|
World Altitude Record (mountaineering)
In the history of mountaineering, the world altitude record referred to the highest point on the Earth's surface which had been reached, regardless of whether that point was an actual summit. The world summit record referred to the highest mountain to have been successfully climbed. The terms are most commonly used in relation to the history of mountaineering in the Himalaya and Karakoram ranges, though modern evidence suggests that it was not until the 20th century that mountaineers in the Himalaya exceeded the heights which had been reached in the Andes. The altitude and summit records rose steadily during the early 20th century until 1953, when the ascent of Mount Everest made the concept obsolete. 19th century and before European exploration of the Himalaya began in earnest during the mid-19th century, and the earliest people known to have climbed in the range were surveyors of the Great Trigonometric Survey (GTS). During the 1850s and 1860s they climbed dozens of peaks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountaineering
Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, and bouldering are also considered variants of mountaineering by some. Unlike most sports, mountaineering lacks widely applied formal rules, regulations, and governance; mountaineers adhere to a large variety of techniques and philosophies when climbing mountains. Numerous local alpine clubs support mountaineers by hosting resources and social activities. A federation of alpine clubs, the International Climbing and Mountaineering Federation (UIAA), is the International Olympic Committee-recognized world organization for mountaineering and climbing. The consequences of mountaineering on the natural environment can be seen in terms of individual components of the environment (land relief, soil, vegetation, fauna, and landscape) and location/z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''huanaco'' (modern spelling ''wanaku''). Young guanacos are called ''chulengos''. Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
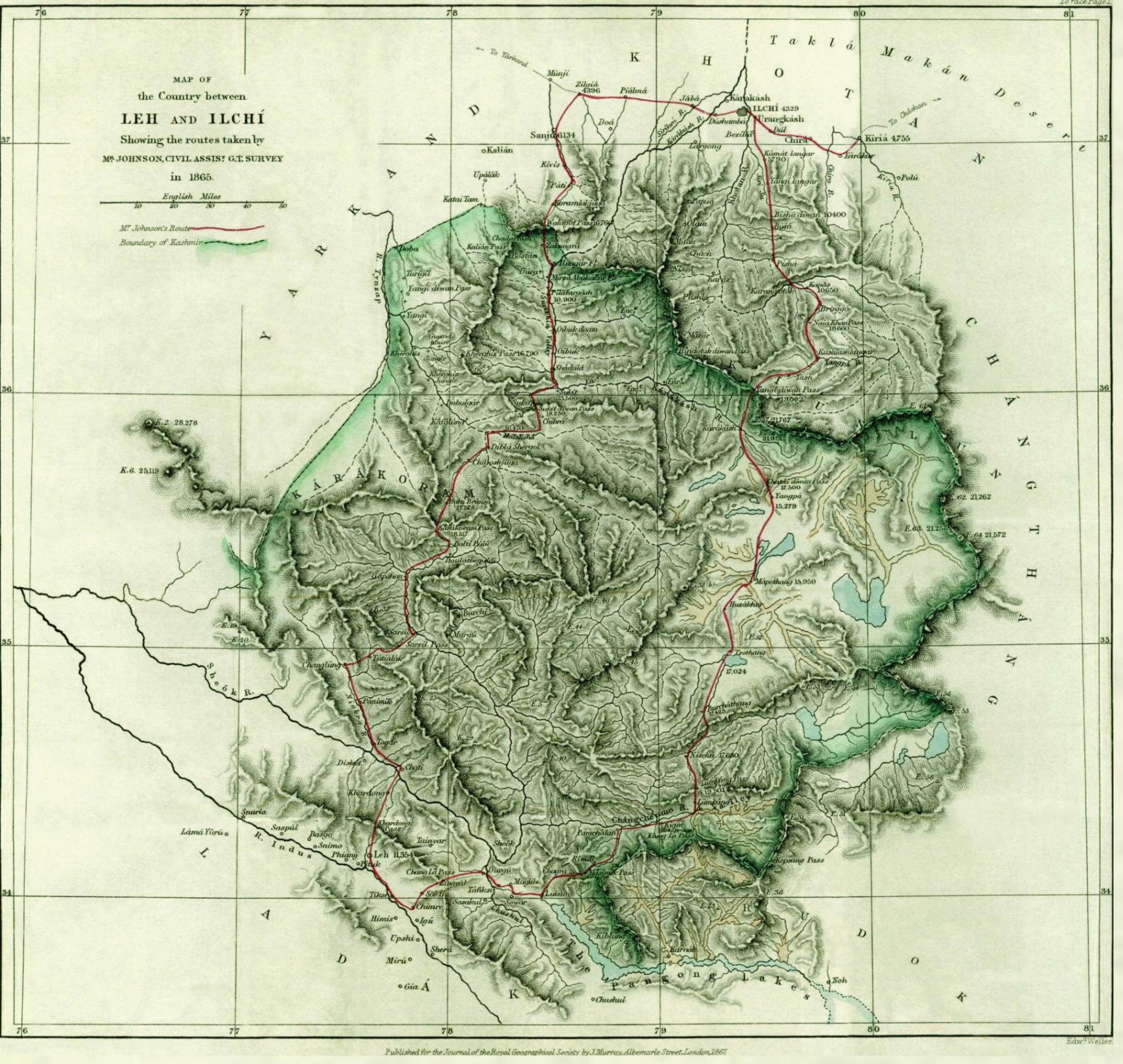
William Johnson (surveyor)
William H. Johnson (died 3 March 1883) was a British surveyor in the Great Trigonometric Survey of India. He is noted for the first definition of the eastern boundary of Ladakh along Aksai Chin in the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, which has come to be called the ' Johnson Line'. After retiring from the Survey of India, Johnson was appointed as the Governor of Ladakh, in which position he served until his death. Early life Johnson was born in India to an Ordinance officer of the East India Company, who lived in "Deyrah". He was educated at Mussorie and joined the Civil Branch of the Great Trigonometric Survey (the precursor of the Survey of India), where he was trained by Andrew Scott Waugh. Career Johnson began his career as a surveyor in 1848 under Captain du Vernet in the North-West Himalayan Survey. After du Vernet moved to Assam in 1852, he worked for some time doing route surveys in Punjab, then the survey of the Chenab River, and the survey of Bhagirathi and Kanawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as , meaning 'Land of Gods' and which means 'Land of the Brave'. The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times, having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas. Through its history, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilla (mountain)
