Adolf Schlagintweit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Adolf von Schlagintweit (9 January 1829 – 26 August 1857) was a German
Adolf von Schlagintweit (9 January 1829 – 26 August 1857) was a German
 The second of five
The second of five
 Adolf von Schlagintweit (9 January 1829 – 26 August 1857) was a German
Adolf von Schlagintweit (9 January 1829 – 26 August 1857) was a German botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek wo ...
and explorer
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. Brothers Hermann, Adolf and Robert Schlagintweit
Robert Schlagintweit (24 October 1833 – 6 June 1885) was a German explorer of Central Asia who also wrote about travels in America. Brothers Hermann, Adolf and Robert Schlagintweit were commissioned by the British East India Company to stud ...
were commissioned by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
to study the earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
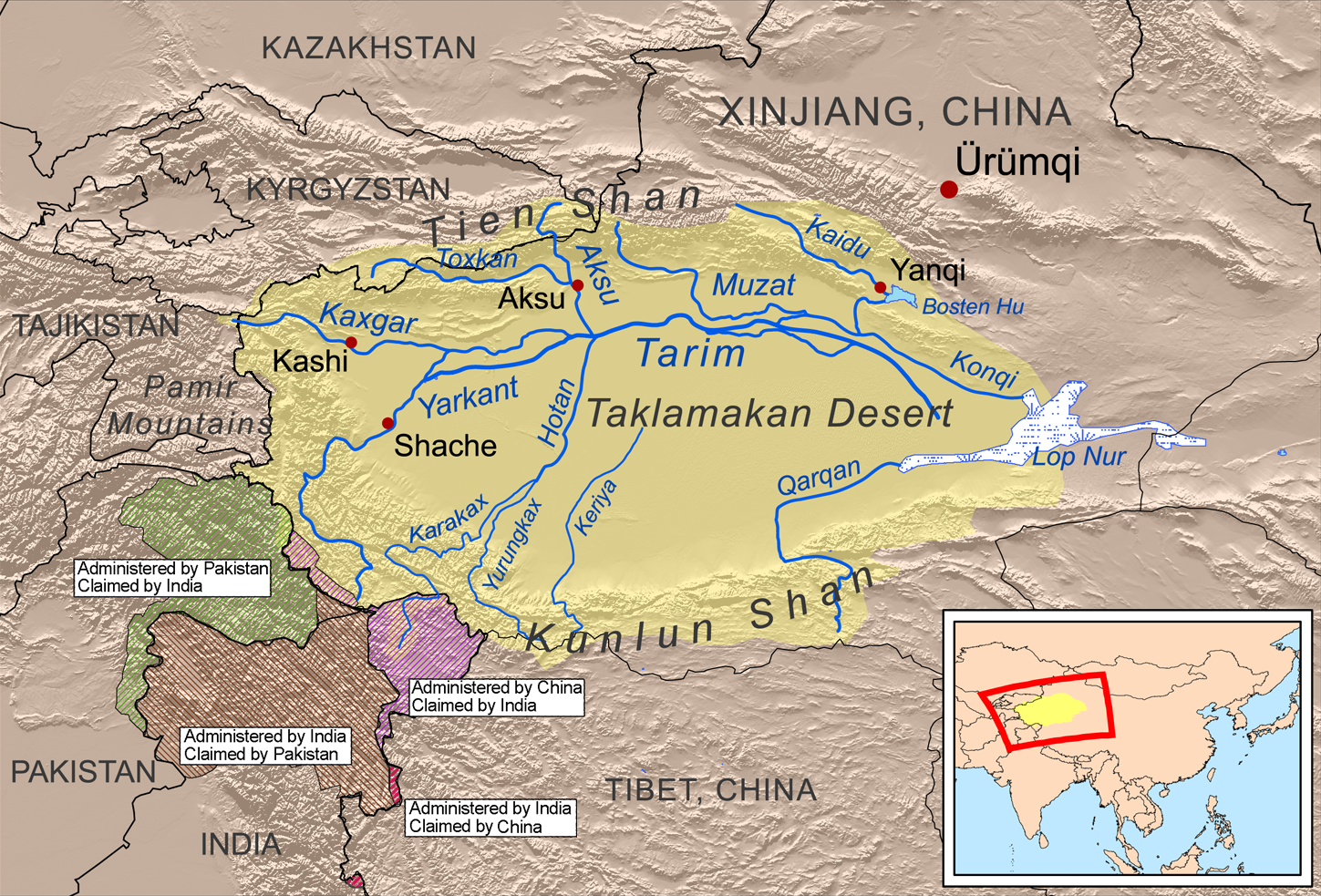
in South and Central Asia. They were the first Europeans to cross the Kunlun mountains
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
and the first to explore the region between Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
and Kunlun. After their joint exploration, Adolf Schlagintweit made a separate expedition of his own, crossing the present day disputed Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is a region administered by China as part of Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang and Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. It is claimed by India to be a part of its Leh District, Ladakh Union Territory. It is a part of the ...
region for the first time. Mistaken for a Chinese spy, he was executed in Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
.
Life

 The second of five
The second of five brothers
A brother is a man or boy who shares one or more parents with another; a male sibling. The female counterpart is a sister. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to non-familia ...
in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the States of Germany, German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the List of cities in Germany by popu ...
, Adolf, with his brother Hermann, published a scientific study of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
in 1846–1848. They established their reputation with the ''Untersuchungen über die physikalische Geographie der Alpen'' (1850), and were afterwards joined by their brother Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
; the three jointly published ''Neue Untersuchungen über die physikalische Geographie und Geologie der Alpen'' in 1854.
In 1854, acting on the recommendation of Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
, the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
commissioned Hermann, Adolf, and Robert to make scientific investigations in their territory and particularly to study the Earth's magnetic field. For the next three years, they travelled through the Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in South India, southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bou ...
, then up into the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
, Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
, and Kunlun mountains
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
.
While Hermann and Robert returned from their travels in early 1857, Adolf went back for further exploration on his own. He followed a new, heretofore unknown road via the Chang Chenmo Valley
Chang Chenmo River or Changchenmo River is a tributary of the Shyok River, part of the Indus River system. It is at the southern edge of the disputed Aksai Chin region and north of the Pangong Lake basin.
The source of Chang Chenmo is near th ...
, Lingzi Tang Plains
(), also called (), refers to a traditional Chinese ornament which uses long pheasant tail feather appendages to decorate some headdress in , Chinese opera costumes. In Chinese opera, the not only decorative purpose but are also used express ...
and the Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is a region administered by China as part of Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang and Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. It is claimed by India to be a part of its Leh District, Ladakh Union Territory. It is a part of the ...
. He gave the name "Great Aksai Chin" to this region, and followed the Karakash River
The Karakash or Black Jade River, also spelled ''Karakax'' (, , Қарақаш Дәряси), is a river in the Xinjiang autonomous region of the People's Republic of China that originates in the disputed Aksai Chin region administered by China. It ...
valley to Turkestan.
Suspected of being a Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
spy, and without benefit of a trial, he was beheaded
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the ...
in Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
by Wali Khan, the emir of Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
in August. The circumstances of his death were not known in Europe until 1859, when Chokan Valikhanov
Shokan Shyngysuly Valikhanov ( kk, Шоқан Шыңғысұлы Уәлихан, russian: Чокан Чингисович Валиханов), given name Mukhammed Kanafiya ( kk, Мұхаммед Қанафия)Shoqan, his pen-name, later becam ...
visited Kashgar disguised as a merchant and successfully returned to the Russian Empire with the scientist's head.
The return of his head provided a plot element in Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's famous story "The Man Who Would Be King
"The Man Who Would Be King" (1888) is a story by Rudyard Kipling about two British adventurers in British India who become kings of Kafiristan, a remote part of Afghanistan. The story was first published in '' The Phantom Rickshaw and other Ee ...
" (1888). In 2017 Lahore Museum Pakistan found 50 masks that Schlangintweits brothers made during their Indian research visit in 1854-58. These ethnographic masks of various Indian communities shed light on Indian ethnic diversity.
Standard author abbreviation
Botanical collections
Botanical specimens collected by the Schlagintweit brothers are held at several herbaria around the world, including the Philadelphia Herbarium at the Academy of Natural Sciences (PH) andNational Herbarium of Victoria
The National Herbarium of Victoria ( Index Herbariorum code: MEL) is one of Australia's earliest herbaria and the oldest scientific institution in Victoria. Its 1.5 million specimens of preserved plants, fungi and algae—collectively known a ...
at the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria
Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria are botanical garden, botanic gardens across two sites–Royal Botanic Gardens, Melbourne, Melbourne and Royal Botanic Gardens, Cranbourne, Cranbourne.
Melbourne Gardens was founded in 1846 when land was rese ...
.
In 1853, botanist Griseb.
August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach () was a German botany, botanist and phytogeography, phytogeographer. He was born in Hannover on 17 April 1814 and died in Göttingen on 9 May 1879.
Biography
Grisebach studied at the Lyceum in Hanover, the clo ...
published '' Schlagintweitia'', a genus of flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s from Europe, belonging to the family Asteraceae
The family Asteraceae, alternatively Compositae, consists of over 32,000 known species of flowering plants in over 1,900 genera within the order Asterales. Commonly referred to as the aster, daisy, composite, or sunflower family, Compositae w ...
, with its name honouring Adolf Schlagintweit and his brothers Herman and Robert.
References
;AttributionFurther reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Schlagintweit, Adolf German explorers Explorers of Central Asia 19th-century German botanists 19th-century executions 1829 births 1857 deaths German people executed abroad Scientists from Munich Executed people from Bavaria