|
X-34
The Orbital Sciences X-34 was intended to be a low-cost testbed for demonstrating "key technologies" that could be integrated into the Reusable Launch Vehicle program. It was intended to be an autonomous pilotless craft powered by a "Fastrac" liquid-propellant rocket engine, capable of reaching Mach 8 and performing 25 test flights per year. The X-34 began as a program for a suborbital reusable-rocket technology demonstrator. In early 2001, the first flight vehicle was near completion, but the program was ended due to budget concerns. Up to this point, the project had encompassed spending of just under $112 million: $85.7M from the original contract with designer Orbital Sciences, $16M from NASA and various government agencies for testing, and an additional $10M for Orbital Sciences to adapt its L-1011 carrier to accommodate the X-34. The program was officially canceled by NASA on March 31, 2001. The unpowered prototype had been used only for towing and captive flight tests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fastrac (engine)
Fastrac was a turbo pump-fed, liquid rocket engine. The engine was designed by NASA as part of the low cost X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) and as part of the Low Cost Booster Technology (LCBT, aka Bantam) project. This engine was later known as the MC-1 engine when it was merged into the X-34 project. Design The turbopump engine was designed to be used in an expendable booster in the LCBT project. As a result this led to the use of composite materials because of their significantly lower costs and production speed; this also reduced engine complexity since the fuel was not used for nozzle cooling. Based on knowledge and experience from the Space Shuttle's Reusable Solid Rocket Motor (RSRM) and the Solid Propulsion Integrity Program (SPIP), a Silica/phenolic material was chosen for the ablative liner with carbon/epoxy structural overlap. The engine fuel was a mixture of liquid oxygen and kerosene (RP-1). These propellants are used by Saturn F1 rocket engine. Kerosene does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Orbital Sciences Corporation (commonly referred to as Orbital) was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other government customers. In 2014, Orbital merged with Alliant Techsystems to create a new company called Orbital ATK, Inc., which in turn was purchased by Northrop Grumman in 2018. The remnants of the former Orbital Sciences Corporation today are a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman, known as Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. Orbital was headquartered in Dulles, Virginia and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange with the ticker symbol ORB. Orbital's primary products were satellites and launch vehicles, including low Earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous Earth orbit and planetary spacecraft for communications, remote sensing, scientific and defense missions; ground- and air-launched launch vehicles that delivered satellites into orbit; missile d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
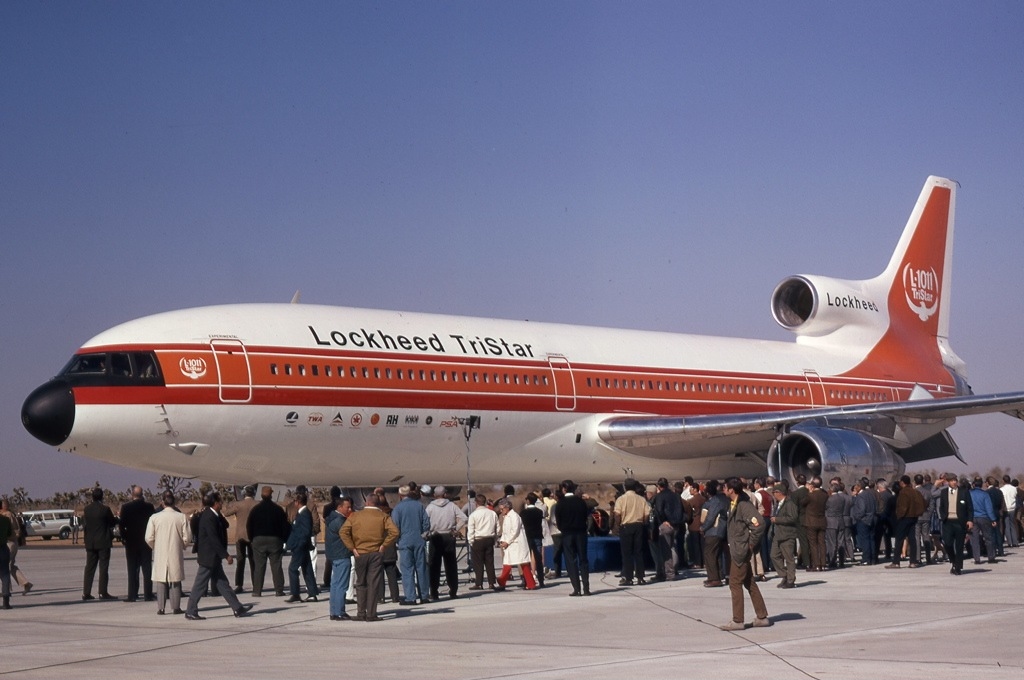
Lockheed L-1011 TriStar
The Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, also known as the L-1011 (pronounced "El-ten-eleven") and TriStar, is an American medium-to-long-range, wide-body trijet airliner built by the Lockheed Corporation. It was the third wide-body airliner to enter commercial operations, after the Boeing 747 and the McDonnell Douglas DC-10. The airliner has a seating capacity of up to 400 passengers and a range of over . Its trijet configuration has three Rolls-Royce RB211 engines with one engine under each wing, along with a third engine center-mounted with an S-duct air inlet embedded in the tail and the upper fuselage. The aircraft has an autoland capability, an automated descent control system, and available lower deck galley and lounge facilities. The L-1011 TriStar was produced in two fuselage lengths. The original L-1011-1 first flew in November 1970 and entered service with Eastern Air Lines in 1972. The shortened, longer range L-1011-500 first flew in 1978 and entered service with British Airways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin X-33
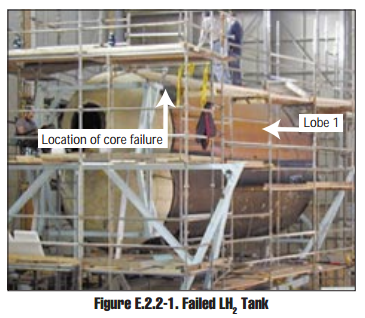
The Lockheed Martin X-33 was a proposed uncrewed, sub-scale technology demonstrator suborbital spaceplane that was developed for a period in the 1990s. The X-33 was a technology demonstrator for the VentureStar orbital spaceplane, which was planned to be a next-generation, commercially operated reusable launch vehicle. The X-33 would flight-test a range of technologies that NASA believed it needed for single-stage-to-orbit reusable launch vehicles (SSTO RLVs), such as metallic thermal protection systems, composite cryogenic fuel tanks for liquid hydrogen, the aerospike engine, autonomous (uncrewed) flight control, rapid flight turn-around times through streamlined operations, and its lifting body aerodynamics. Failures of its 21-meter wingspan and multi-lobed, composite-material fuel tank during pressure testing ultimately led to the withdrawal of federal support for the program in early 2001. Lockheed Martin has conducted unrelated testing, and has had a single success after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Experimental Aircraft
As used here, an experimental or research and development aircraft, sometimes also called an X-plane, is one which is designed or substantially adapted to investigate novel flight technologies. Argentina * FMA I.Ae. 37 glider – testbed for production fighter Australia * GAF Pika – manned test craft for drone program Brazil * Baumgartl PB-60 – towed experimental rotor kite Canada *AEA Silver Dart (1909) – First aircraft to fly in Canada *Avro Canada Avrocar – Ducted fan VTOL * Birdman Project 102 – * Canadair CL-52 – jet engine testbed (converted Boeing B-47) * Canadair CL-84 Dynavert – tilt-wing VTOL * de Havilland Canada C-8A – Quiet Short-Haul Research Aircraft * de Havilland Canada C-8A – Air-Cushion Landing System * de Havilland Canada C-8A – Augmentor Wing *Marsden Gemini – variable-geometry glider *NRC tailless glider – tailless flying wing *UTIAS Ornithopter No.1 France * Aérocentre NC.130 1939 – High-altitude flight * Aérospatiale Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County and a southern arm is in Los Angeles County. The hub of the base is Edwards, California. The base was named after World War II USAAF veteran and test pilot Capt. Glen Edwards in 1950; prior to then the facility was named Muroc Air Force Base. It is the home of the Air Force Test Center, Air Force Test Pilot School, and NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center. It is the Air Force Materiel Command center for conducting and supporting research and development of flight, as well as testing and evaluating aerospace systems from concept to combat. It also hosts many test activities conducted by America's commercial aerospace industry. Notable occurrences at Edwards include Chuck Yeager's flight that broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1, test flights of the North American X-15, the first landings of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reusable Launch System
A reusable launch vehicle have parts that can be recovered and reflown, while carrying payloads from the surface to outer space. Rocket stages are the most common launch vehicle parts aimed for reuse. Smaller parts such as rocket engines and boosters can also be reused, though reusable spacecraft may be launched on top of an expendable launch vehicle. Reusable launch vehicles do not need to make these parts for each launch, therefore reducing its launch cost significantly. However, these benefits are diminished by the cost of recovery and refurbishment. Reusable launch vehicles may contain additional avionics and propellant, making them heavier than their expendable counterparts. Reused parts may need to enter the atmosphere and navigate through it, so they are often equipped with heat shields, grid fins, and other flight control surfaces. By modifying their shape, spaceplanes can leverage aviation mechanics to aid in its recovery, such as gliding or lift. In the atmosphere, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered but then landed as unpowered gliders. Four types of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese CSSHQ. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2019 all past, current, and planned orbital vehicles launch vertically on a separate rocket. Orbital spaceflight takes place at high velocities, with orbital kinetic energies typically at least 50 times greater than suborbital trajectories. Consequently, heavy heat shielding is required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser
Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane being developed by Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) Space Systems. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the cargo variant, Dream Chaser Cargo System, is operational. The crewed variant is planned to carry up to seven people and cargo to and from low Earth orbit. The cargo Dream Chaser is designed to resupply the International Space Station with both pressurized and unpressurized cargo. It is intended to launch vertically on the Vulcan Centaur rocket and autonomously land horizontally on conventional runways. A proposed version to be operated by ESA would launch on an Arianespace vehicle. Spacecraft The Dream Chaser design is derived from NASA's HL-20 Personnel Launch System spaceplane concept, which in turn is descended from a series of test vehicles, including the X-20 Dyna-Soar, Northrop M2-F2, Northrop M2-F3, Northrop HL-10, Martin X-24A and X-24B, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prometheus (spacecraft)
Prometheus was a proposed crewed vertical-takeoff, horizontal-landing (VTHL) lifting body spaceplane concept put forward by Orbital Sciences Corporation in late 2010 as part of the second phase of NASA's Commercial Crew Development (CCDev) program. Design The Prometheus design was based on an earlier NASA design, the HL-20 Personnel Launch System. Prometheus also included other NASA-funded design improvements to HL-20 by Orbital Sciences that were done some years ago as part of NASA's Orbital Space Plane program. Whereas the HL-20 was a pure lifting body, the Prometheus design was for a Blended Lifting Body (BLB). This design combines volumetric efficiency with superior aerodynamic qualities. Prometheus could have initially carried four astronauts to the International Space Station or future commercial space stations but further development could have increased the seating capacity to six. The baselined launch vehicle was the Atlas V, but the design could have accommodated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnus (spacecraft)
Cygnus is an expendable American cargo spacecraft developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation and now manufactured and launched by Northrop Grumman Space Systems as part of NASA's Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program. It is launched by Northrop Grumman's Antares rocket or ULA's Atlas V and is designed to transport supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) following the retirement of the American Space Shuttle. Since August 2000, ISS resupply missions have been regularly flown by the Russian Progress spacecraft, as well as by the European Automated Transfer Vehicle, and the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle. With the Cygnus spacecraft and the SpaceX Dragon, NASA seeks to increase its partnerships with domestic commercial aviation and aeronautics industry. ''Cygnus'' is the Latinized Greek word for swan and a northern constellation. Development With Rocketplane Kistler unable to meet funding obligations for its K-1 launch vehicle under the terms of the COTS agreeme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryden Research Center
The NASA Neil A. Armstrong Flight Research Center (AFRC) is an aeronautical research center operated by NASA. Its primary campus is located inside Edwards Air Force Base in California and is considered NASA's premier site for aeronautical research. AFRC operates some of the most advanced aircraft in the world and is known for many aviation firsts, including critical support for the first crewed airplane to exceed the speed of sound in level flight with the Bell X-1, highest speed ever recorded by a crewed, powered aircraft (North American X-15), the first pure digital fly-by-wire aircraft (F-8 DFBW), and many others. AFRC also operates a second site in Palmdale, Ca. known as Building 703, once the former Rockwell International/North American Aviation production facility, next to Air Force Plant 42. There, AFRC houses and operates several of NASA's Science Mission Directorate aircraft including SOFIA (Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy), a DC-8 Flying Laboratory, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