Shilla is a mountain peak close to Spiti Valley, part of the Himalaya mountains. Its peak is above sea level. It is in Himachal Pradesh in Northern India North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central .... The name may be derived from: Shi = death, Shi-la = range or peak death. Other meanings locally offered are 'a place of monastery' or 'a gateway to heaven’. The Shilla peak is on the divide between Lingti and Shilla Nullah/nala. Climbing history Notes References Bibliography * {{Authority control Mountains of Himachal Pradesh Geography of Lahaul and Spiti district Six-thousanders of the Himalayas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Smythe
Francis Sydney Smythe, better known as Frank Smythe or F. S. Smythe (6 July 1900 – 27 June 1949), was an English mountaineer, author, photographer and botanist. He is best remembered for his mountaineering in the Alps as well as in the Himalayas, where he identified a region that he named the "Valley of Flowers", now a protected park. His ascents include two new routes on the Brenva Face of Mont Blanc, Kamet, and attempts on Kangchenjunga and Mount Everest in the 1930s. It was said that he had a tendency for irascibility, something some of his mountaineering contemporaries said "decreased with altitude". Biography Smythe was born at Maidstone in Kent and educated in Switzerland after an initial period at Berkhamsted School. He trained as an electrical engineer and worked for brief periods with the Royal Air Force and Kodak before devoting himself to writing and public lecturing. Smythe enjoyed mountaineering, photography, collecting plants, and gardening; he toured as a lec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abi Gamin
Abi Gamin (also known as Ibi Gamin) is a Himalayan mountain peak mostly situated in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand state in India, northeast of Kamet. Its summit is on the border with Tibet and its northern slope is in the Ngari Prefecture of Tibet. Abi Gamin is located in the central Himalayas and at the culminating point of the Zaskar Range. It is situated on the watershed of the upper Alaknanda and Dhauli rivers between the famous Manna and Niti passes on the Indo-Tibetan border. Abi Gamin is the second highest peak in the immediate region, after Kamet. It is also one of the fifteen seven thousand metre peaks of Uttarakhand, and as such it is a significant peak. However it is not particularly independent, lying as it does close to the higher peak of Kamet, and separated from it by the high saddle known as Meade's Col, . Abi Gamin was surveyed (along with the rest of the group) by Richard Strachey in 1848; this was the first time that the great heights of these peaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai regions. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north; the Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal to the east; the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh to the south and Himachal Pradesh to the west and north-west. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital of Uttarakhand is Dehradun, the largest city of the state, which is a rail head. Bhararisain, a town in Chamoli district, is the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital. Archaeological evidence supports the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garhwal Division
Garhwal (IPA: /ɡəɽʋːɔɭ/) is one of the two administrative divisions of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Lying in the Himalayas The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ..., it is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Kumaon division, Kumaon, on the south by Uttar Pradesh state, and on the northwest by Himachal Pradesh state. It includes the districts of Chamoli District, Chamoli, Dehradun District, Dehradun, Haridwar District, Haridwar, Pauri Garhwal, Rudraprayag District, Rudraprayag, Tehri Garhwal District, Tehri Garhwal, and Uttarkashi District, Uttarkashi. The people of Garhwal are known as Garhwali people, Garhwali and speak the Garhwali language. The administrative center for Garhwal division is the town of Pauri. The Divisional Commissioner is the admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamet
Kamet ( hi, कामेत) is the second highest mountain in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, India, after Nanda Devi. It lies in the Chamoli District of Uttarakhand. Its appearance resembles a giant pyramid topped by a flat summit area with two peaks. Climbing Due to its position near the Tibetan Plateau, Kamet is very remote and not as accessible as some Himalayan peaks. It also receives a great deal of wind from the Plateau. However, by modern standards, it is a relatively straightforward ascent for such a high mountain. Early explorers of the region faced long approach marches of around from Ranikhet through dense mountain forest; access is easier today. While attempts to climb Kamet began in 1855, the first ascent was not made until 1931 by Frank Smythe, Eric Shipton, R.L. Holdsworth, Dr Raymond Greene, the expedition's doctor, Bill Birnie and Lewa Sherpa, members of a British expedition. Kamet was the first summit over to be climbed, and was the highest summit r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Schlagintweit
Robert Schlagintweit (24 October 1833 – 6 June 1885) was a German explorer of Central Asia who also wrote about travels in America. Brothers Hermann, Adolf and Robert Schlagintweit were commissioned by the British East India Company to study the earth's magnetic field in South and Central Asia. They were the first Europeans to cross the Kunlun mountains and the first to explore the region between Karakoram and Kunlun. Life The fourth of the five Schlagintweit brothers of Munich joined his brothers Hermann and Adolf at an early age in their Alpine researches and jointly published ''Neue Untersuchungen über die physikalische Geographie und Geologie der Alpen'' in 1854. In 1854, acting on the recommendation of Alexander von Humboldt, the East India Company commissioned Hermann, Adolf, and Robert to make scientific investigations in their territory and particularly to study the Earth's magnetic field. For the next three years they travelled through the Deccan, then up into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Schlagintweit
Adolf von Schlagintweit (9 January 1829 – 26 August 1857) was a German botanist and explorer of Central Asia. Brothers Hermann, Adolf and Robert Schlagintweit were commissioned by the British East India Company to study the earth's magnetic field in South and Central Asia. They were the first Europeans to cross the Kunlun mountains and the first to explore the region between Karakoram and Kunlun. After their joint exploration, Adolf Schlagintweit made a separate expedition of his own, crossing the present day disputed Aksai Chin region for the first time. Mistaken for a Chinese spy, he was executed in Kashgar. Life The second of five brothers in Munich, Adolf, with his brother Hermann, published a scientific study of the Alps in 1846–1848. They established their reputation with the ''Untersuchungen über die physikalische Geographie der Alpen'' (1850), and were afterwards joined by their brother Robert; the three jointly published ''Neue Untersuchungen über die physikali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






Schlegel_Julius_btv1b84503133_(cropped).jpg)