|
Yoko Gake
is one of the original forty throws of judo as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the fifth group, Gokyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current 67 throws of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a side sacrifice technique, Yoko-sutemi. Considered one of the techniques most dangerous for the Uke, its use in competition is infrequent; contributing to the risk is that Uke does not have sufficient space to dissipate the impact of the fall adequately. Another contributing factor is the necessity for Uke to compensate in order to achieve proper rotation in executing the breakfall; if the Uke does not succeed in meeting these criteria, the force of the impact can be severe, even to the point of possible spinal injury. For these reasons, the technique is generally reserved for expert judoka. Technique description Ideal conditions for Yoko-gake include; a slight imbalance toward the front, simultaneous, coordinated action w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nage-waza
In martial arts, a throw is a grappling technique that involves off-balancing or lifting an opponent, and throwing them to the ground, in Japanese martial arts referred to as ''nage-waza'', 投げ技, "throwing technique". Throws are a subset of takedown (grappling). Certain throwing techniques called sacrifice throws (''sutemi-waza'', 捨身技, "sacrifice technique") involve putting oneself in a potentially disadvantageous position, such as on the ground, in order to execute a throw. Types of throws There are several major types of throw, among Asian martial arts, Judo has the most developed throwing techniques and throws are considered its specialty. Most throws are named by describing the circumvention point of the throw (e.g., hip throw, shoulder throw, wrist throw etc.), or the nature of effect of the throw on the opponent (e.g., heaven and earth throw, valley drop, body drop) with variations are given descriptive names. The names used here are attributed to Jujutsu throw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
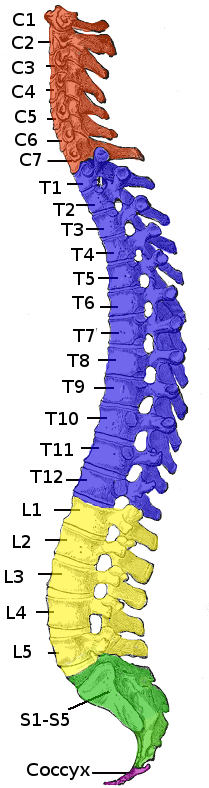
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deashi Harai
, more accurately romanized: Deashibarai, is one of the original 40 throws of Judo as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the first group, Dai-Ikkyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo-no-Nagewaza, of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current 67 Throws of Kodokan Judo.Mifune, Kyuzo: ''The Canon of Judo'', Kodansha International Ltd. (Tokyo) 2004, , p.pp. 46–47 It is classified as a foot technique, Ashi-Waza. Deashi Harai is also one of the 20 techniques in Danzan Ryu's (DZR) Nagete list. Description Deashi Harai is one of the basic foot sweeps learned in the martial arts. As with most basic techniques, Deashi Harai has numerous variations. One common method used in Danzan-ryu Jujitsu is the outside-in method of sweeping an opponent's foot. It is accomplished by initially having a firm grip on the opponent while facing him or her. The attacker then moves the foot to the opposite side of his opponent (right foot to opponent's left side, or vice versa), to swee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harai Tsurikomi Ashi
is one of the original 40 throws of Judo as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the third group, Sankyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current 67 Throws of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a foot technique, Ashi-waza. Similar techniques, variants, and aliases English aliases: Similar techniques: * De Ashi Harai: sweeping of one foot either to the front or sideways. * Sasae Tsuri Komi Ashi: Blocking of the foot to prevent it from stepping forward in contrast to the sweeping motion backwards in Harai Tsuri Komi Ashi. Further reading * See also *The Canon Of Judo The Canon of Judo is a book that was originally published in 1956, and written by Kodokan 10th dan, Kyuzo Mifune (1883-1965). The book covers almost all of the Kodokan recognized techniques, adds variations and new techniques, including Do-Jime in ... References Judo technique Throw (grappling) Grappling hold Grappling positions Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweep (martial Arts)
A sweep is either of two categories of martial arts techniques. From standing, sweeps are throws or takedowns that primarily use the legs to attack an opponent's legs. On the ground, sweeps are techniques for reversing a grappling position from a guard position. Standing When standing it is a technique used to take an opponent to the ground by knocking their legs out from under them, so is classed as a throw or takedown. The force of the sweep either runs perpendicular to the opponent's leg or rises as it strikes the leg, lifting the foot from the ground. A sweep can be used to take the opponent to the ground or it can simply disrupt the opponent's balance long enough to make an opening for a punch or kick. In Japanese it is known as ''ashi-barai''. Illustration in kick boxing Image: balayage_cuillère.jpg , '' 'Spoon-type' Sweep'' Image: Crochetage3.svg , ''Using a hook kick'' Image: balayage_retourné.jpg , ''Using a spinning kick'' Ground work A sweep, when referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tori (martial Arts)
is a term used in Japanese martial arts to refer to the executor of a technique in partnered practice. The term "tori" comes from the verb , meaning "to take", "to pick up", or "to choose". In judo and some other martial arts, ''tori'' is the person who completes the technique against the training partner, called ''uke''. Regardless of the situation, the principle is that "tori" is always the one who successfully ''completes'' a technique. The terms "tori" and "uke" are not synonymous with attacker and defender, because the role is determined by who completes a successful technique, not who initiates one. In aikido and related martial arts, ''tori'' executes a defensive technique against a designated attack initiated by ''uke''. Aikido has alternative terms describing the role of ''tori'', depending on the particular style or situation, including and .Shite can also refer to the principal character in a Japanese Noh is a major form of classical Japanese dance-drama that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judoka
is an unarmed modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo"). Judo was created in 1882 by Kanō Jigorō () as an eclectic martial art, distinguishing itself from its predecessors (primarily Tenjin Shinyo-ryu jujutsu and Kitō-ryū jujutsu) due to an emphasis on "randori" (, lit. 'free sparring') instead of " kata" (pre-arranged forms) alongside its removal of striking and weapon training elements. Judo rose to prominence for its dominance over established jujutsu schools in tournaments hosted by the Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department (警視庁武術大会, ''Keishicho Bujutsu Taikai''), resulting in its adoption as the department's primary martial art. A judo practitioner is called a , and the judo uniform is called . The objective of competitive judo is to throw an opponent, immobilize them wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakfall
() is in Japanese martial arts the person who "receives" a technique. The exact role of ''uke'' varies between the different arts and often within the art itself depending on the situation. For instance, in aikido, judo kata, and bujinkan ninjutsu, ''uke'' initiates an attack against their partner, who then defends, whereas in competition judo, there is no designated ''uke''. An ''uke'' typically partners with a partner or nominal opponent. The latter person may be referred to by any of several terms, again depending on the art or situation. They include , and . Ukemi The action of ''uke'' is called "taking ." Literally translated as "receiving body", it is the art of knowing how to respond correctly to an attack and often incorporates skills to allow one to do so safely. These skills can include moves similar to tumbling and are often used as a valid exercise in itself. In aikido and judo training for instance, many classes begin with ''ukemi'' training as conditioning. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutemi-waza
In martial arts, a throw is a grappling technique that involves off-balancing or lifting an opponent, and throwing them to the ground, in Japanese martial arts referred to as ''nage-waza'', 投げ技, "throwing technique". Throws are a subset of takedown (grappling). Certain throwing techniques called sacrifice throws (''sutemi-waza'', 捨身技, "sacrifice technique") involve putting oneself in a potentially disadvantageous position, such as on the ground, in order to execute a throw. Types of throws There are several major types of throw, among Asian martial arts, Judo has the most developed throwing techniques and throws are considered its specialty. Most throws are named by describing the circumvention point of the throw (e.g., hip throw, shoulder throw, wrist throw etc.), or the nature of effect of the throw on the opponent (e.g., heaven and earth throw, valley drop, body drop) with variations are given descriptive names. The names used here are attributed to Jujutsu throw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uke (martial Arts)
() is in Japanese martial arts the person who "receives" a technique. The exact role of ''uke'' varies between the different arts and often within the art itself depending on the situation. For instance, in aikido, judo kata, and bujinkan ninjutsu, ''uke'' initiates an attack against their partner, who then defends, whereas in competition judo, there is no designated ''uke''. An ''uke'' typically partners with a partner or nominal opponent. The latter person may be referred to by any of several terms, again depending on the art or situation. They include , and . Ukemi The action of ''uke'' is called "taking ." Literally translated as "receiving body", it is the art of knowing how to respond correctly to an attack and often incorporates skills to allow one to do so safely. These skills can include moves similar to tumbling and are often used as a valid exercise in itself. In aikido and judo training for instance, many classes begin with ''ukemi'' training as conditioning. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judo Technique
This is a list of judo techniques. They are categorized into throwing techniques (''nage-waza''), grappling techniques (''katame-waza''), body-striking techniques (''atemi-waza)'', blocks and parries (''uke-waza''), receiving/breakfall techniques (''ukemi''), and resuscitation techniques (''kappo''). Nage-waza (投げ技): throwing techniques Te-waza (手技): hand throwing techniques # Ippon seoinage (一本背負投): Single-handed back throw # Kata guruma (肩車): Shoulder wheel # Kibisu gaeshi (踵返): One-hand reversal # Morote gari (双手刈): Two-hand reap # Obi otoshi (帯落): Belt drop # Seoi nage (背負投): Back throw # Seoi otoshi (背負落): Back drop # Sukui nage (掬投): Scoop throw # Sumi otoshi (隅落): Corner drop # Tai otoshi (体落): Body drop # Uchi mata sukashi (内股透): Inner thigh void throw # Uki otoshi (浮落): Floating drop # Yama arashi (山嵐): Mountain storm # Kouchi gaeshi (小内返): Small inner reap reversal # Kuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |