|
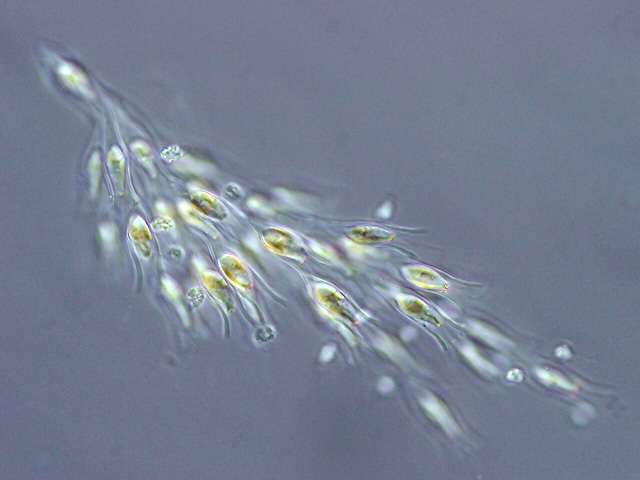
Xanthophyceae
Yellow-green algae or the Xanthophyceae (xanthophytes) are an important group of heterokont algae. Most live in fresh water, but some are found in marine and soil habitats. They vary from single-celled flagellates to simple colonial and filamentous forms. Xanthophyte chloroplasts contain the photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll ''a'', chlorophyll ''c'', β-carotene, and the carotenoid diadinoxanthin. Unlike other heterokonts, their chloroplasts do not contain fucoxanthin, which accounts for their lighter colour. Their storage polysaccharide is chrysolaminarin. Xanthophyte cell walls are produced of cellulose and hemicellulose. They appear to be the closest relatives of the brown algae. Classifications The species now placed in the Xanthophyceae were formerly included in the Chlorophyceae. In 1899, Lüther created the group Heterokontae for green algae with unequal flagella. Pascher (1914) included the Heterokontae in the Chrysophyta. In 1930, Allorge renamed the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokont
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including ''Phytophthora'', which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and ''Pythium'', which causes seed rot and damping off. The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile life cycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently arranged flagella (see zoospore). History In 1899, Alexander Luther created the term "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) included other groups in Heterokonta, expanding the name's sense. The term continues to be applied in different ways, leading to Heterokontophyta being applied al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Algae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. They are dominant on rocky shores throughout cooler areas of the world. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, '' Macrocystis'', a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests. Kelp forests like these contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is '' Sargassum'', which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food. Between 1,5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysophyta
Chrysophyta or golden algae is a term used to refer to certain heterokonts. It can be used to refer to: * Chrysophyceae ( golden algae), Bacillariophyceae (diatoms), and Xanthophyceae (yellow-green algae) together. E.g., Pascher (1914). * Chrysophyceae ( golden algae) E.g., Margulis et al. (1990). Margulis, L., J.O. Corliss, M. Melkonian, D.J. Chapman. ''Handbook of Protoctista''. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston, 1990. Chrysophyta has some characteristics which includes their possession of the photosynthetic pigments which are chlorophylls a and c, they also possess a yellow carotenoid called fucoxanthin, this is responsible for their unique and characteristic color. They also store food as oil and not starch Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ..., their cells con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botrydiales
Botrydiaceae is a family of yellow-green algae Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ... comprising 13 species in three genera. It is the only family in the order Botrydiales. References Heterokont families Xanthophyceae {{heterokont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiresias (alga)
In Greek mythology, Tiresias (; grc, Τειρεσίας, Teiresías) was a blind prophet of Apollo in Thebes, famous for clairvoyance and for being transformed into a woman for seven years. He was the son of the shepherd Everes and the nymph Chariclo. Tiresias participated fully in seven generations in Thebes, beginning as advisor to Cadmus himself. Mythology Eighteen allusions to mythic Tiresias, noted by Luc Brisson, fall into three groups: the first recounts Tiresias' sex-change episode and later his encounter with Zeus and Hera; the second group recounts his blinding by Athena; the third, all but lost, seems to have recounted the misadventures of Tiresias. Blindness and gift of prophecy Like other oracles, how Tiresias obtained his information varied: sometimes, he would receive visions; other times he would listen for the songs of birds, or ask for a description of visions and pictures appearing within the smoke of burnt offerings or entrails, and so interpret them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |