|
YAKINDU Statechart Tools
YAKINDU Statechart Tools (YAKINDU SCT) is a tool for the specification and development of reactive, event-driven systems with the help of finite-state machines. It comprises a tool for the graphical editing of statecharts and provides validation, simulation, and source code generators for various target platforms and programming languages. YAKINDU Statechart Tools are available with standard and professional editions, with no-cost licenses for non-commercial resp. academic usage. Users are coming from both industry and academia. Concepts YAKINDU Statechart Tools implement the concept of statecharts as invented by David Harel in 1984. Statecharts have been adopted by the UML later. The software can be used to model finite-state machines. Important theoretical models for finite-state machines are Mealy machines and Moore machines. YAKINDU Statechart Tools can be used to model both these types. Functionality The main features of YAKINDU Statechart Tools are: * Smart combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itemis
itemis AG, headquartered in Lünen (North Rhine-Westphalia), is a German IT consulting and software development company, active among other things in the field of model-driven software development (MDSD). With the YAKINDU product family, itemis sells a number of self-developed software products. History itemis AG was founded in 2003 as a GmbH & Co. KG by Wolfgang Neuhaus and Jens Wagener. In September 2007, the change of the legal form took place. itemis AG is one of the largest IT companies in the Lünen region. The company's headquarters are located on the premises of the LÜNTEC Technology Center in the Brambauer part of town. Other German locations are in Berlin, Bonn, Essen, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Heide, Leipzig, Paderborn, and Stuttgart. International locations exist in Vélizy-Villacoublay near the French capital Paris and since 2017, in the Tunisian capital Tunis. From 2009 to 2020, itemis was also represented in Windisch in the Swiss canton of Aargau. On 2020-12-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Harel
David Harel ( he, דוד הראל; born 12 April 1950) is a computer scientist, currently serving as President of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities. He has been on the faculty of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel since 1980, and holds the William Sussman Professorial Chair of Mathematics. Born in London, England, he was Dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science at the institute for seven years. Biography Harel is best known for his work on dynamic logic, computability, database theory, software engineering and modelling biological systems. In the 1980s he invented the graphical language of Statecharts for specifying and programming reactive systems, which has been adopted as part of the UML standard. Since the late 1990s he has concentrated on a scenario-based approach to programming such systems, launched by his co-invention (with W. Damm) of Live Sequence Charts. He has published expository accounts of computer science, such as his awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source License
An open-source license is a type of license for computer software and other products that allows the source code, blueprint or design to be used, modified and/or shared under defined terms and conditions. This allows end users and commercial companies to review and modify the source code, blueprint or design for their own customization, curiosity or troubleshooting needs. Open-source licensed software is mostly available free of charge, though this does not necessarily have to be the case. Licenses which only permit non-commercial redistribution or modification of the source code for personal use only are generally not considered as open-source licenses. However, open-source licenses may have some restrictions, particularly regarding the expression of respect to the origin of software, such as a requirement to preserve the name of the authors and a copyright statement within the code, or a requirement to redistribute the licensed software only under the same license (as in a copyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain-specific Language
A domain-specific language (DSL) is a computer language specialized to a particular application domain. This is in contrast to a general-purpose language (GPL), which is broadly applicable across domains. There are a wide variety of DSLs, ranging from widely used languages for common domains, such as HTML for web pages, down to languages used by only one or a few pieces of software, such as MUSH soft code. DSLs can be further subdivided by the kind of language, and include domain-specific ''markup'' languages, domain-specific ''modeling'' languages (more generally, specification languages), and domain-specific ''programming'' languages. Special-purpose computer languages have always existed in the computer age, but the term "domain-specific language" has become more popular due to the rise of domain-specific modeling. Simpler DSLs, particularly ones used by a single application, are sometimes informally called mini-languages. The line between general-purpose languages and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into the software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
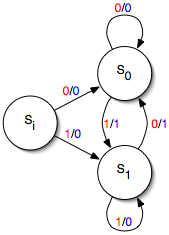
Finite-state Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of '' states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. A deterministic finite-state machine can be constructed equivalent to any non-deterministic one. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore Machine
In the theory of computation, a Moore machine is a finite-state machine whose current output values are determined only by its current state. This is in contrast to a Mealy machine, whose output values are determined both by its current state and by the values of its inputs. Like other finite state machines, in Moore machines, the input typicallinfluences the next state Thus the input may indirectly influence subsequent outputs, but not the current or immediate output. The Moore machine is named after Edward F. Moore, who presented the concept in a 1956 paper, “ Gedanken-experiments on Sequential Machines.” Formal definition A Moore machine can be defined as a 6-tuple (Q, q_0, \Sigma, O, \delta, G) consisting of the following: * A finite set of states Q * A start state (also called initial state) q_0 which is an element of Q * A finite set called the input alphabet \Sigma * A finite set called the output alphabet O * A transition function \delta : Q \times \Sigma \right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mealy Machine
In the theory of computation, a Mealy machine is a finite-state machine whose output values are determined both by its current state and the current inputs. This is in contrast to a Moore machine, whose output values are determined solely by its current state. A Mealy machine is a deterministic finite-state transducer: for each state and input, at most one transition is possible. History The Mealy machine is named after George H. Mealy, who presented the concept in a 1955 paper, "A Method for Synthesizing Sequential Circuits". Formal definition A Mealy machine is a 6-tuple (S, S_0, \Sigma, \Lambda, T, G) consisting of the following: * a finite set of states S * a start state (also called initial state) S_0 which is an element of S * a finite set called the input alphabet \Sigma * a finite set called the output alphabet \Lambda * a transition function T : S \times \Sigma \rightarrow S mapping pairs of a state and an input symbol to the corresponding next state. * an output f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
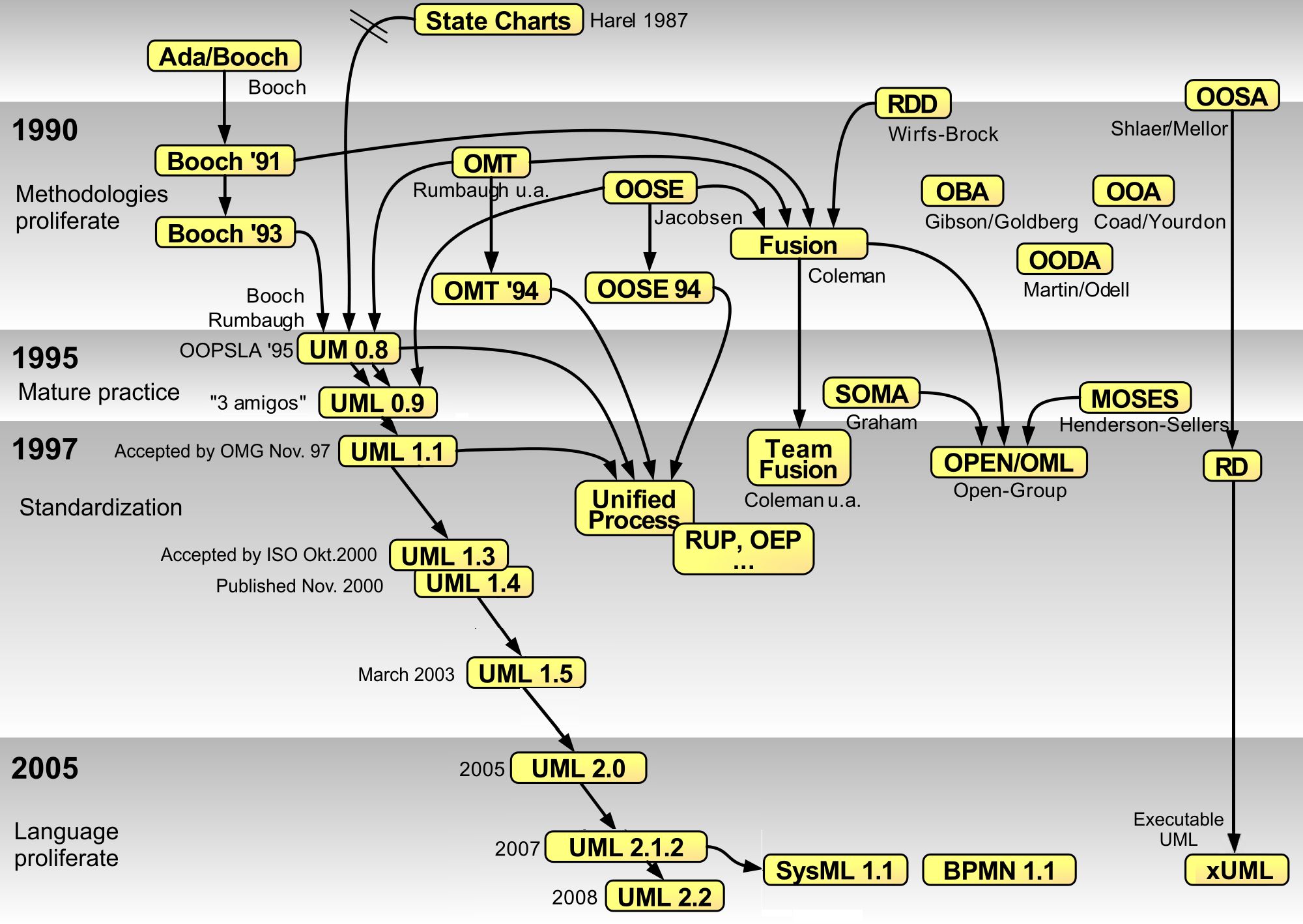
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose, developmental modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG), and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as an approved ISO standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In software engineering, most practitioners do not use UML, but instead produce informal hand drawn diagrams; these diagrams, however, often include elements from UML. History Before UM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Diagram
A state diagram is a type of diagram used in computer science and related fields to describe the behavior of systems. State diagrams require that the system described is composed of a finite number of states; sometimes, this is indeed the case, while at other times this is a reasonable abstraction. Many forms of state diagrams exist, which differ slightly and have different semantics. Overview State diagrams are used to give an abstract description of the behavior of a system. This behavior is analyzed and represented by a series of events that can occur in one or more possible states. Hereby "each diagram usually represents objects of a single class and track the different states of its objects through the system". State diagrams can be used to graphically represent finite-state machines (also called finite automata). This was introduced by Claude Shannon and Warren Weaver Warren Weaver (July 17, 1894 – November 24, 1978) was an American scientist, mathematician, and sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' ( WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. , Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub, particularly for client–server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers. Java was originally de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |