|
X-ray Pulsar
X-ray pulsars or accretion-powered pulsars are a class of astronomical objects that are X-ray sources displaying strict periodic variations in X-ray intensity. The X-ray periods range from as little as a fraction of a second to as much as several minutes. Characteristics An X-ray pulsar consists of a magnetized neutron star in orbit with a normal stellar companion and is a type of binary star system. The magnetic-field strength at the surface of the neutron star is typically about 108 Tesla, over a trillion times stronger than the strength of the magnetic field measured at the surface of the Earth (60 μT). Gas is accreted from the stellar companion and is channeled by the neutron star's magnetic field on to the magnetic poles producing two or more localized X-ray hot spots, similar to the two auroral zones on Earth, but far hotter. At these hotspots the infalling gas can reach half the speed of light before it impacts the neutron star surface. So much gravitational potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
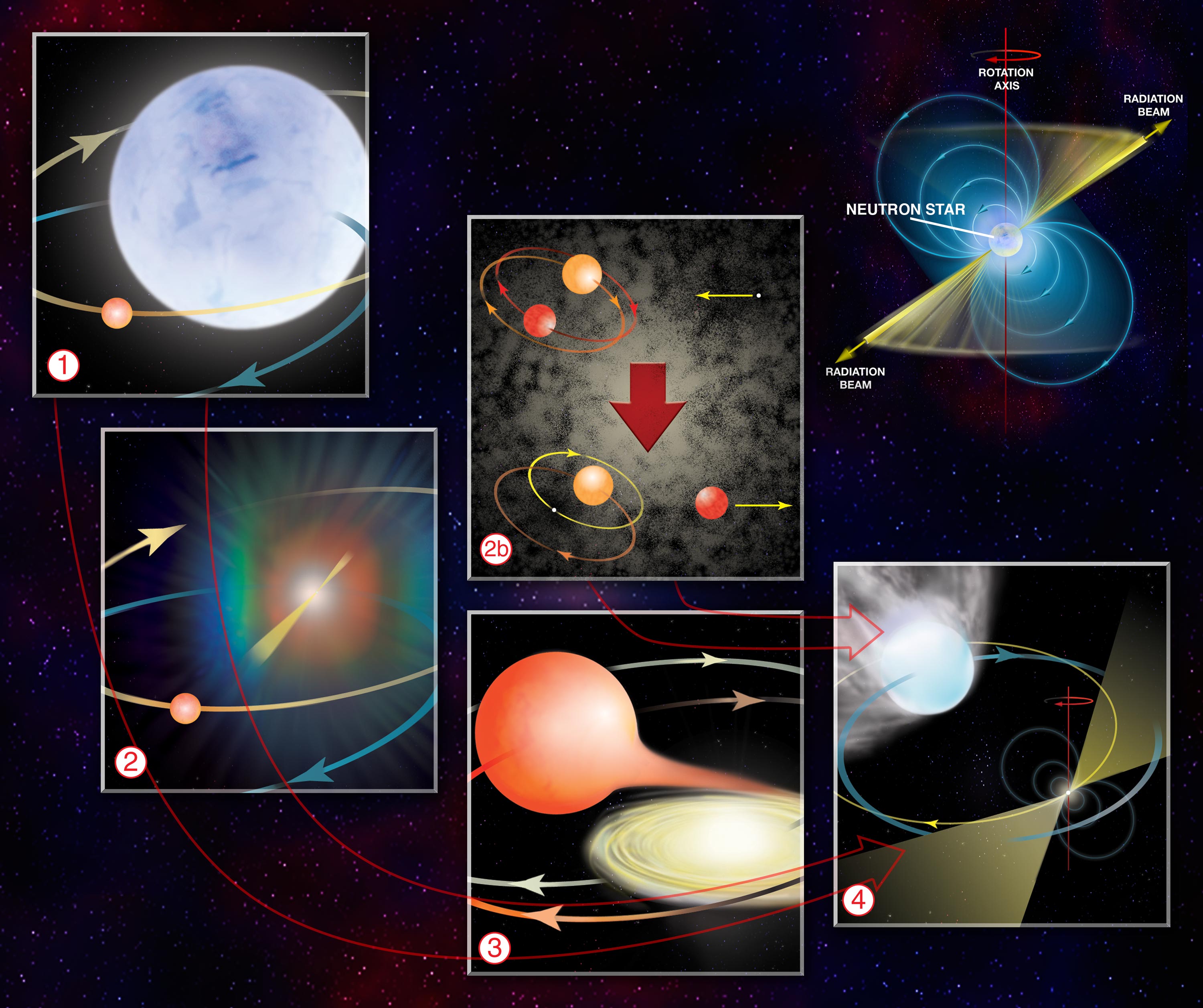
Radio Pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. (See also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration.) The periods of pulsars make them very useful tools for astronomers. Observations of a pulsar in a binary neutron star system were used to indirectly confirm the existence of gravitational radiation. The first extrasolar planets were discovered aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond Pulsar
A millisecond pulsar (MSP) is a pulsar with a rotational period less than about 10 milliseconds. Millisecond pulsars have been detected in radio, X-ray, and gamma ray portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The leading theory for the origin of millisecond pulsars is that they are old, rapidly rotating neutron stars that have been spun up or "recycled" through accretion of matter from a companion star in a close binary system. For this reason, millisecond pulsars are sometimes called recycled pulsars. Millisecond pulsars are thought to be related to low-mass X-ray binary systems. It is thought that the X-rays in these systems are emitted by the accretion disk of a neutron star produced by the outer layers of a companion star that has overflowed its Roche lobe. The transfer of angular momentum from this accretion event can theoretically increase the rotation rate of the pulsar to hundreds of times per second, as is observed in millisecond pulsars. There has been recent evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetar
A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (∼109 to 1011 T, ∼1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays and gamma rays.Ward; Brownlee, p.286 The existence of magnetars was proposed in 1992 by Robert Duncan and . Their proposal sought to explain the properties of transient sources of gamma rays, now known as soft gamma repeaters (SGRs). Over the following decade, the magnetar hypothesis became widely accepted, and was extended to explain anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs). , 24 confirmed magnetars were known. It has been suggested that magnetars are the source of fast radio bursts (FRB), in particular as a result of findings in 2020 by scientists using the Australian Square Kilometre Array. Description Like other neutron stars, magnetars are around in diameter, and have a mass about 1.4 solar masses. They are formed by the collapse of a star with a mass 10– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous X-ray Pulsar
Anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) are an observational manifestation of magnetars—young, isolated, highly magnetized neutron stars. These energetic X-ray pulsars are characterized by slow rotation periods of ~2–12 seconds and large magnetic fields of ~1013–1015 gauss (1 to 100 gigateslas). , there were 12 confirmed and 2 candidate AXPs known. (An online catalog of SGR/AXP properties maintained by the pulsar group at McGill University) The identification of AXPs with magnetars was motivated by their similarity to soft gamma repeater
A soft gamma repeater (SGR) is an astronomical object which emits large bursts of gamma-rays and X-rays at irregular inter ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. (See also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration.) The periods of pulsars make them very useful tools for astronomers. Observations of a pulsar in a binary neutron star system were used to indirectly confirm the existence of gravitational radiation. The first extrasolar planets were discovered aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uhuru (satellite)
Uhuru was the first satellite launched specifically for the purpose of X-ray astronomy. It was also known as the X-ray Explorer Satellite, SAS-A (for Small Astronomy Satellite A, being first of the three-spacecraft SAS series), SAS 1, or Explorer 42. The space observatory, observatory was launched on December 12, 1970 into an initial orbit of about 560 km apogee, 520 km perigee, 3 degrees inclination, with a period of 96 minutes. The mission ended in March 1973. Uhuru was a scanning mission, with a spin period of ~12 minutes. It performed the first comprehensive survey of the entire sky for X-ray sources, with a sensitivity of about 0.001 times the intensity of the Crab nebula. Objectives The main objectives of the mission were: * To survey the sky for cosmic X-ray sources in the 2–20 keV range to a limiting sensitivity of 1.5 × 10−18 joule/(cm2-sec), 5 × 10−4 the flux from the Crab Nebula * To determine discrete source locations with a precision of a few square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaurus X-3
Centaurus X-3 (4U 1118-60) is an X-ray pulsar with a period of 4.84 seconds. It was the first X-ray pulsar to be discovered, and the third X-ray source to be discovered in the constellation Centaurus. The system consists of a neutron star orbiting a massive, O-type supergiant star dubbed Krzeminski's star after its discoverer, Wojciech Krzemiński. Matter is being accreted from the star onto the neutron star, resulting in X-ray emission. History Centaurus X-3 was first observed during experiments of cosmic X-ray sources made on May 18, 1967. These initial X-ray spectrum and location measurements were performed using a sounding rocket. In 1971, further observations were performed with the Uhuru satellite, in the form of twenty-seven 100-second duration sightings. These sightings were found to pulsate with an average period of 4.84 seconds, with a variation in the period of 0.02 seconds. Later, it became clear that the period variations followed a 2.09 day sinusoidal cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |