|
Wolfring's Glands
Ciaccio's glands or Wolfring's glands are small tubular accessory lacrimal glands (''glandulae lacrimales accessoriae'') found in the lacrimal caruncle of the eyelid. These accessory lacrimal glands are located in the upper border of the tarsus, approximately in the middle between the extremities of the tarsal glands. Sometimes they are situated slightly above the tarsus. There are usually 2 to 5 of these glands in the upper eyelid, and their function is to produce tears which are secreted onto the surface of the conjunctiva. They are named after Italian anatomist Giuseppe Vincenzo Ciaccio (1824–1901), who described these glands in 1874. They are sometimes called "Wolfring's glands" after Polish ophthalmologist Emilj von Wolfring (1832-1906), who described them during the same time period as did Ciaccio. Another type of accessory lacrimal gland are "Krause's glands Krause's glands or Krause glands are small, mucous accessory lacrimal glands that are found underneath the eyeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Lacrimal Glands
Krause's glands, Wolfring's glands (or Ciaccio's glands) and Popov's gland are the accessory lacrimal glands of the lacrimal system of human eye. These glands are structurally and histologically similar to the main lacrimal gland. Glands of Krause are located in the stroma of the conjunctival fornix, and the glands of Wolfring are located along the orbital border of the tarsal plate. These glands are oval and display numerous acini. The acini are surrounded, sometimes incompletely, by a row of myoepithelial cells. Animal studies suggest that the ducts of Wolfring glands have a tortuous course and open onto the palpebral conjunctiva. Like the main lacrimal gland, the accessory lacrimal glands are also densely innervated, but they lack parasympathetic innervation. These glands are exocrine glands, responsible for the basal (unstimulated) secretion of the middle aqueous layer of the tear film. 20 to 40 glands of Krause are found in the upper fornix, and 6-8 glands appear in the lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Caruncle
The lacrimal caruncle, or caruncula lacrimalis, is the small, pink, globular nodule at the inner corner (the medial canthus) of the eye. It consists of tissue types of neighbouring eye structures. It may suffer from lesions and allergic inflammation. Structure The lacrimal caruncle is found at the medial canthus of the eye. It consists of skin, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, accessory lacrimal tissue and other tissues that are present in the skin and accessory lacrimal glands. Its non-keratinized epithelium resembles the conjunctival epithelium. Clinical significance Lesions The lacrimal caruncle may have a lesion. This can have any one of a number of causes, which may be difficult to diagnose. Cancer is a rare cause. These lesions include papillomas and oncocytomas. Allergies With ocular allergies, the lacrimal caruncle and the plica semilunaris of the conjunctiva may be inflamed and pruritic (itchy) due to histamine Histamine is an organic nitroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyelid features a row of eyelashes along the eyelid margin, which serve to heighten the protection of the eye from dust and foreign debris, as well as from perspiration. "Palpebral" (and "blepharal") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies. The appearance of the human upper eyelid often varies between different populations. The prevalence of an epicanthic fold covering the inner corner of the eye account for the majority of East Asian and Southeast Asian populations, and is also found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose. Anatomists divide the gland into two sections, a palpebral lobe, or portion, and an orbital lobe or portion. The smaller ''palpebral lobe'' lies close to the eye, along the inner surface of the eyelid; if the upper eyelid is everted, the palpebral portion can be seen. The orbital lobe of the gland, contains fine interlobular ducts that connect the orbital lobe and the palpebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (eyelids)
The tarsi (tarsal plates) are two comparatively thick, elongated plates of dense connective tissue, about in length for the upper eyelid and 5 mm for the lower eyelid; one is found in each eyelid, and contributes to its form and support. They are located directly above the lid margins. The tarsus has a lower and upper part making up the palpebrae. Superior The ''superior tarsus'' (''tarsus superior''; superior tarsal plate), the larger, is of a semilunar form, about in breadth at the center, and gradually narrowing toward its extremities. It is adjoined by the superior tarsal muscle. To the anterior surface of this plate the aponeurosis of the levator palpebræ superioris is attached. Inferior The ''inferior tarsus'' (''tarsus inferior''; inferior tarsal plate) is smaller, is thin, is elliptical in form, and has a vertical diameter of about . The free or ciliary margins of these plates are thick and straight. Relations The attached or orbital margins are connected to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsal Glands
Meibomian glands (also called tarsal glands, palpebral glands, and tarsoconjunctival glands) are sebaceous glands along the rims of the eyelid inside the tarsal plate. They produce meibum, an oily substance that prevents evaporation of the eye's tear film. Meibum prevents tears from spilling onto the cheek, traps them between the oiled edge and the eyeball, and makes the closed lids airtight. There are about 25 such glands on the upper eyelid, and 20 on the lower eyelid. Dysfunctional meibomian glands is believed to be the most often cause of dry eyes. They are also the cause of posterior blepharitis. History The glands were mentioned by Galen in 200 AD and were described in more detail by Heinrich Meibom (1638–1700), a German physician, in his work ''De Vasis Palpebrarum Novis Epistola'' in 1666. This work included a drawing with the basic characteristics of the glands. Anatomy Although the upper lid have greater number and volume of meibomian glands than the lower li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
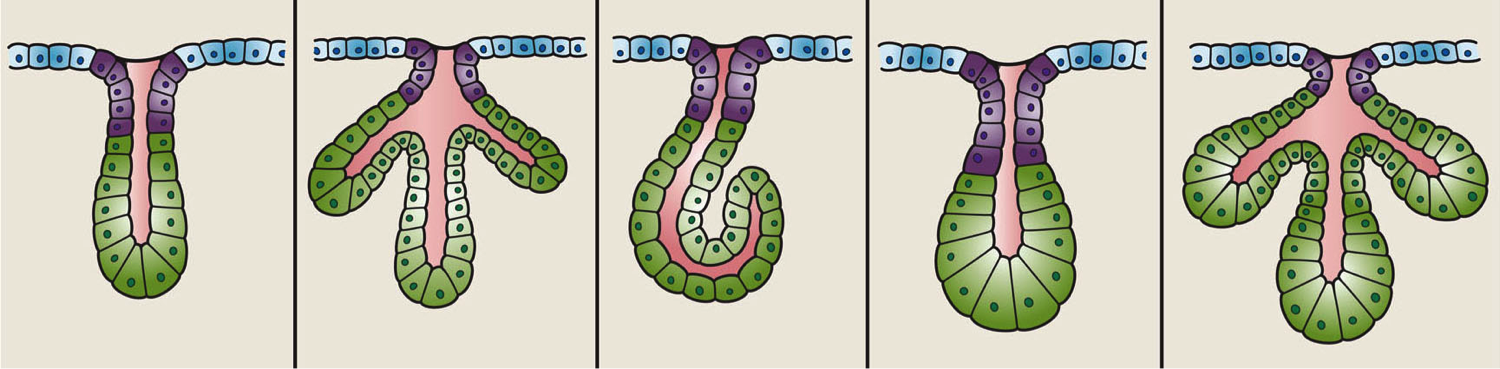
Gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of tears—basal, reflex, and emotional—vary significantly in composition. The functions of tears include lubricating the eyes (basal tears), removing irritants (reflex tears), and also aiding the immune system. Tears also occur as a part of the body's natural pain response. Emotional secretion of tears may serve a biological function by excreting stress-inducing hormones built up through times of emotional distress. Tears have symbolic significance among humans. Physiology Chemical composition Tears are made up of three layers: lipid, aqueous, and mucous. Tears are composed of water, salts, antibodies, and lysozymes (antibacterial enzymes); though composition varies among different tear types. The composition of tears caused by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Sensory innervation of the conjunctiva is divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Vincenzo Ciaccio
Giuseppe Vincenzo Ciaccio (15 October 1824 in Catanzaro – 15 June 1901 in Bologna) was an Italian anatomist and histologist. His name is associated with accessory lacrimal glands known as "Ciaccio's glands". In 1845, he earned his degree in medicine and surgery in Naples, afterwards opening a medical practice in Catanzaro, where in 1855 he attained the chair of theoretical surgery and obstetrics at the royal university-school. In 1860 he relocated to Turin, subsequently receiving a scholarship to study and work abroad. In London, he met with Thomas Spencer Wells (1818-1897) and Lionel Smith Beale (1828-1906), who was an important influence to Ciaccio in his decision to dedicate himself to microscopic anatomy. Following his stay in England, he traveled to Berlin, where he attended lectures by Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) and performed histological studies of Pacinian corpuscles in the laboratory of Wilhelm Kühne (1837-1900). In 1865, he was named professor of microscopic anat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgery, surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency (medicine), residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |