|
YCSU Young Democrats
The Youth Christian Social Union – Young Democrats, often shortened to the YCSU Young Democrats ( be, МХСЗ Маладыя дэмакраты, MChSZ Maładyja demakraty) is a Christian democratic youth organisation from Belarus. Since 2004 the YCSU has been a member of the Youth of the European People's Party, an umbrella organization of European political youth organisations that is the official youth wing of the European People's Party. The YEPP brings together over 54 centre-right youth political organisations from over 35 countries across Europe and is considered to be the largest political youth organisation in Europe. The YCSU Young Democrats was admitted as an observer member of the European Christian Political Youth Network in 2004. History The Youth Christian Social Union was founded in 1997 and officially registered by the Ministry of Justice of Belarus from 1998 until 2003. On the eve of the 2004 parliamentary elections, it lost its legal status when the Supr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democracy
Christian democracy (sometimes named Centrist democracy) is a political ideology that emerged in 19th-century Europe under the influence of Catholic social teaching and neo-Calvinism. It was conceived as a combination of modern democratic ideas and traditional Christian values, incorporating social justice and the social teachings espoused by the Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed, Pentecostal, and other denominational traditions of Christianity in various parts of the world. After World War II, Catholic and Protestant movements of neo-scholasticism and the Social Gospel shaped Christian democracy. On the traditional left-right political spectrum Christian Democracy has been difficult to pinpoint as Christian democrats rejected liberal economics and individualism and advocated state intervention, but simultaneously defended private property rights against excessive state intervention. This has meant that Christian Democracy has historically been considered centre left on eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
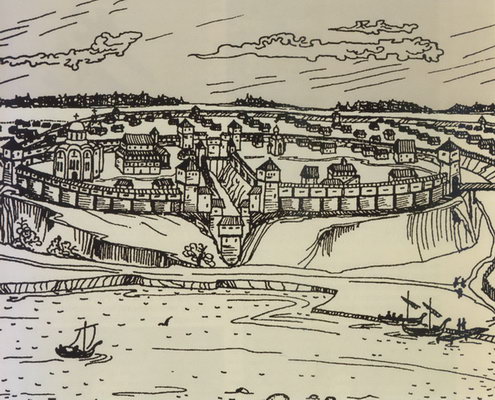
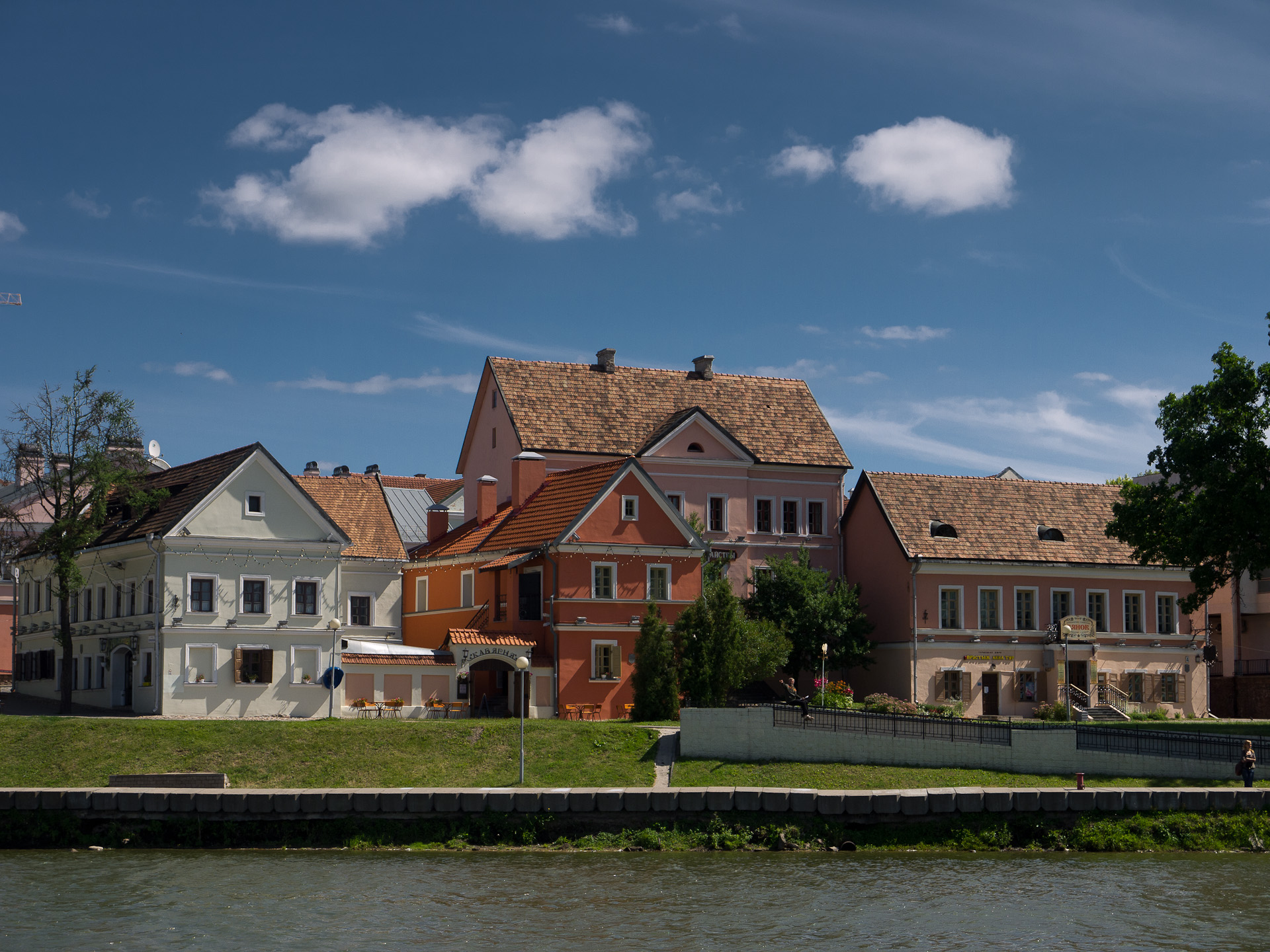
Rogachev
Rahachow or Rahačoŭ ( be, Рагачо́ў, ; russian: Рогачёв, Rogachyov, also transliterated Rogachev; pl, Rohaczów; yi, ראגאטשאוו, ''Rogatshov'', ) is a town in the Gomel Region of Belarus. It is center of Rahachow District. Rahachow is located at , between the Drut and Dnieper rivers. The population is 34,727 (2004 estimate). The town is first mentioned in 1142 in Russian chronicles. From the late thirteenth century it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and then the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1772 the Rahačoŭ District was annexed by the Russian Empire. On 16 July 1863 the local landowner Tomasz Hryniewicz was executed here by a Russian firing squad for leading the Rahačoŭ detachment of Polish insurgents. During World War II, Rahačoŭ was occupied by the German Army from 2 July 1941 to 13 July 1941, and again from 14 August 1941 to 24 February 1944. The notable Rabbi, Yosef Rosen (1858–1936), known as the Rogatshover Gaon ("The G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youth Wings Of Pan-European Political Parties
Youth is the time of life when one is young. The word, youth, can also mean the time between childhood and adulthood ( maturity), but it can also refer to one's peak, in terms of health or the period of life known as being a young adult. Youth is also defined as "the appearance, freshness, vigor, spirit, etc., characteristic of one, who is young". Its definitions of a specific age range varies, as youth is not defined chronologically as a stage that can be tied to specific age ranges; nor can its end point be linked to specific activities, such as taking unpaid work, or having sexual relations. Youth is an experience that may shape an individual's level of dependency, which can be marked in various ways according to different cultural perspectives. Personal experience is marked by an individual's cultural norms or traditions, while a youth's level of dependency means the extent to which they still rely on their family emotionally and economically. Terminology and definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democratic Parties In Europe
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Opposition
The Belarusian opposition consists of groups and individuals in Belarus seeking to challenge, from 1988 to 1991, the authorities of Soviet Belarus, and since 1995, the leader of the country Alexander Lukashenko, whom supporters of the movement often consider to be a dictator. Supporters of the movement tend to call for a parliamentary democracy based on a Western model, with freedom of speech and political and religious pluralism. Background The modern Belarusian democracy movement originated in the late 1980s when Mikhail Gorbachev's Perestroika and the Chernobyl disaster exposed the serious shortcomings of the Soviet system and galvanized a significant section of Belarusians around the issues of environment, de-Stalinization, national revival and democratic change. The dissolution of the Soviet Union brought about a brief period of democracy from 1991 to 1994. However, since his election in 1994, Alexander Lukashenko established an authoritarian rule creating a political syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 Establishments In Belarus
File:1997 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The movie set of ''Titanic (1997 film), Titanic'', the List of highest-grossing films, highest-grossing movie in history at the time; ''Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'', is published; Comet Hale-Bopp passes by Earth and becomes one of the most observed comet, comets of the 20th century; Golden Bauhinia Square, where sovereignty of Hong Kong is Handover of Hong Kong, handed over from the United Kingdom to the People's Republic of China; the 1997 Central European flood kills 114 people in the Czech Republic, Poland, and Germany; Korean Air Flight 801 crashes during heavy rain on Guam, killing 229; Mars Pathfinder and Sojourner (rover), Sojourner land on Mars; flowers left outside Kensington Palace following the death of Diana, Princess of Wales, in a car crash in Paris., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Titanic (1997 film) rect 200 0 400 200 Harry Potter rect 400 0 600 200 Comet Hale-Bopp rect 0 200 300 400 Death of Diana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Security Agency Of The Republic Of Belarus
The State Security Committee of the Republic of Belarus (KGB RB; russian: Комитет государственной безопасности Республики Беларусь, КГБ РБ; be, Камітэт дзяржаўнай бяспекі Рэспублікі Беларусь, КДБ РБ, Kamitet dziaržaŭnaj biaspieki Respubliki Belarus', KDB RB) is the national intelligence agency of Belarus. Along with its counterparts in Transnistria and South Ossetia, it kept the unreformed name after declaring independence. It is the successor to the KGB of the Byelorussian SSR, a branch of the Soviet KGB which operated in the Byelorussian republic. Felix Dzerzhinsky, who founded the first Soviet secret police, the Cheka, was born in present-day Belarus and remains an important figure in the state ideology of Belarus under president Alexander Lukashenko as well as a patron of the Belarusian KGB. It is governed by the law ''About State Security Bodies of the Republic of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Lukashenko
Alexander Grigoryevich Lukashenko (as transliterated from Russian language, Russian; also transliterated from Belarusian language, Belarusian as Alyaksand(a)r Ryhoravich Lukashenka;, ; rus, Александр Григорьевич Лукашенко, Aleksandr Grigoryevich Lukashenko, ɐlʲɪkˈsandr ɡrʲɪˈɡorʲjɪvʲɪtɕ lʊkɐˈʂɛnkə. In English language, English, both transliterations are used, and his first name is often anglicized to ''Alexander''. born 30 August 1954) is a Belarusian politician who has been the first and only president of Belarus since the establishment of the office on 20 July 1994, making him the List of current state leaders by date of assumption of office, longest-sitting European president. Before his political career, Lukashenko worked as director of a state farm (''sovkhoz''), and served in the Soviet Border Troops and in the Soviet Army. Lukashenko continued state ownership of key industries in Belarus after the dissolution of the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomel
Gomel (russian: Гомель, ) or Homiel ( be, Гомель, ) is the administrative centre of Gomel Region and the second-largest city in Belarus with 526,872 inhabitants (2015 census). Etymology There are at least six narratives of the origin of the city's name. The most plausible is that the name is derived from the name of the stream Homeyuk, which flowed into the river Sozh near the foot of the hill where the first settlement was founded. Names of other Belarusian cities are formed along these lines: for example, the name Minsk is derived from the river Menka, Polatsk from the river Palata, and Vitsebsk from the river Vitsba. The first appearance of the name, as "Gomy", dates from 1142. Up to the 16th century, the city was mentioned as Hom', Homye, Homiy, Homey, or Homyi. These forms are tentatively explained as derivatives of an unattested ''*gomŭ'' of uncertain meaning. The modern name for the city has been in use only since the 16th or 17th centuries. History Unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk Region (voblast) and Minsk District (raion). As of January 2021, its population was 2 million, making Minsk the 11th most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First documented in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of the Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of a region annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Partition of Poland. From 1919 to 1991, aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maladzyechna
Maladzyechna ( be, Маладзе́чна, Maladziečna, ; russian: Молоде́чно, Molodechno; pl, Mołodeczno) is a city in the Minsk Region of Belarus, an administrative centre of the Maladzyechna District (and formerly of the Maladzyechna Voblast). It has 98,514 inhabitants (2006 estimate) and is located 72 km northwest of Minsk. Located on the Usha River, it has been a settlement since 1388 when it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It was also home to the Cold War facility Maladzyechna air base. History The fortification on the right bank of the Uša was first mentioned in 1388, although it is probable it was erected even before that date. Rectangular earthworks with stone walls 3,5 metres high and 11 metres wide formed the basis of the future castles and military camps formed on that location. The town itself was first mentioned the following year in a document issued by Kaributas, Prince of Severian Novgorod, who on December 16 assured his tributary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Democratic Forces Of Belarus
The United Democratic Forces of Belarus ( be, Аб'яднаныя дэмакратычныя сілы Беларусі; russian: Объединённые демократические силы) is a coalition of political parties that oppose the presidency of Alexander Lukashenko, who has been in power since 1994. It was the main opposition group during the 2006 presidential election and chose Alexander Milinkevich as their candidate. Official Belarusian statistics reported Milinevich gained 6% of the vote, however Belarusian opposition and critics from Western countries have not accepted the official results as legitimate and believe this is an example of election fraudulence. Belarusian authorities have denied all accusations of election fraud. Currently the United Civic Party and Belarusian Left Party "A Just World" make up the majority of the coalition. The BPF Party keeps its membership in the coalition, however concentrates more on the newly created coalition of conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |