeated by a Göktürk rebellion which subsequently led to the rise of the Turks in world history. Their Khaganate overthrown, some Rouran remnants possibly became TatarsXu Elina-Qian''Historical Development of the Pre-Dynastic Khitan'' University of Helsinki, 2005. pp. 179–180 while others possibly migrated west and bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yujiulü Anagui
Yujiulü Anagui (Rouran: Anakay; ; pinyin: Yùjiǔlǘ Ānàguī) (?–552) was ruler of the Rouran (520–552) with the title of Chiliantoubingdoufa Khagan (敕連頭兵豆伐可汗). First reign His reign started with troubles. First rebellion started after 10 days of his coronation when his brother-in-law Qilifa Shifa (俟力發示發) rose against him, killing Anagui's younger brother Yujiulü Yijufa (郁久閭乙居伐) and his mother Hou Luling (侯呂陵) on his attack, paving way for Anagui's cousin Yujiulü Poluomen. Having lost the fight, Anagui fled to Northern Wei. Emperor Xiaoming sheltered him and ordered his advisors to bring him to palace. As Khagan asked for troops to regain his throne, emperor recognized him but postponed any idea of going to war. Restless Anagui bribed Yuan Cha to leave capital. Emperor suddenly changed his idea when Anagui was about to leave in 521, helped him from martial and economic perspective. Second reign Back in Rouran, Qilifa Shifa t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese form, to learners already familiar with the Latin alphabet. The system includes four diacritics denoting tones, but pinyin without tone marks is used to spell Chinese names and words in languages written in the Latin script, and is also used in certain computer input methods to enter Chinese characters. The word ' () literally means "Han language" (i.e. Chinese language), while ' () means "spelled sounds". The pinyin system was developed in the 1950s by a group of Chinese linguists including Zhou Youguang and was based on earlier forms of romanizations of Chinese. It was published by the Chinese Government in 1958 and revised several times. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) adopted pinyin as an international standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpeg/1200px-Siège_de_Beijing_(1213-1214).jpeg)


