|
XOD (programming Language)
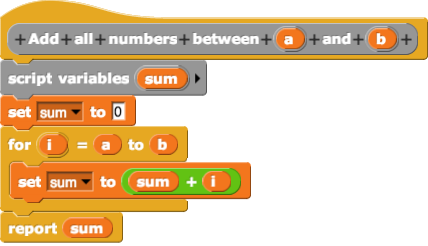
XOD is a visual programming language for microcontrollers, started in 2016. As a supported platform, XOD started with Arduino boards compatibility and Raspberry Pi. It is free and open-source software released under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3.0. Basics The basic elements of XOD programming are nodes. XOD is based on functional reactive programming principles and provides graphical flow-based application programming interface. XOD can compile a native machine code for the low-ended controllers. A node is a block that represents either some physical device like a sensor, motor, or relay, or some operation such as addition, comparison, or text concatenation In formal language theory and computer programming, string concatenation is the operation of joining character strings end-to-end. For example, the concatenation of "snow" and "ball" is "snowball". In certain formalizations of concatenati .... XOD is also able to let the user build up some missing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declarative Programming
In computer science, declarative programming is a programming paradigm—a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow. Many languages that apply this style attempt to minimize or eliminate side effects by describing ''what'' the program must accomplish in terms of the problem domain, rather than describing ''how'' to accomplish it as a sequence of the programming language primitives (the ''how'' being left up to the language's implementation). This is in contrast with imperative programming, which implements algorithms in explicit steps. Declarative programming often considers programs as theories of a formal logic, and computations as deductions in that logic space. Declarative programming may greatly simplify writing parallel programs. Common declarative languages include those of database query languages (e.g., SQL, XQuery), regular expressions, logic programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dataflow Programming
In computer programming, dataflow programming is a programming paradigm that models a program as a directed graph of the data flowing between operations, thus implementing dataflow principles and architecture. Dataflow programming languages share some features of functional languages, and were generally developed in order to bring some functional concepts to a language more suitable for numeric processing. Some authors use the term ''datastream'' instead of ''dataflow'' to avoid confusion with dataflow computing or dataflow architecture, based on an indeterministic machine paradigm. Dataflow programming was pioneered by Jack Dennis and his graduate students at MIT in the 1960s. Considerations Traditionally, a program is modelled as a series of operations happening in a specific order; this may be referred to as sequential, procedural, control flow (indicating that the program chooses a specific path), or imperative programming. The program focuses on commands, in line with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Reactive Programming
Functional reactive programming (FRP) is a programming paradigm for reactive programming (asynchronous dataflow programming) using the building blocks of functional programming (e.g., map, reduce, filter). FRP has been used for programming graphical user interfaces (GUIs), robotics, games, and music, aiming to simplify these problems by explicitly modeling time. Formulations of FRP The original formulation of functional reactive programming can be found in the ICFP 97 paper Functional Reactive Animation by Conal Elliott and Paul Hudak. FRP has taken many forms since its introduction in 1997. One axis of diversity is discrete vs. continuous semantics. Another axis is how FRP systems can be changed dynamically. Continuous The earliest formulation of FRP used continuous semantics, aiming to abstract over many operational details that are not important to the meaning of a program. The key properties of this formulation are: * Modeling values that vary over continuous time, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arduino
Arduino () is an Italian open-source hardware and open-source software, software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardware products are licensed under a Creative Commons license, CC BY-SA license, while the software is licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) or the GNU General Public License (GPL), permitting the manufacture of Arduino boards and software distribution by anyone. Arduino boards are available commercially from the official website or through authorized distributors. Arduino board designs use a variety of microprocessors and controllers. The boards are equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards ('shields') or breadboards (for prototyping) and other circuits. The boards feature serial communications interfaces, including Universal Serial Bus (USB) on som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi ( ) is a series of small single-board computers (SBCs) developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in collaboration with Broadcom Inc., Broadcom. To commercialize the product and support its growing demand, the Foundation established a commercial entity, Raspberry Pi Holdings, a public company that trades on the London Stock Exchange. The Raspberry Pi was originally created to help teach computer science in schools, but gained popularity for many other uses due to its low cost, compact size, and flexibility. It is now used in areas such as Industrial Automation and Control Systems, industrial automation, robotics, home automation, IoT devices, and hobbyist projects. The company's products range from simple microcontrollers to computers that the company markets as being powerful enough to be used as a general purpose PC. Computers are built around a custom designed system on a chip and offer features such as HDMI video/audio output, USB ports, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Affero General Public License
The GNU Affero General Public License (GNU AGPL) is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU GPL version 3 and the ''Affero General Public License'' (non-GNU). It is intended for software designed to be run over a network, adding a provision requiring that the corresponding source code of modified versions of the software be prominently offered to all users who interact with the software over a network. The Open Source Initiative approved the GNU AGPLv3 as an open source license in March 2008 after the company Funambol submitted it for consideration through its CEO Fabrizio Capobianco. History In 2000, while developing an e-learning and e-service business model at Mandriva, Henry Poole met with Richard Stallman in Amsterdam and discussed the issue of the GPLv2 license not requiring Web application providers to share source code with the users interacting with their software over a network. Over the followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). A SoC may include a microcontroller as one of its components but usually integrates it with advanced peripherals like a graphics processing unit (GPU), a Wi-Fi module, or one or more coprocessors. Microcontrollers are used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Open-source Software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free software and open-source software. The rights guaranteed by FOSS originate from the "Four Essential Freedoms" of '' The Free Software Definition'' and the criteria of '' The Open Source Definition''. All FOSS can have publicly available source code, but not all source-available software is FOSS. FOSS is the opposite of proprietary software, which is licensed restrictively or has undisclosed source code. The historical precursor to FOSS was the hobbyist and academic public domain software ecosystem of the 1960s to 1980s. Free and open-source operating systems such as Linux distributions and descendants of BSD are widely used, powering millions of servers, desktops, smartphones, and other devices. Free-software licenses and open-so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Reactive Programming
Functional reactive programming (FRP) is a programming paradigm for reactive programming (asynchronous dataflow programming) using the building blocks of functional programming (e.g., map, reduce, filter). FRP has been used for programming graphical user interfaces (GUIs), robotics, games, and music, aiming to simplify these problems by explicitly modeling time. Formulations of FRP The original formulation of functional reactive programming can be found in the ICFP 97 paper Functional Reactive Animation by Conal Elliott and Paul Hudak. FRP has taken many forms since its introduction in 1997. One axis of diversity is discrete vs. continuous semantics. Another axis is how FRP systems can be changed dynamically. Continuous The earliest formulation of FRP used continuous semantics, aiming to abstract over many operational details that are not important to the meaning of a program. The key properties of this formulation are: * Modeling values that vary over continuous time, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |