|
Woods–Saxon Potential
The Woods–Saxon potential is a mean field potential for the nucleons ( protons and neutrons) inside the atomic nucleus, which is used to describe approximately the forces applied on each nucleon, in the nuclear shell model for the structure of the nucleus. The potential is named after Roger D. Woods and David S. Saxon. The form of the potential, in terms of the distance ''r'' from the center of nucleus, is: V(r) = -\frac where ''V''0 (having dimension of energy) represents the potential well depth, ''a'' is a length representing the "surface thickness" of the nucleus, and R = r_0 A^ is the nuclear radius where and ''A'' is the mass number. Typical values for the parameters are: , . For large atomic number ''A'' this potential is similar to a potential well. It has the following desired properties * It is monotonically increasing with distance, i.e. attracting. * For large ''A'', it is approximately flat in the center. * Nucleons near the surface of the nucleus (i.e. havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woods Saxon Potential2
Woods or The Woods may refer to: Common meanings * Woodland * Forest * Wood, solid material from trees or shrubs Places United States * Woods, Kentucky * Woods, Oregon * Woods, a municipality in Liberty County, Florida * The Woods, a neighborhood in Shenandoah, Louisiana Elsewhere * Woods, Ontario, an area of Carling, Ontario, Canada * Woods, South Australia, an area of Owen * The Woods, a locality in Sandwell, England Culture Film * ''The Woods'' (2006 film), a film directed by Lucky McKee * ''The Woods'' (2011 film), a film directed by Matthew Lessner * ''The Woods'', a false working title used for the 2016 film ''Blair Witch'' (film) Music * ''The Woods'' (album), 2005 album by Sleater-Kinney * Woods (band) Woods is an American folk rock band from Brooklyn, New York, formed in 2005. The band consists of Jeremy Earl (vocals, guitar), Jarvis Taveniere (various instruments, production), Aaron Neveu (drums), Chuck Van Dyck (bass), and Kyle Forester (k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields. This includes nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, ''Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publication in 1913 and star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
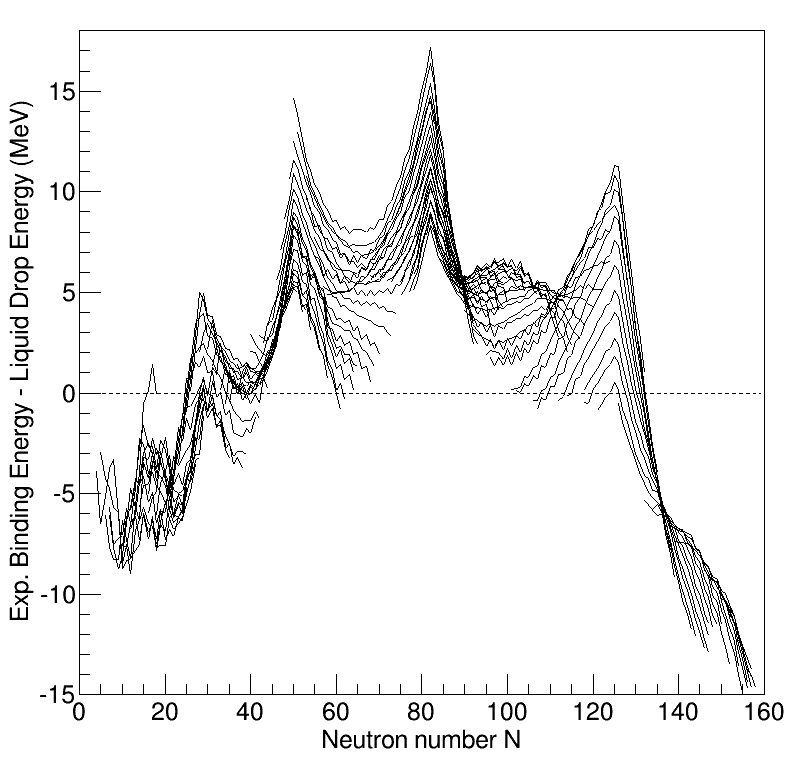
Nuclear Shell Model
In nuclear physics, atomic physics, and nuclear chemistry, the nuclear shell model is a model of the atomic nucleus which uses the Pauli exclusion principle to describe the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels. The first shell model was proposed by Dmitri Ivanenko (together with E. Gapon) in 1932. The model was developed in 1949 following independent work by several physicists, most notably Eugene Paul Wigner, Maria Goeppert Mayer and J. Hans D. Jensen, who shared the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics for their contributions. The nuclear shell model is partly analogous to the atomic shell model, which describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom in that filled shell results in better stability. When adding nucleons (protons or neutrons) to a nucleus, there are certain points where the binding energy of the next nucleon is significantly less than the last one. This observation that there are specific magic quantum numbers of nucleons (2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126) wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Structure
Understanding the structure of the atomic nucleus is one of the central challenges in nuclear physics. Models The liquid drop model The liquid drop model is one of the first models of nuclear structure, proposed by Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker in 1935. It describes the nucleus as a semiclassical fluid made up of neutrons and protons, with an internal repulsive electrostatic force proportional to the number of protons. The quantum mechanical nature of these particles appears via the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two nucleons of the same kind can be at the same state. Thus the fluid is actually what is known as a Fermi liquid. In this model, the binding energy of a nucleus with Z protons and N neutrons is given by :E_ = a_ A - a_ A^ - a_ \frac - a_ \frac - \delta(A,Z) where A=Z+N is the total number of nucleons (Mass Number). The terms proportional to A and A^ represent the volume and surface energy of the liquid drop, the term proportional to Z^ represents t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |