|
York Minster Astronomical Clock
The York Minster astronomical clock is a memorial to the airmen operating from bases in Yorkshire, Durham, and Northumberland who were killed in action during World War II, designed by R. Atkinson, and installed in York Minster in 1955. History The clock was first conceived in 1944 and designed by Robert d'Escourt Atkinson, chief assistant at the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Atkinson based the design on the appearance of the sun and stars from the viewpoint of a pilot flying over York. The mechanism and two dials were constructed by A.C.S. Westcott and Royal Greenwich Observatory craftsmen, and installed in the north transept of York Minster in 1955. Damage to the clock's mechanism was sustained during a fire, on 9 July 1984; after 10 years' work attempting repair, vergers ceased winding it, owing to its inaccuracies of time-keeping. Display dials The front dial shows the locations of the Sun and certain navigational stars as would be seen by a pilot flying south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Clock (7569108538)
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanism (technology), mechanisms and dial (measurement), dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets. Definition The term is loosely used to refer to any clock that shows, in addition to the time of day, astronomical information. This could include the location of the Sun and Moon in the sky, the age and Lunar phases, the position of the Sun on the ecliptic and the current zodiac sign, the sidereal time, and other astronomical data such as the Moon's nodes (for indicating eclipses) or a rotating star map. The term should not be confused with ''astronomical regulator'', a high precision but otherwise ordinary pendulum clock used in observatories. Astronomical clocks usually represent the Solar System using the geocentric model. The center of the dial is often marked with a disc or sphere representing the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Position Of The Sun
The position of the Sun in the sky is a function of both the time and the geographic location of observation on Earth's surface. As Earth orbits the Sun over the course of a year, the Sun appears to move with respect to the fixed stars on the celestial sphere, along a circular path called the ecliptic. Earth's rotation about its axis causes diurnal motion, so that the Sun appears to move across the sky in a Sun path that depends on the observer's geographic latitude. The time when the Sun transits the observer's meridian depends on the geographic longitude. To find the Sun's position for a given location at a given time, one may therefore proceed in three steps as follows: # calculate the Sun's position in the ecliptic coordinate system, # convert to the equatorial coordinate system, and # convert to the horizontal coordinate system, for the observer's local time and location. This is the coordinate system normally used to calculate the position of the Sun in terms of solar zen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotations Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hertz, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time from vernal equinox to vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to summer solstice. It is the type of year used by tropical solar calendars. The solar year is one type of astronomical year and particular orbital period. Another type is the sidereal year (or sidereal orbital period), which is the time it takes Earth to complete one full orbit around the Sun as measured with respect to the fixed stars, resulting in a duration of 20 minutes longer than the tropical year, because of the precession of the equinoxes. Since antiquity, astronomers have progressively refined the definition of the tropical year. The entry for "year, tropical" in the '' Astronomical Almanac Online Glossary'' states: An equivalent, more descriptive, definition is "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Tropical Year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time from vernal equinox to vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to summer solstice. It is the type of year used by tropical solar calendars. The solar year is one type of astronomical year and particular orbital period. Another type is the sidereal year (or sidereal orbital period), which is the time it takes Earth to complete one full orbit around the Sun as measured with respect to the fixed stars, resulting in a duration of 20 minutes longer than the tropical year, because of the precession of the equinoxes. Since antiquity, astronomers have progressively refined the definition of the tropical year. The entry for "year, tropical" in the '' Astronomical Almanac Online Glossary'' states: An equivalent, more descriptive, definition is "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worm Gear
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm wheel (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear). The two elements are also called the worm screw and worm gear. The terminology is often confused by imprecise use of the term ''worm gear'' to refer to the worm, the worm wheel, or the worm drive as a unit. The worm drive or "endless screw" was invented by either Archytas of Terentum, Apollonius of Perga, or Archimedes, the last one being the most probable author.Witold Rybczynski, '' One good turn : a natural history of the screwdriver and the screw''. London, 2000. Page 139. The worm drive later appeared in the Indian subcontinent, for use in roller cotton gins, during the Delhi Sultanate in the thirteenth or fourteenth centuries.Irfan Habib''Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500'', page 53 Pearson Education Explanation A gearbox designed using a worm and worm wheel is considerably smaller than on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive ' W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
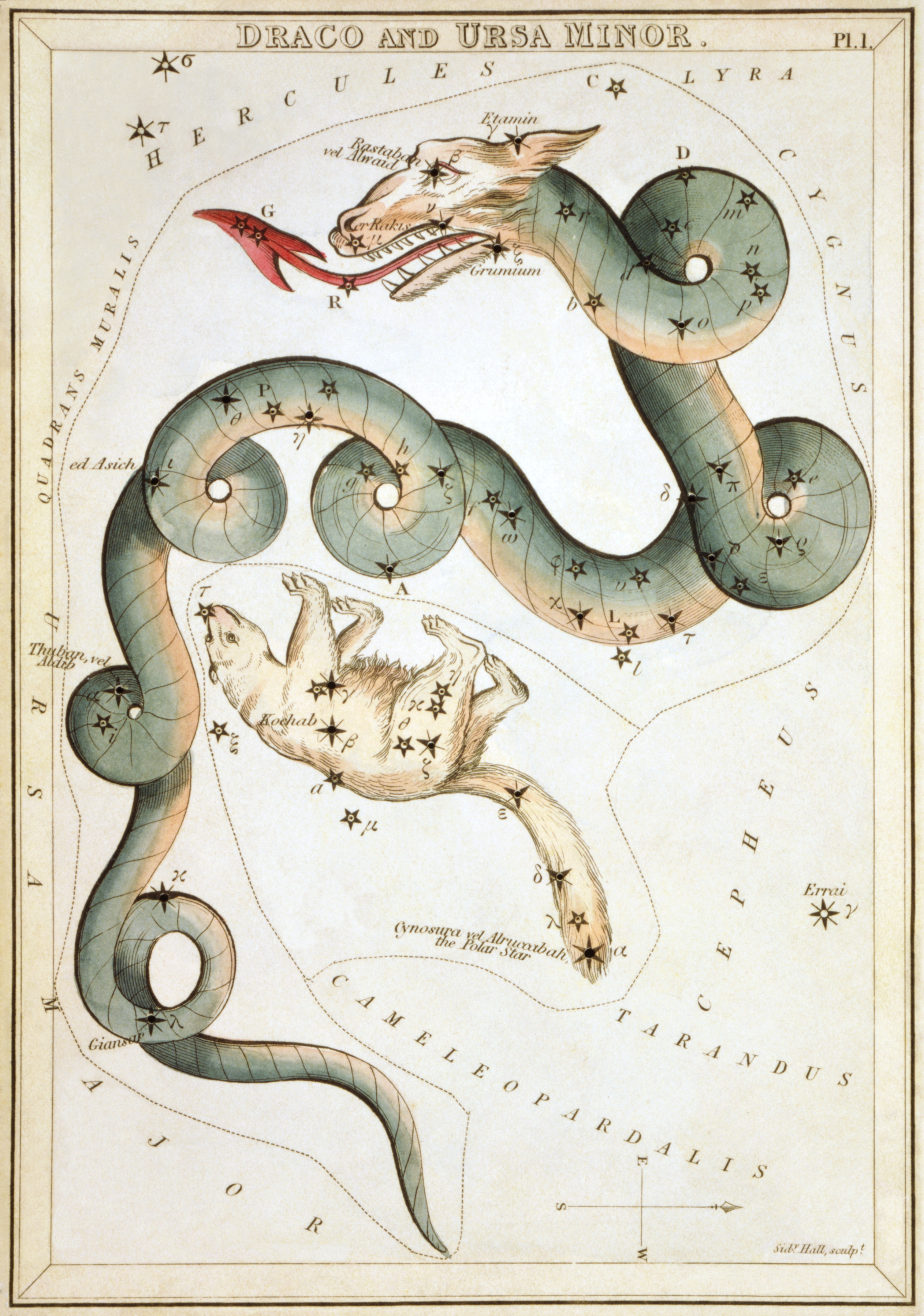
Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star. Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging in apparent magnitude from 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper," "the Wagon," "Charles's Wain," or "the Plough," among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the "Little Dipper." Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation Of Time
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropic Of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun to its maximum extent. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the December Solstice. Using a continuously updated formula, the circle is currently north of the Equator. Its Southern Hemisphere counterpart, marking the most southerly position at which the Sun can be directly overhead, is the Tropic of Capricorn. These tropics are two of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth, the others being the Arctic and Antarctic circles and the Equator. The positions of these two circles of latitude (relative to the Equator) are dictated by the tilt of Earth's axis of rotation relative to the plane of its orbit, and since the tilt changes, the location of these two circles also changes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Calendar
A solar calendar is a calendar whose dates indicate the season or almost equivalently the apparent position of the Sun relative to the stars. The Gregorian calendar, widely accepted as a standard in the world, is an example of a solar calendar. The main other type of calendar is a lunar calendar, whose months correspond to cycles of Moon phases. The months of the Gregorian calendar do not correspond to cycles of the Moon phase. The Egyptians appear to have been the first to develop a solar calendar, using as a fixed point the annual sunrise reappearance of the Dog Star—Sirius, or Sothis—in the eastern sky, which coincided with the annual flooding of the Nile River. They constructed a calendar of 365 days, consisting of 12 months of 30 days each, with 5 days added at the year’s end. The Egyptians’ failure to account for the extra fraction of a day, however, caused their calendar to drift gradually into error. Examples The oldest solar calendars include the Julian calendar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Phang_Nga_Bay%2C_Thailand.jpg)