|
Xu Xurong
Xu Xurong (; 23 April 1922 – 12 July 2022) was a Chinese physicist, and an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He was a delegate to the 12th National People's Congress. Biography Xu was born in Linyi County (now Linyi), Shandong, on 23 April 1922. He attended Confucius Temple School (). After the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War, he escaped to central China's Hubei province, where he studied at Yunyang National Shandong Middle School (), then fled to southwest China's Sichuan province, and studied in Mianyang National No. 6 High School (now Mianyang Nanshan High School; ). In 1941, he was admitted to National Southwestern Associated University, majoring in physics. After graduating in 1945, he became an assistant at Peking University and was a graduate student under the supervision of Rao Yutai. In 1950, he was transferred to the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to engage in solid-state luminescence research. One year later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu (surname 徐)
Xu () is a Chinese surname, Chinese-language surname. In the Wade-Giles system of Romanization of Chinese, romanization, it is spelled as "Hsu", which is commonly used in Taiwan. It is different from Xu (surname 許), represented by a different character. Variations in other Chinese varieties and languages In Wu Chinese including Shanghainese, the surname 徐 is transcribed as Zee, as seen in the historical place name Zikawei in Shanghai (Xujiahui in Pinyin). In Gan Chinese, it can be spelled Hi or Hé. In Cantonese, 徐 is often transcribed as Tsui, T'sui, Choi, Chui or even Tsua. In modern Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, the character 徐 is written Từ and Sy when migrating to the English-speaking World, particularly the United States. Other spellings include Hee and Hu. In Japanese language, Japanese, the surname 徐 is transliterated as Omomuro (kunyomi) or Jo (onyomi or Sino-Japanese). In Korean, 徐 is romanized as Seo in the Revised Romanization of Korean and writt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
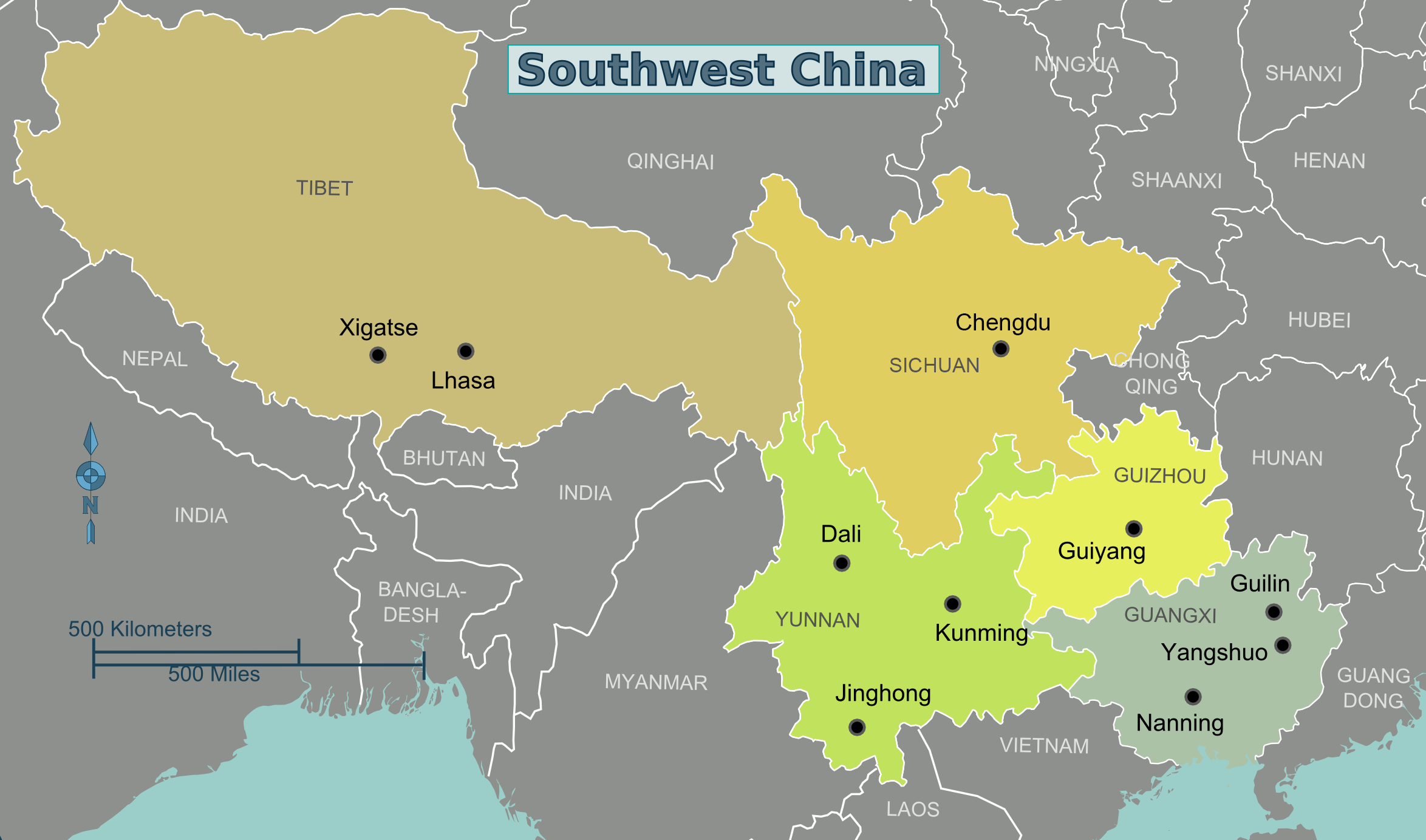
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China. Geography Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and plains to the east. Key geographic features in the region include the Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Sichuan Basin in the northeast, and the karstic Yungui Plateau in the east. The majority of the region is drained by the Yangtze River which forms the Three Gorges in the northeast of the region. The narrowest concept of Southwest China consists of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, while wider definitions often include Guangxi and western portions of Hunan. The official government definition of Southwest China includes the core provinces of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, in addition to the Tibet Autonomous Region. History Portions of Southwest China were incorporated in the 3nd century BCE into the Qin dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of Beijing Jiaotong University
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |