|
X-ray Welding
X-ray welding is an experimental welding process that uses a high powered X-ray source to provide thermal energy required to welding, weld materials. The phrase "X-ray welding" also has an older, unrelated usage in quality control. In this context, an X-ray welder is a tradesman who consistently welds at such a high proficiency that he rarely introduces Welding defect, defects into the weld pool, and is able to recognize and correct Welding defect, defects in the weld pool, during the welding process. It is assumed (''or trusted'') by the Quality control, Quality Control Department of a fabrication or manufacturing shop that the welding work performed by an X-ray welder would pass an Radiographic testing, X-ray inspection. For example, Welding defect, defects like porosity, concavities, cracks, cold laps, slag and tungsten inclusions, lack of fusion & penetration, etc., are rarely seen in a radiographic Radiographic testing, X-ray inspection of a weldment performed by an X-ray welder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Welding is distinct from lower temperature techniques such as brazing and soldering, which do not melting, melt the base metal (parent metal). In addition to melting the base metal, a filler material is typically added to the joint to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to form a joint that, based on weld configuration (butt, full penetration, fillet, etc.), can be stronger than the base material. Pressure may also be used in conjunction with heat or by itself to produce a weld. Welding also requires a form of shield to protect the filler metals or melted metals from being contaminated or Oxidation, oxidized. Many different energy sources can be used for welding, including a gas flame (chemical), an electric arc (electrical), a laser, an electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welding Defect
In metalworking, a welding defect is any flaw that compromises the usefulness of a weldment. There is a great variety of welding defects. Welding imperfections are classified according to ISO 6520, while their acceptable limits are specified in ISO 5817 and ISO 10042. Major causes According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), causes of welding defects can be broken down as follows: 41% poor process conditions, 32% operator error, 12% wrong technique, 10% incorrect consumables and 5% bad weld grooves. Hydrogen embrittlement Residual stresses The magnitude of stress that can be formed from welding can be roughly calculated using: :E \alpha \Delta T Where E is Young's modulus, α is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and ΔT is the temperature change. For steel this calculates out to be approximately . Types Cracks Defects related to fracture. Arc strikes An Arc Strike is a discontinuity resulting from an arc, consisting of any localized remelted met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weld Pool
Weld pool diagram In metalworking, weld pool commonly refers to the dime-sized workable portion of a weld where the base metal has reached its melting point and is ready to be infused with filler material. The weld pool is central to the success of the welding process. It was first observed in oxy-fuel welding by Fouché & Picard in 1903, after the discovery of acetylene Acetylene ( systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure ... by Edmund Davy in 1836. The weld pool must be carried along the joint in a consistent width and depth, and the motion used to carry the weld pool has a direct effect on the quality of the weld bead. A weld made by starting and carrying a weld pool, without the addition of a filler material, is called an autogenous weld. References {{Reflist Welding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements". This approach places emphasis on three aspects (enshrined in standards such as ISO 9001): # Elements such as controls, job management, defined and well managed processes, performance and integrity criteria, and identification of records # Competence, such as knowledge, skills, experience, and qualifications # Soft elements, such as personnel, integrity, confidence, organizational culture, motivation, team spirit, and quality relationships. Inspection is a major component of quality control, where physical product is examined visually (or the end results of a service are analyzed). Product inspectors will be provided with lists and descriptions of unacceptable product defects such as cracks or surface blemishes for example. History and introduction Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
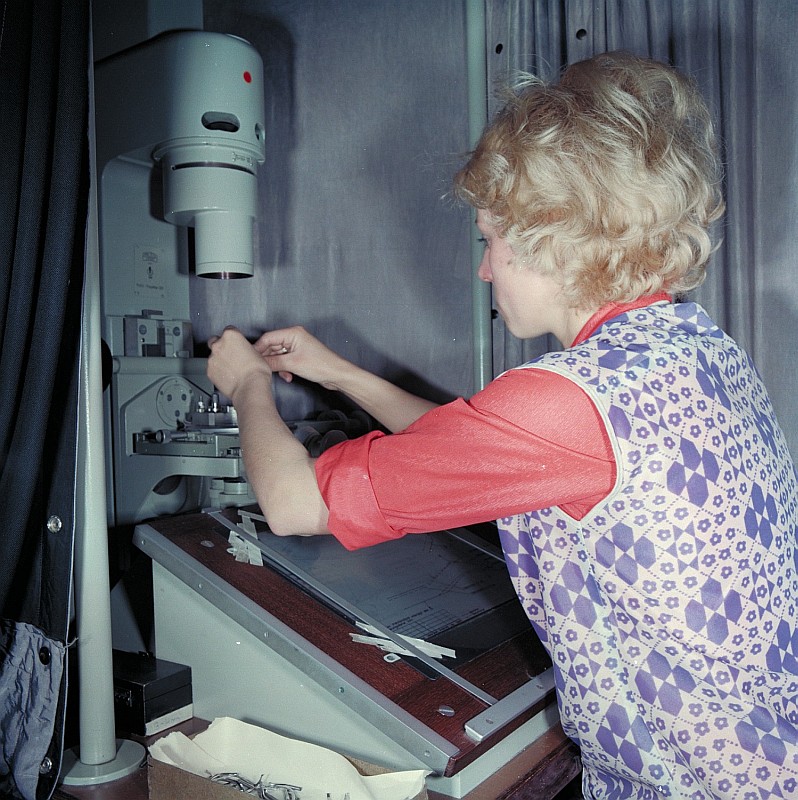
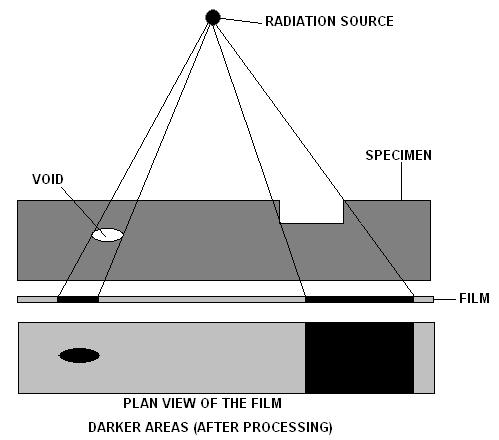
Radiographic Testing
Industrial radiography is a modality of non-destructive testing that uses ionizing radiation to inspect materials and components with the objective of locating and quantifying defects and degradation in material properties that would lead to the failure of engineering structures. It plays an important role in the science and technology needed to ensure product quality and reliability. In Australia, industrial radiographic non-destructive testing is colloquially referred to as "bombing" a component with a "bomb". Industrial Radiography uses either X-rays, produced with X-ray generators, or gamma rays generated by the natural radioactivity of sealed radionuclide sources. Neutrons can also be used. After crossing the specimen, photons are captured by a detector, such as a silver halide film, a phosphor plate, flat panel detector or CdTe detector. The examination can be performed in static 2D (named radiography), in real time 2D (fluoroscopy), or in 3D after image reconstruction ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weldment
Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending and assembling processes. It is a value-added process involving the creation of machines, parts, and structures from various raw materials. Typically, a fabrication shop bids on a job, usually based on engineering drawings, and if awarded the contract, builds the product. Large fab shops employ a multitude of value-added processes, including welding, cutting, forming and machining. As with other manufacturing processes, both human labor and automation are commonly used. A fabricated product may be called a ''fabrication'', and shops specializing in this type of work are called ''fab shops''. The end products of other common types of metalworking, such as machining, metal stamping, forging, and casting, may be similar in shape and function, but those processes are not classified as fabrication. Processes *''Cutting'' is done by sawing, shearing, or chiselling (all with manual and powered variants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
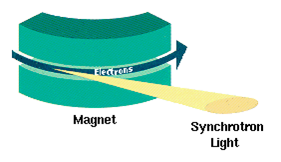
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode are protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas (argon or helium). A filler metal is normally used, though some welds, known as ''autogenous welds'', or ''fusion welds'' do not require it. When helium is used, this is known as heliarc welding. A constant-current welding power supply produces electrical energy, which is conducted across the arc through a column of highly ionized gas and metal vapors known as a plasma. GTAW is most commonly used to weld thin sections of stainless steel and non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys. The process grants the operator greater control over the weld than competing processes such as shielded metal arc welding and gas metal arc welding, allowing for stronger, higher qualit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Metal Arc Welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), sometimes referred to by its subtypes metal inert gas (MIG) and metal active gas (MAG) is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable MIG wire electrode and the workpiece metal(s), which heats the workpiece metal(s), causing them to fuse (melt and join). Along with the wire electrode, a shielding gas feeds through the welding gun, which shields the process from atmospheric contamination. The process can be semi-automatic or automatic. A constant voltage, direct current power source is most commonly used with GMAW, but constant current systems, as well as alternating current, can be used. There are four primary methods of metal transfer in GMAW, called globular, short-circuiting, spray, and pulsed-spray, each of which has distinct properties and corresponding advantages and limitations. Originally developed in the 1940s for welding aluminium and other non-ferrous materials, GMAW was soon applied to steels because it provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submerged Arc Welding
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a common arc welding process. The first SAW patent was taken out in 1935. The process requires a continuously fed consumable solid or tubular (metal cored) electrode. The molten weld and the arc zone are protected from atmospheric contamination by being "submerged" under a blanket of granular fusible flux consisting of lime, silica, manganese oxide, calcium fluoride, and other compounds. When molten, the flux becomes conductive, and provides a current path between the electrode and the work. This thick layer of flux completely covers the molten metal thus preventing spatter and sparks as well as suppressing the intense ultraviolet radiation and fumes that are a part of the shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process. SAW is normally operated in the automatic or mechanized mode, however, semi-automatic (hand-held) SAW guns with pressurized or gravity flux feed delivery are available. The process is normally limited to the flat or horizontal-fillet w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Beam Welding
Electron-beam welding (EBW) is a fusion welding process in which a beam of high-velocity electrons is applied to two materials to be joined. The workpieces melt and flow together as the kinetic energy of the electrons is transformed into heat upon impact. EBW is often performed under vacuum conditions to prevent dissipation of the electron beam. History Electron-beam welding was developed by the German physicist Karl-Heinz Steigerwald in 1949, who was at the time working on various electron-beam applications. Steigerwald conceived and developed the first practical electron-beam welding machine, which began operation in 1958. American inventor James T. Russell has also been credited with designing and building the first electron-beam welder. Physics of electron-beam heating Electrons are elementary particles possessing a mass ''m'' = 9.1 · 10−31 kg and a negative electrical charge ''e'' = 1.6 · 10−19 C. They exist either bound to an at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |