|
Yrjö Vartia
Yrjö O. Vartia (born June 3, 1946 in Helsinki, Finland) is the professor of econometrics in the Department of Political and Economic Studies at the University of Helsinki, Finland. Career He received his B.S. (mathematics) in 1968 and his M.A. (statistics) in 1971 from the University of Helsinki and Licentiate of Philosophy and Ph.D. (statistics) from the University of Tampere, Finland in 1976. Associate professor of Statistics at the University of Helsinki in 1980. Professor of Statistics at the Helsinki School of Economics HSE in 1984 and professor of Economics (especially econometrics) at the University of Helsinki since 1987. He is student of Leo Törnqvist, the creator of the ''Törnqvist index''. Research on Index Numbers Vartia is best known for his 1983 paper in ''Econometrica'', ''Efficient Methods of Measuring Welfare Change and Compensated Income in Terms of Ordinary Demand Functions''. It explains a numerical technique for solving a system of demand equations to deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki ( fi, Helsingin yliopisto, sv, Helsingfors universitet, abbreviated UH) is a public research university located in Helsinki, Finland since 1829, but founded in the city of Turku (in Swedish ''Åbo'') in 1640 as the Royal Academy of Åbo, at that time part of the Swedish Empire. It is the oldest and largest university in Finland with the widest range of disciplines available. In 2020, around 31,600 students were enrolled in the degree programs of the university spread across 11 faculties and 11 research institutes. As of 1 August 2005, the university complies with the harmonized structure of the Europe-wide Bologna Process and offers bachelor, master, licenciate, and doctoral degrees. Admission to degree programmes is usually determined by entrance examinations, in the case of bachelor's degrees, and by prior degree results, in the case of master and postgraduate degrees. Entrance is particularly selective (circa 15% of the yearly applicants are admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Törnqvist Index
In economics, the Törnqvist index is a price or quantity index. In practice, Törnqvist index values are calculated for consecutive periods, then these are strung together, or "'' chained''". Thus, the core calculation does not refer to a single base year. Computation The price index for some period is usually normalized to be 1 or 100, and that period is called "base period." A Törnqvist or Törnqvist-Theil price index is the weighted geometric mean of the price relatives using arithmetic averages of the value shares in the two periods as weights. The data used are prices and quantities in two time-periods, (t-1) and (t), for each of ''n'' goods which are indexed by ''i''. If we denote the price of item ''i'' at time t-1 by p_, and, analogously, we define q_ to be the quantity purchased of item ''i'' at time t, then, the Törnqvist price index P_t at time t can be calculated as follows: :\frac = \prod_^\left(\frac\right)^ The denominators in the exponent are the sums of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Econometrica
''Econometrica'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal of economics, publishing articles in many areas of economics, especially econometrics. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the Econometric Society. The current editor-in-chief is Guido Imbens. History ''Econometrica'' was established in 1933. Its first editor was Ragnar Frisch, recipient of the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, who served as an editor from 1933 to 1954. Although ''Econometrica'' is currently published entirely in English, the first few issues also contained scientific articles written in French. Indexing and abstracting ''Econometrica'' is abstracted and indexed in: * Scopus * EconLit * Social Science Citation Index According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 5.844, ranking it 22/557 in the category "Economics". Awards issued The Econometric Society aims to attract high-quality applied work in economics for publication in ''Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Welfare Provision
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance programs which provide support only to those who have previously contributed (e.g. most pension systems), as opposed to ''social assistance'' programs which provide support on the basis of need alone (e.g. most disability benefits). The International Labour Organization defines social security as covering support for those in old age, support for the maintenance of children, medical treatment, parental and sick leave, unemployment and disability benefits, and support for sufferers of occupational injury. More broadly, welfare may also encompass efforts to provide a basic level of well-being through free or subsidized ''social services'' such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, vocational training, and publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (economics)
In Statistics, Economics and Finance, an index is a statistical measure of change in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from different perspectives. Influential global financial indices such as the Global Dow, and the NASDAQ Composite track the performance of selected large and powerful companies in order to evaluate and predict economic trends. The Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500 primarily track U.S. markets, though some legacy international companies are included. The consumer price index tracks the variation in prices for different consumer goods and services over time in a constant geographical location and is integral to calculations used to adjust salaries, bond interest rates, and tax thresholds for inflation. The GDP Deflator Index, or real GDP, measures the level of prices of all- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithms
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 of is , or . The logarithm of to ''base'' is denoted as , or without parentheses, , or even without the explicit base, , when no confusion is possible, or when the base does not matter such as in big O notation. The logarithm base is called the decimal or common logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The natural logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics, because of its very simple derivative. The binary logarithm uses base and is frequently used in computer science. Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculations. They were rapidly adopted by navigators, scientists, engineers, surveyors and others to perform high-accur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Mean
In mathematics, the logarithmic mean is a function of two non-negative numbers which is equal to their difference divided by the logarithm of their quotient. This calculation is applicable in engineering problems involving heat and mass transfer. Definition The logarithmic mean is defined as: :\begin M_\text(x, y) &= \lim_ \frac \\ pt &= \begin x & \textx = y ,\\ \frac & \text \end \end for the positive numbers x, y. Inequalities The logarithmic mean of two numbers is smaller than the arithmetic mean and the generalized mean with exponent one-third but larger than the geometric mean, unless the numbers are the same, in which case all three means are equal to the numbers. : \sqrt \leq \frac\leq \left(\frac2\right)^3 \leq \frac \qquad \text x > 0 \text y > 0. Toyesh Prakash Sharma generalizes the arithmetic logarithmic geometric mean inequality for any n belongs to the whole number as : \sqrt (\ln(\sqrt))^ (\ln(\sqrt)+n)\leq \frac\leq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Date Of Birth Missing (living People)
Date or dates may refer to: *Date (fruit), the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'') Social activity *Dating, a form of courtship involving social activity, with the aim of assessing a potential partner **Group dating *Play date, an appointment for children to get together for a few hours * Meeting, when two or more people come together Chronology * Calendar date, a day on a calendar ** Old Style and New Style dates, from before and after the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar ** ISO 8601, an international standard covering date formats *Date (metadata), a representation term to specify a calendar date **DATE command, a system time command for displaying the current date *Chronological dating, attributing to an object or event a date in the past **Radiometric dating, dating materials such as rocks in which trace radioactive impurities were incorporated when they were formed Arts, entertainment and media Music *Date (band), a Swedish dans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1946 Births
Events January * January 6 - The 1946 North Vietnamese parliamentary election, first general election ever in Vietnam is held. * January 7 – The Allies recognize the Austrian republic with its 1937 borders, and divide the country into four Allied-occupied Austria, occupation zones. * January 10 ** The first meeting of the United Nations is held, at Methodist Central Hall Westminster in London. ** ''Project Diana'' bounces radar waves off the Moon, measuring the exact distance between the Earth and the Moon, and proves that communication is possible between Earth and outer space, effectively opening the Space Age. * January 11 - Enver Hoxha declares the People's Republic of Albania, with himself as prime minister of Albania, prime minister. * January 16 – Charles de Gaulle resigns as head of the Provisional Government of the French Republic, French provisional government. * January 17 - The United Nations Security Council holds its first session, at Church House, Westmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
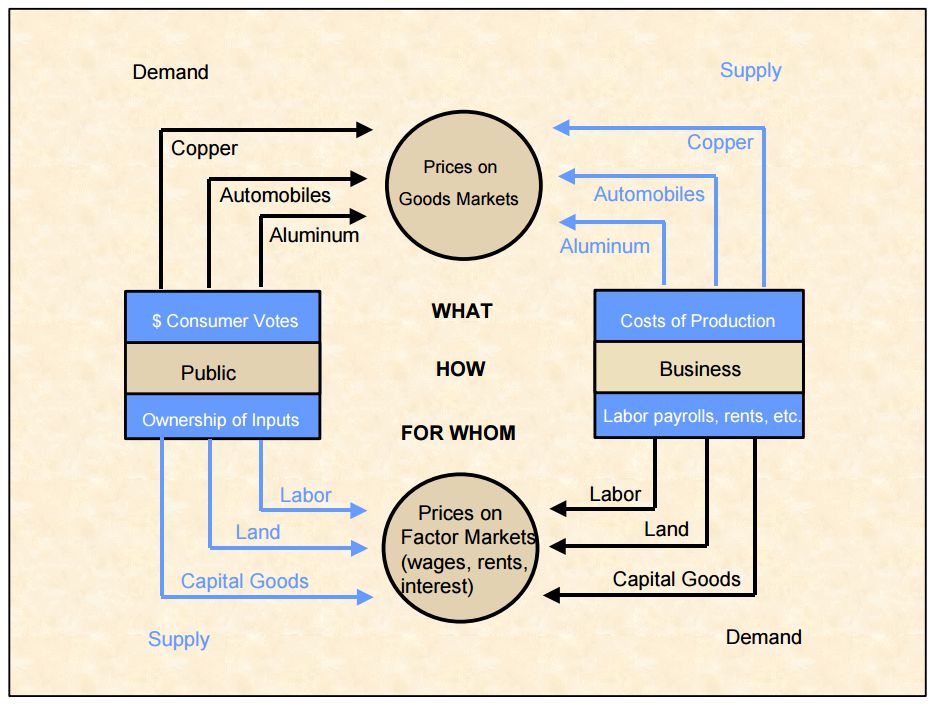
Price Index Theory
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the commercial exchange, the payment for this product will likely be called its "price". However, if the product is "service", there will be other possible names for this product's name. For example, the graph on the bottom will show some situations A good's price is influenced by production costs, supply of the desired item, and demand for the product. A price may be determined by a monopolist or may be imposed on the firm by market conditions. Price can be quoted to currency, quantities of goods or vouchers. * In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency. (More specifically, for raw materials they are expressed as currency per unit weight, e.g. euros per kilogram or Rands per KG.) * Although prices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)