|
Yarrow Shipbuilders Ltd
Yarrow Shipbuilders Limited (YSL), often styled as simply Yarrows, was a major shipbuilding firm based in the Scotstoun district of Glasgow on the River Clyde. It is now part of BAE Systems Surface Ships, owned by BAE Systems, which has also operated the nearby Govan shipyard (formerly Fairfields) since 1999. History Origins in London The company was founded by Alfred Yarrow, later Sir Alfred Yarrow, 1st Baronet, in the year 1865 as Yarrow & Company, Limited. Originally it was based at Folly Wall, Poplar, then in 1898 as the company grew, Yarrow moved his shipyard to London Yard, Cubitt Town.History of London Yard by Angela Brown and Ron Coverson, 2001 Hundreds of steam launches, lake and river vessels, and eventually the |
British Shipbuilders
British Shipbuilders (BS) was a public corporation that owned and managed the shipbuilding industry in Great Britain from 1977 through the 1980s. Its head office was at Benton House in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. History The corporation was founded as a result of the Aircraft and Shipbuilding Industries Act 1977, which nationalised 27 major shipbuilding and marine engineering companies in Great Britain. A further 6 ship repair companies and a further shipyard were also acquired by the corporation, with British Shipbuilders initially comprising 32 shipyards, 6 marine engine works and 6 general engineering plants. Collectively, British Shipbuilders accounted for 97% of the UK's merchant shipbuilding capacity, 100% of its warship-building capacity, 100% of slow speed diesel engine manufacturing and approximately 50% of ship-repair capacity. Harland & Wolff, the only shipbuilder based in Northern Ireland was deemed to be a special political case and remained out of the control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-tube Boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam passes through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater) to become superheated. Superheated steam is defined as steam that is heated above the boiling point at a given pressure. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines, since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower drum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
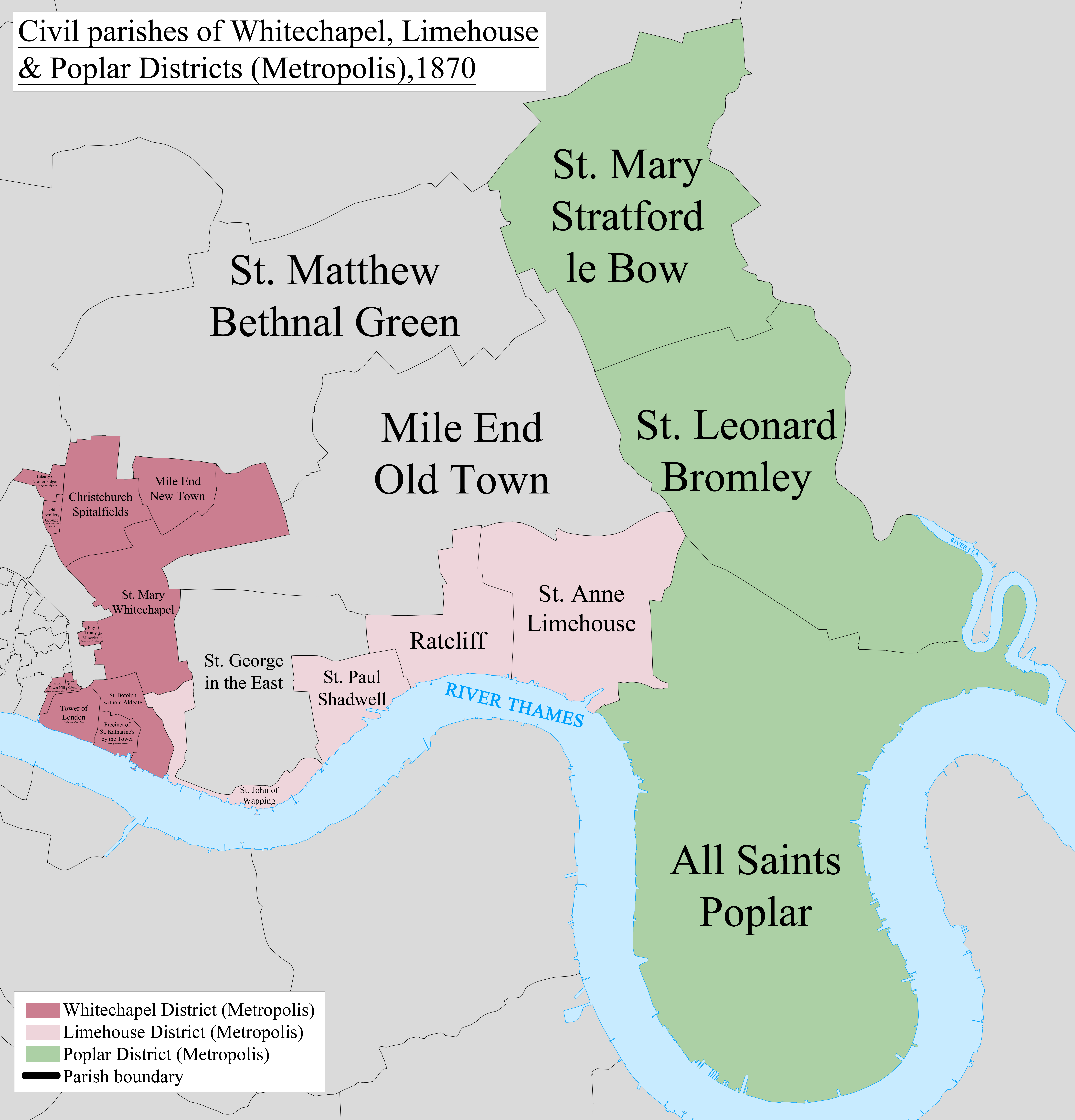
Cubitt Town
Cubitt Town is a district on the eastern side of the Isle of Dogs in London, England. This part of the former Metropolitan Borough of Poplar was redeveloped as part of the Port of London in the 1840s and 1850s by William Cubitt, Lord Mayor of London (1860–1862), after whom it is named. It is on the east of the Isle, facing the Royal Borough of Greenwich across the River Thames. To the west is Millwall, to the east and south is Greenwich, to the northwest Canary Wharf, and to the north — across the Blue Bridge — is Blackwall. The district is situated within the Blackwall & Cubitt Town Ward of Tower Hamlets London Borough Council. History It is named after William Cubitt, Lord Mayor of London (1860–1862), who was responsible for the development of the housing and amenities of the area in the 1840s and 1850s, mainly to house the growing population of workers in the local docks, shipbuilding yards and factories. As it grew, Cubitt also created many local businesses employi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Yard
London Yard was a shipyard in London, in use between around 1856 and 1908 by various shipbuilding companies, including Westwood, Baillie and Yarrow Shipbuilders. Location The site is on the north bank of the Thames immediately to the south of the Samuda Estate in Cubitt Town on the Isle of Dogs, and lies between the river and Manchester Road. It occupies around , with around of river frontage. History The site, immediately upstream of the yard of Samuda Brothers, was acquired in 1856 by Robert Baillie and Joseph Westwood. Westwood and Baillie built a number of ships at the yard including HMS ''Resistance'', but subsequently concentrated mainly on the manufacture of iron and steel bridges. Westwood and Ballie went out of business in 1893. The yard was taken over in 1898 by Yarrows, who had outgrown their original yard to the north at Folly Wall. Yarrows built many torpedo boat destroyers at the yard. As shipbuilding in London declined, Yarrows subsequently transferred to Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar, London
Poplar is a district in East London, England, the administrative centre of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, borough of Tower Hamlets. Five miles (8 km) east of Charing Cross, it is part of the East End of London, East End. It is identified as a major district centre in the London Plan, with its district centre being Chrisp Street Market, a significant commercial and retail centre surrounded by extensive residential development. Poplar includes Poplar Baths, Blackwall Yard and Trinity Buoy Wharf and the locality of Blackwall, London, Blackwall. Originally part of the Stepney#Manor and Ancient Parish, Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, the ''Hamlet of Poplar'' had become an autonomous area of Stepney by the 17th century, and an independent parish in 1817. The Hamlet and Parish of Poplar included Blackwall, London, Blackwall and the Isle of Dogs. After a series of mergers, Poplar became part of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in 1965. History Origin and administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvaerner Govan
Kvaerner Govan Ltd (KGL), located at Govan in Glasgow on the River Clyde, was a shipyard subsidiary formed in 1988 when the Norwegian group Kværner Industrier purchased the Govan Shipbuilders division of the nationalised British Shipbuilders corporation. Prior to the Govan Shipyard's nationalisation in 1977, as a result of the Aircraft and Shipbuilding Industries Act, it had been operated by Govan Shipbuilders Ltd, which emerged from the collapse of the previous Upper Clyde Shipbuilders (UCS) joint venture in 1972. Prior to the formation of UCS in 1968, the Shipyard was operated by the Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, which had a history extending back to 1834. Kvaerner Govan Ltd invested £30m in modernisation of the shipyard during the early 1990s to enable it to specialise in the construction of liquefied natural gas and chemical tankers. This included the construction of a large Tank Assembly Shop (TAS), later known as the Ship Block Outfit Hall (SBOH), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Clyde
The River Clyde ( gd, Abhainn Chluaidh, , sco, Clyde Watter, or ) is a river that flows into the Firth of Clyde in Scotland. It is the ninth-longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third-longest in Scotland. It runs through the major city of Glasgow. Historically, it was important to the British Empire because of its role in shipbuilding and trade. To the Romans, it was , and in the early medieval Cumbric language, it was known as or . It was central to the Kingdom of Strathclyde (). Etymology The exact etymology of the river's name is unclear, though it is known that the name is ancient: It was called or by the Britons and by the Romans. It is therefore likely that the name comes from a Celtic language—most likely Old British. But there is more than one old Celtic word that the river's name could plausibly derive from. One possible root is the Common Brittonic , meaning 'loud' or 'loudly'. More likely, the river was named after a local Celtic goddess, '' Clōta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)