|
X-ray Raman Spectroscopy
X-ray Raman scattering (XRS) is non-resonant inelastic scattering of X-rays from core electrons. It is analogous to vibrational Raman scattering, which is a widely used tool in optical spectroscopy, with the difference being that the wavelengths of the exciting photons fall in the X-ray regime and the corresponding excitations are from deep core electrons. XRS is an element-specific spectroscopic tool for studying the electronic structure of matter. In particular, it probes the excited-state density of states (DOS) of an atomic species in a sample. Description XRS is an inelastic X-ray scattering process, in which a high-energy X-ray photon gives energy to a core electron, exciting it to an unoccupied state. The process is in principle analogous to X-ray absorption (XAS), but the ''energy transfer'' plays the role of the X-ray photon ''energy absorbed'' in X-ray absorption, exactly as in Raman scattering in optics vibrational low-energy excitations can be observed by studying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Scattering Techniques
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy. Note that X-ray diffraction is now often considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the distinction has not always existed. Thus Guinier's classic text from 1963 is titled "X-ray diffraction in Crystals, Imperfect Crystals and Amorphous Bodies" so 'diffraction' was clearly not restricted to crystals at that time. Scattering techniques Ela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
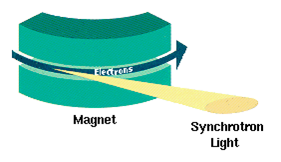
Synchrotron Light
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Scattering
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films. These techniques are based on observing the scattered intensity of an X-ray beam hitting a sample as a function of incident and scattered angle, polarization, and wavelength or energy. Note that X-ray diffraction X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ... is now often considered a sub-set of X-ray scattering, where the scattering is elastic and the scattering object is crystalline, so that the resulting pattern contains sharp spots analyzed by X-ray crystallography (as in the Figure). However, both scattering and diffraction are related general phenomena and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering
Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) is an X-ray spectroscopy technique used to investigate the electronic structure of molecules and materials. Inelastic X-ray scattering is a fast developing experimental technique in which one scatters high energy, X-ray photons inelastically off matter. It is a photon-in/photon-out spectroscopy where one measures both the energy and momentum change of the scattered photon. The energy and momentum lost by the photon are transferred to intrinsic excitations of the material under study and thus RIXS provides information about those excitations. The RIXS process can also be described as a resonant X-ray Raman or resonant X-ray emission process. RIXS is a resonant technique because the energy of the incident photon is chosen such that it coincides with, and hence resonates with, one of the atomic X-ray absorption edges of the system. The resonance can greatly enhance the inelastic scattering cross section, sometimes by many orders of magni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compton Scattering
Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon (which may be an X-ray or gamma ray photon), it is called the Compton effect. Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the recoiling electron. Inverse Compton scattering occurs when a charged particle transfers part of its energy to a photon. Introduction Compton scattering is an example of elastic scattering of light by a free charged particle, where the wavelength of the scattered light is different from that of the incident radiation. In Compton's original experiment (see Fig. 1), the energy of the X ray photon (≈17 keV) was significantly larger than the binding energy of the atomic electron, so the electrons could be treated as being free after scattering. The amount by which the light's wavelength changes is called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Electron
In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron in the outer shell associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with both atoms in the bond each contributing one valence electron. The presence of valence electrons can determine the element's chemical properties, such as its valence—whether it may bond with other elements and, if so, how readily and with how many. In this way, a given element's reactivity is highly dependent upon its electronic configuration. For a main-group element, a valence electron can exist only in the outermost electron shell; for a transition metal, a valence electron can also be in an inner shell. An atom with a closed shell of valence electrons (corresponding to a noble gas configuration) tends to be chemically inert. Atoms with one or two valence electrons more than a closed shell are highly reactive due to the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmon
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light (an optical oscillation) consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective (a discrete number) oscillations of the free electron gas density. For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton. Derivation The plasmon was initially proposed in 1952 by David Pines and David Bohm and was shown to arise from a Hamiltonian for the long-range electron-electron correlations. Since plasmons are the quantization of classical plasma oscillations, most of their properties can be derived directly from Maxwell's equations. Explanation Plasmons can be described in the classical picture as an oscillation of electron densit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson Scattering
Thomson scattering is the elastic scattering of electromagnetic radiation by a free charged particle, as described by classical electromagnetism. It is the low-energy limit of Compton scattering: the particle's kinetic energy and photon frequency do not change as a result of the scattering. This limit is valid as long as the photon energy is much smaller than the mass energy of the particle: \nu\ll mc^2/h , or equivalently, if the wavelength of the light is much greater than the Compton wavelength of the particle (e.g., for electrons, longer wavelengths than hard x-rays). Description of the phenomenon In the low-energy limit, the electric field of the incident wave (photon) accelerates the charged particle, causing it, in turn, to emit radiation at the same frequency as the incident wave, and thus the wave is scattered. Thomson scattering is an important phenomenon in plasma physics and was first explained by the physicist J. J. Thomson. As long as the motion of the particle is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (physics)
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place when some kind of radiant excitation (e.g. a particle beam, sound wave, light, or an X-ray) intersects a localized phenomenon (e.g. a particle or density fluctuation). For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted ( sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. In classical physics, this probability often converges to a deterministic proportion of excitation energy involved in the process, so that, for example, with light scattering off of a particle, the cross section specifies the amount of optical power scattere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), along with X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), is a subset of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). Like other absorption spectroscopies, XAS techniques follow Beer's law. The X-ray absorption coefficient of a material as a function of energy is obtained using X-rays of a narrow energy resolution are directed at a sample and the incident and transmitted x-ray intensity is recorded as the incident x-ray energy is incremented. When the incident x-ray energy matches the binding energy of an electron of an atom within the sample, the number of x-rays absorbed by the sample increases dramatically, causing a drop in the transmitted x-ray intensity. This results in an absorption edge. Every element has a set of unique absorption edges corresponding to different binding energies of its electrons, giving XAS element selectivity. XAS spectra are most often collected at synchrotrons because of the high intensity of synchrotron X- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XANES
X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES), also known as near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS), is a type of absorption spectroscopy that indicates the features in the X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) of condensed matter due to the photoabsorption cross section for electronic transitions from an atomic core level to final states in the energy region of 50–100 eV above the selected atomic core level ionization energy, where the wavelength of the photoelectron is larger than the interatomic distance between the absorbing atom and its first neighbour atoms. Terminology Both XANES and NEXAFS are acceptable terms for the same technique. XANES name was invented in 1980 by Antonio Bianconi to indicate strong absorption peaks in X-ray absorption spectra in condensed matter due to multiple scattering resonances above the ionization energy. The name NEXAFS was introduced in 1983 by Jo Stohr and is synonymous with XANES, but is generally used when applied to surface and molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensity (physics)
In physics, the intensity or flux of radiant energy is the Power (physics), power transferred per unit area, where the area is measured on the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the energy. In the SI system, it has units watts per square metre (W/m2), or kilogram, kg⋅second, s−3 in SI base unit, base units. Intensity is used most frequently with waves such as acoustic waves (sound) or electromagnetic waves such as light or radio waves, in which case the time averaging, ''average'' power transfer over one Period (physics), period of the wave is used. ''Intensity'' can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "wikt:strength, strength", "wikt:amplitude, amplitude", "wikt:magnitude, magnitude", or "wikt:level, level", as it sometimes is in colloquial speech. Intensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |