|
Wuzhi (Qi)
Wuzhi (; died 685 BC), also called Gongsun Wuzhi (公孫無知, ''Gongsun'' meaning grandson of a duke), was for a few months in early 685 BC ruler of the State of Qi during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Wuzhi (呂無知), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜). Unlike most rulers, he was not given a posthumous title because he killed the monarch and usurped the throne. Early life Wuzhi's father Yi Zhongnian was a son of Duke Zhuang I of Qi and younger brother of Duke Xi of Qi. Yi Zhongnian died in 699 BC, but Wuzhi's uncle Duke Xi loved him and gave him the same treatment as his son, Crown Prince Zhu'er. However, the next year Duke Xi died and Zhu'er, Wuzhi's cousin, ascended the throne (posthumously known as Duke Xiang of Qi). Duke Xiang disliked Wuzhi and demoted his status. Murdering Duke Xiang In the twelfth month of 686 BC, the twelfth year of his reign, Duke Xiang injured his foot on a hunting trip. When the duke was recovering in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a state of the Zhou dynasty-era in ancient China, variously reckoned as a march, duchy, and independent kingdom. Its capital was Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou overthrow of Shang in the 11th centuryBC. Its first marquis was Jiang Ziya, minister of King Wen and a legendary figure in Chinese culture. His family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was replaced by the Tian family in 386BC. In 221BC, Qi was the final major state annexed by Qin during its unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou conquest of Shang, Jiang Ziya, a native of Ju County served as the chief minister to King Wu. After King Wu's death, Ziya remained loyal to the Duke of Zhou during the Three Guards' failed rebellion against his regency. The Shang prince Wu Geng had joined the revolt along with the Dongyi states of Yan, Xu, and Pugu. These were suppressed by 1039 BC and Jiang w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Xi Of Qi
Duke Xi of Qi (; died 698 BC) was from 730 to 698 BC the thirteenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Lufu (呂祿甫), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Xi was his posthumous title. Reign Duke Xi succeeded his father Duke Zhuang I of Qi, who died in 731 BC after a reign of 64 years, as ruler of Qi. In 706 BC, Qi was attacked by the Northern Rong tribes (also called Mountain Rong). Duke Zhuang of the State of Zheng sent Crown Prince Hu (later Duke Zhao of Zheng) to help Qi repel the Northern Rong. Succession Duke Xi reigned for 33 years and died in 698 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Duke Xiang of Qi, who would later be murdered by Duke Xi's nephew Wuzhi. Wuzhi himself was also killed soon afterward, and Duke Xi's younger son Xiaobai ascended the throne, posthumously known as Duke Huan of Qi. Qi grew strong under Duke Huan's rule and he became the first of the Five Hegemons of the Spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
685 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 685 ( DCLXXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 685 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * September – Emperor Constantine IV dies of dysentery at Constantinople after a 17-year reign, and is succeeded by his 16-year-old son Justinian II. Europe * Kuber, brother of Asparukh of Bulgaria, defeats the Avars in Syrmia (Pannonia). He leads his followers of around 70,000 people to Macedonia (modern North Macedonia). Britain * May 20 – Battle of Dun Nechtain: The Picts under King Bridei III revolt against their Northumbrian overlords. Cuthbert, bishop of Lindisfarne, advises King Ecgfrith of Northumbria (Bridei's cousin) not to invade Pictland (modern Scotland). Undeterred, Ecgfrith marches his army north to engage the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century BC Chinese Monarchs
The 7th century is the period from 601 (DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Qi (state)
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Wen Of Qi
Duke Wen of Qi (; died 804 BC) was from 815 to 804 BC the tenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Chi (呂赤), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Wen was his posthumous title. Duke Wen's father Duke Li of Qi was a despotic ruler, and in 816 BC the people of Qi rebelled and tried to make the son of Duke Hu of Qi, Duke Li's grand-uncle, the new ruler. Duke Li was killed by the rebels, but Duke Hu's son also died in the fighting. Subsequently, Duke Wen ascended the throne, and executed 70 people who were responsible for his father's death. Duke Wen reigned for 12 years and died in 804 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Duke Cheng of Qi. Family Sons: * Prince Tuo (; d. 795 BC), ruled as Duke Cheng of Qi from 803–795 BC * Prince Gao (), the grandfather of Gao Xi (), who was the progenitor of the Gao lineage Daughters: * Qi Jiang () ** Married Marquis Mu of Jin (d. 785 BC) in 808 BC, and had issue (Marqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Cheng Of Qi
Duke Cheng of Qi (; died 795 BC) was from 803 to 795 BC the eleventh recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Yue (呂說), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Cheng was his posthumous title. Duke Cheng succeeded his father Duke Wen of Qi, who died in 804 BC, as ruler of Qi. He reigned for 9 years and died in 795 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Duke Zhuang I of Qi. Family Sons: * Prince Gou (; d. 731 BC), ruled as Duke Zhuang I of Qi Duke Zhuang I of Qi (; died 731 BC) was from 794 to 731 BC the twelfth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Gou (呂購), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Zhuang was his posth ... from 794–731 BC Ancestry References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cheng of Qi, Duke Year of birth unknown Monarchs of Qi (state) 9th-century BC Chinese monarchs 8th-century BC Chinese monarchs 795 BC deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
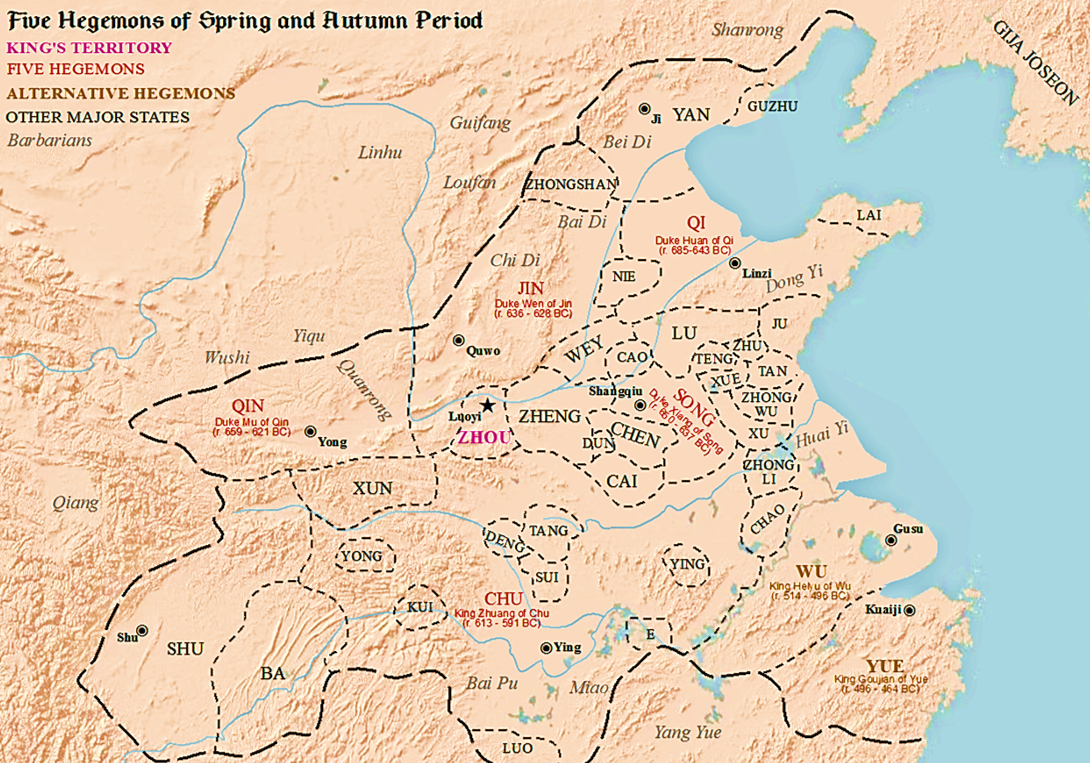
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Zhuang I Of Qi
Duke Zhuang I of Qi (; died 731 BC) was from 794 to 731 BC the twelfth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Gou (呂購), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Zhuang was his posthumous title. He was the first of the two Qi rulers called Duke Zhuang. Reign Duke Zhuang succeeded his father Duke Cheng of Qi, who died in 795 BC, as ruler of Qi. He had a long reign during an era of upheaval in China. In 771 BC, the Quanrong tribes from the west attacked Haojing, capital of the Zhou dynasty, and killed King You of Zhou. Duke Xiang of the state of Qin sent his army to escort King You's son King Ping of Zhou to the new capital Luoyi, marking the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty. As a reward for Qin's protection King Ping formally granted Duke Xiang of Qin a nobility rank and elevated Qin to the status of a vassal state on par with other major states such as Qi and Jin. Although Qi was little affected by the turmoil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Xiang Of Qi
Duke Xiang of Qi (; died 686 BC) was from 697 to 686 BC the fourteenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi, a major power during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Zhu'er (呂諸兒), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Xiang was his posthumous title. Although under Duke Xiang the state of Qi conquered the neighbouring state of Ji, its traditional enemy, Duke Xiang is best known for his depravity, having had an incestuous relationship with his sister Wen Jiang and murdered his brother-in-law Duke Huan of Lu. At the end Duke Xiang was himself murdered by his cousin Wuzhi, who subsequently usurped the Qi throne. Murdering Duke Huan of Lu Duke Xiang succeeded his father Duke Xi of Qi, who died in 698 BC after 33 years of reign. Duke Xiang had had an incestuous relationship with his younger half-sister Wen Jiang, who in 709 BC married Duke Huan, ruler of the neighbouring State of Lu. In 694 BC, Duke Huan of Lu visited Qi with his wife, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)