|
XXIII Corps (ACW)
XXIII Corps was a corps of the Union Army during the American Civil War. It served in the Western Theater as part of the Army of the Ohio. The corps was organized in April 1863 by order of the departmental commander, Ambrose E. Burnside. Along with Burnside's old IX Corps, which had been sent west with him after Fredericksburg, it was to maintain a primarily defensive position in Eastern Tennessee and Kentucky. It originally consisted of two divisions under the overall command of General George L. Hartsuff. The corps played a major role during the Knoxville Campaign, its first major action, distinguishing itself at the battles of Campbell's Station and Knoxville, and also took part in some minor actions in early 1864. During this time it was commanded by Maj. Gen. Mahlon D. Manson. The Army of the Ohio joined William T. Sherman for the Atlanta Campaign that spring. IX Corps was detached and sent back to rejoin the Army of the Potomac, so the "army" consisted entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies greatly, but from two to five divisions and anywhere from 40,000 to 80,000 are the numbers stated by the US Department of Defense. Within military terminology a corps may be: *an military organization, operational formation, sometimes known as a field corps, which consists of two or more division (military), divisions, such as the I Corps (Grande Armée), , later known as ("First Corps") of Napoleon I's ); *an administrative corps (or Muster (military), mustering) – that is a #Administrative corps, specialized branch of a military service (such as an artillery corps, a medical corps, or a force of military police) or; *in some cases, a distinct service within a national military (such as the United States Marine Corps). These usages often ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
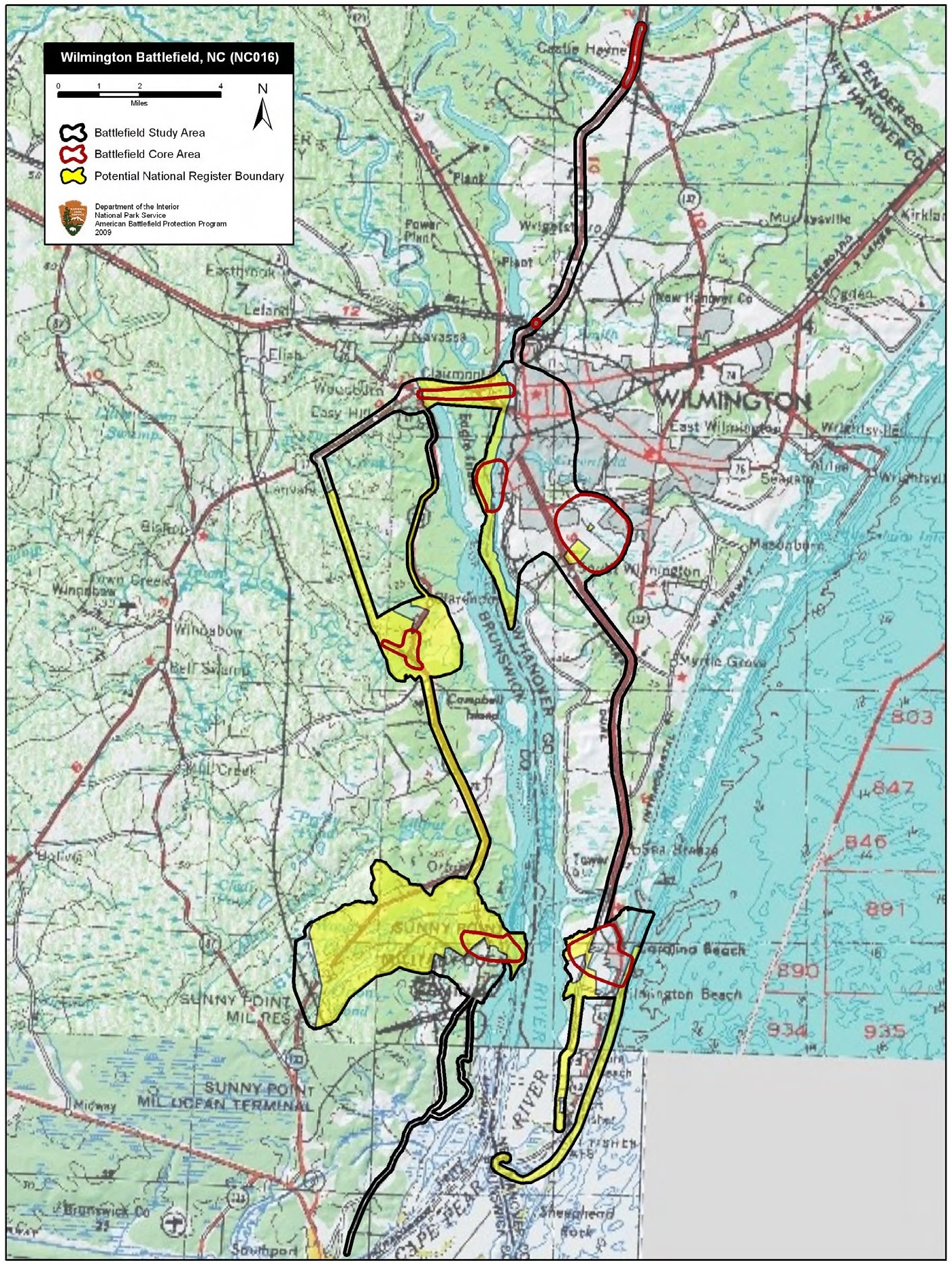
Battle Of Wilmington
The Battle of Wilmington was fought February 11–22, 1865, during the American Civil War, mostly outside the city of Wilmington, North Carolina, between the opposing Union and Confederate Departments of North Carolina. The Union victory in January in the Second Battle of Fort Fisher meant that Wilmington, 30 miles upriver, could no longer be used by the Confederacy as a port. It fell to Union (American Civil War), Union troops after they overcame Confederate defenses along the Cape Fear River south of the city. The Confederate General Braxton Bragg burned stores of tobacco and cotton, among other supplies and equipment, before leaving the city, to prevent the Union from seizing them. Background After the fall of Fort Fisher, the port city of Wilmington was sealed to any further blockade runners; the Confederates had no remaining major ports along the Atlantic seaboard. Confederate forces evacuated the other defensive works near the mouth of the Cape Fear River; they were fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Fort Fisher
The Second Battle of Fort Fisher was a successful assault by the Union Army, Navy and Marine Corps against Fort Fisher, south of Wilmington, North Carolina, near the end of the American Civil War in January 1865. Sometimes referred to as the "Gibraltar of the South" and the last major coastal stronghold of the Confederacy, Fort Fisher had tremendous strategic value during the war, providing a port for blockade runners supplying the Army of Northern Virginia.Kennedy, p. 402. Background Wilmington was the last major port open to the Confederacy on the Atlantic seacoast. Ships leaving Wilmington via the Cape Fear River and setting sail for the Bahamas, Bermuda or Nova Scotia to trade cotton and tobacco for needed supplies from the British were protected by the fort. Based on the design of the Malakoff redoubt in Sevastopol, Russian Empire, Fort Fisher was constructed mostly of earth and sand. This made it better able to absorb the pounding of heavy fire from Union ships than olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nashville
The Battle of Nashville was a two-day battle in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign that represented the end of large-scale fighting west of the coastal states in the American Civil War. It was fought at Nashville, Tennessee, on December 15–16, 1864, between the Confederate States Army, Confederate Army of Tennessee under Lieutenant General (CSA), Lieutenant General John Bell Hood and the Union Department of the Cumberland, Army of the Cumberland (Dept. of the Cumberland) under Major general (United States), Major General George H. Thomas. In one of the largest victories achieved by the Union Army during the war, Thomas attacked and routed Hood's army, largely destroying it as an effective fighting force. Military situation Hood followed up his defeat in the Atlanta Campaign by moving northwest to disrupt the supply lines of Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman from Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga, hoping to challenge Sherman into a battle that could be fought to Hood's advanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Franklin (1864)
The Second Battle of Franklin was fought on November 30, 1864, in Franklin, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin–Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It was one of the worst disasters of the war for the Confederate States Army. Confederate Lt. Gen. John Bell Hood's Army of Tennessee conducted numerous frontal assaults against fortified positions occupied by the Union forces under Maj. Gen. John Schofield and was unable to prevent Schofield from executing a planned, orderly withdrawal to Nashville. The Confederate assault of six infantry divisions containing eighteen brigades with 100 regiments numbering almost 20,000 men, sometimes called the "Pickett's Charge of the West", resulted in devastating losses to the men and the leadership of the Army of Tennessee—fourteen Confederate generals (six killed, seven wounded, and one captured) and 55 regimental commanders were casualties. After its defeat against Maj. Gen. George H. Thomas in the subsequent Battle of Nashvil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John B
John Bryn Williams (born 1977), known as John B, is an English disc jockey and electronic music producer. He is widely recognised for his eccentric clothing and wild hair and his production of several cutting edge drum and bass tracks. John B ranked number 76 in '' DJ Magazine''s 2010 Top 100 DJs annual poll, announced on 27 October 2010. Career Williams was born on 12 July 1977 in Maidenhead, Berkshire. He started producing music around the age of 14, and now is the head of drum and bass record label A record label, or record company, is a brand or trademark of music recordings and music videos, or the company that owns it. Sometimes, a record label is also a publishing company that manages such brands and trademarks, coordinates the prod ... Beta Recordings, together with its more specialist drum and bass sub-labels Nu Electro, Tangent, and Chihuahua. He also has releases on Formation Records, Metalheadz and Planet Mu. Williams was ranked 92nd drum and bass DJ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in April. History The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861 but was then only the size of a corps (relative to the size of Union armies later in the war). Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen. Irvin McDowell, and it was the army that fought (and lost) the war's first major battle, the First Battle of Bull Run. The arrival in Washington, D.C., of Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan dramatically changed the makeup of that army. McClellan's original assignment was to command the Division of the Potomac, which included the Department of Northeast Virginia under McDowell and the Department of Washington under Brig. Gen. Joseph K. Mansfield. On July 26, 1861, the Departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William T
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahlon D
Mahlon ( ''Maḥlōn'') and Chilion (כִּלְיוֹן ''Ḵilyōn'') were two brothers mentioned in the Book of Ruth. They were the sons of Elimelech of the tribe of Judah and his wife Naomi. Together with their parents, they settled in the land of Moab during the period of the Israelite Judges. On foreign soil, Mahlon married the Moabite convert Ruth (Ruth 4:10) while Chilion married the Moabite convert Orpah. Biography The test of childless Ruth and Orpah Elimelech and his sons all died in Moab, leaving Naomi, Ruth, and Orpah widowed. Ruth and Orpah did not bear Jewish children, too. The story in the book tells that Naomi plans to return to Israel, and that she tests her daughters-in-law. She gives them the advice to return to their mother's home: which would mean drastically violating Jewish Law and reverting to Moabite culture and idol worship. Ruth in Israel While Orpah returns and leaves Judaism, Ruth chooses to stay with Naomi, thus proving her former conversion to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14764293712)_Badge_of_the_XXIII_Corps_(Union_Army)_(cropped).jpg)