|
Yorgia Sketch
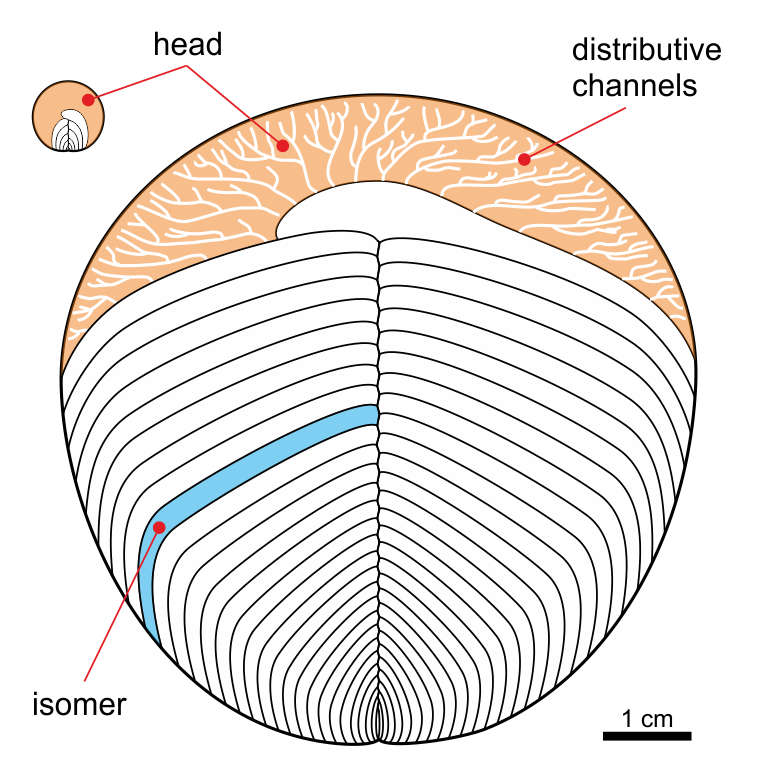
''Yorgia waggoneri'' is a discoid Ediacaran organism. It has a low, segmented body consisting of a short wide "head", no appendages, and a long body region, reaching a maximum length of . It is classified within the extinct animal phylum Proarticulata. Etymology The generic name ''Yorgia'' comes from the Yorga river on the Zimnii Bereg (Winter Coast) of the White Sea, where the first specimens were found. The specific name ''Yorgia waggoneri'' honors the American paleontologist Ben Waggoner, who found the first specimen. Morphology The body plan of the ''Yorgia'' and other proarticulates is unusual for solitary (non-colonial) metazoans. These bilateral organisms have segmented metameric bodies, but left and right transverse elements (isomers) are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body – they are not direct mirror images. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of glide reflection, which is a characteristic also found in the similar ''Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sea
The White Sea (russian: Белое море, ''Béloye móre''; Karelian and fi, Vienanmeri, lit. Dvina Sea; yrk, Сэрако ямʼ, ''Serako yam'') is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the northeast. The whole of the White Sea is under Russian sovereignty and considered to be part of the internal waters of Russia.A. D. Dobrovolskyi and B. S. Zalogi"Seas of USSR. White Sea" Moscow University (1982) (in Russian) Administratively, it is divided between Arkhangelsk and Murmansk oblasts and the Republic of Karelia. The major port of Arkhangelsk is located on the White Sea. For much of Russia's history this was Russia's main centre of international maritime trade, conducted by the Pomors ("seaside settlers") from Kholmogory. In the modern era it became an important Soviet naval and submarine base. The White Sea–Baltic Canal connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Life
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were composed of enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The Ediacaran biota may have undergone evolutionary radiation in a proposed event called the Avalon explosion, . This was after the Earth had thawed from the Cryogenian period's extensive glaciation. This biota largely disappeared with the rapid increase in biodiversity known as the Cambrian explosion. Most of the currently existing body plans of animals first appeared in the fossil record of the Cambrian rather than the Ediacaran. For macroorganisms, the Cambrian biota appears to have almost completely replaced the organisms that dominated the Ediacaran fossil record, although relationships are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalozoa
Cephalozoa are an extinct class of primitive segmented marine organisms within the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran period. They possessed bilateral symmetry and were characterized by a thin, rounded body. Description Unlike the other classes of proarticulates, the segmentation of the body is not complete and shows a "head" with fine distribution channels. Some species of the Yorgiidae family also show some asymmetry.Ivantsov, A. Y. (2004"Vendian Animals in the Phylum Proarticulata" The Rise and Fall of the Vendian Biota. IGSP Project 493. Abstracts. Prato, Italy, . They were discovered in Russia near the White Sea in the Arkhangelsk region, where they lived during the Ediacaran, approximately 635 to 540 Ma (millions of years ago). Taxonomy Cephalozoa includes the families Yorgiidae and Sprigginidae: Yorgiidae *† ''Archaeaspinus'' Ivantsov, 2007 (synonym of ''Archaeaspis'') **† ''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Ivantsov, 2001 *† ''Yorgia'' Ivantsov, 1999 **† ''Yorgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ediacaran Genera ...
This is a list of all described Ediacaran genera, including the Ediacaran biota. It contains 227 genera. References {{reflist, 30em * Ediacaran The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Mat
A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, or bacteria alone. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. A few are found as endosymbionts of animals. Although only a few centimetres thick at most, microbial mats create a wide range of internal chemical environments, and hence generally consist of layers of microorganisms that can feed on or at least tolerate the dominant chemicals at their level and which are usually of closely related species. In moist conditions mats are usually held together by slimy substances secreted by the microorganisms. In many cases some of the bacteria form tangled webs of filaments which make the mat tougher. The best known physical forms are flat mats and stubby pillars called stromatolites, but there are also spherical forms. Microbial mats are the earliest form of life on Earth for which there is good fossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epibaion
''Epibaion'' is a trace fossil imprint of the Ediacaran animals of the phylum Proarticulata, which became extinct in the Precambrian. Imprints often occurring in chains, that is interpreted as a feeding trace; some chains terminate in a body fossil, allowing their maker to be identified. Several specimens are known; ''E. waggoneris'' was produced by ''Yorgia waggoneri''; ''E. costatus'' by ''Dickinsonia costata'', and ''E. axiferus'', the type species, has as yet not been found with a trace-maker. It is proposed that the Australian fossil ''Phyllozoon'' is also a feeding trace of Proarticulata. See also * List of Ediacaran genera References {{Taxonbar, from=Q5382415 Proarticulata Fossil taxa described in 2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorgia Trace
''Yorgia waggoneri'' is a discoid Ediacaran organism. It has a low, segmented body consisting of a short wide "head", no appendages, and a long body region, reaching a maximum length of . It is classified within the extinct animal phylum Proarticulata. Etymology The generic name ''Yorgia'' comes from the Yorga river on the Zimnii Bereg (Winter Coast) of the White Sea, where the first specimens were found. The specific name ''Yorgia waggoneri'' honors the American paleontologist Ben Waggoner, who found the first specimen. Morphology The body plan of the ''Yorgia'' and other proarticulates is unusual for solitary (non-colonial) metazoans. These bilateral organisms have segmented metameric bodies, but left and right transverse elements (isomers) are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body – they are not direct mirror images. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of glide reflection, which is a characteristic also found in the similar ''Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flinders Ranges
The Flinders Ranges are the largest mountain range in South Australia, which starts about north of Adelaide. The ranges stretch for over from Port Pirie to Lake Callabonna. The Adnyamathanha people are the Aboriginal group who have inhabited the range for tens of thousands of years. Its most well-known landmark is Wilpena Pound / Ikara, a formation that creates a natural amphitheatre covering and containing the range's highest peak, St Mary Peak (). The ranges include several national parks, the largest being the Ikara-Flinders Ranges National Park, as well as other protected areas. It is an area of great geological and palaeontological significance, and includes the oldest fossil evidence of animal life was discovered. The Ediacaran Period and Ediacaran biota take their name from the Ediacara Hills within the ranges. In August 2022, a nomination for the Flinders Ranges to be named a World Heritage Site was lodged. History The first humans to inhabit the Flinders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through European Russia, western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the Boundaries between the continents of Earth, conventional boundary between the regions of Europe and Asia. Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya form a further continuation of the chain to the north into the Arctic Ocean. The Ural Mountains are one of the richest mineral regions in the world, containing more than 1,000 varieties of valuable minerals. The mountains lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |