|
Wirth Research
Wirth Research is a group of engineering companies, founded by Nicholas Wirth in 2003, specialising in research, development, design and manufacture for the motor racing industry and other high technology sectors. The companies use virtual engineering technologies to enable a completely simulated vehicle design, development and testing process. The group is known for deviating from traditional physical development models; most notably neglecting to use a wind tunnel and instead relying solely upon computational fluid dynamics to design the 2010 Virgin Racing VR-01 Formula 1 car. The Wirth Research group have a long-standing partnership with Honda Performance Development Inc (HPD) which is responsible for the design, development and manufacture of the ARX sports cars. Wirth Research also provides client IndyCar teams with full technical support. Design Wirth Research encompasses design disciplines that include: :* Composite structures :* Suspension :* Transmission :* Ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Wirth
Nicholas John Peter Wirth (born 26 March 1966) is an automotive engineer and the founder and owner of Wirth Research. He is also the former owner of the Simtek Formula One team, a former aerodynamicist at March and former technical director at the Benetton, and Virgin Racing teams. Education and early life Wirth attended Sevenoaks School from 1977 to 1984 and has B.Sc(Hons) in Mechanical Engineering ( First Class) from University College London and is the youngest-ever Fellow of the Royal Institution of Mechanical Engineers. March Wirth started his Formula One career as an aerodynamicist for March Engineering, responsible for all aerodynamic concepts, schematics and design of windtunnel model components for the and Leyton House March cars. In addition, he conceived and designed all components of the March active suspension system, which ran successfully in February 1989. Simtek Simtek Research was founded in 1989 by Max Mosley and Nick Wirth. It originally was involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda Performance Development
Honda Performance Development, Inc. (HPD) is a subsidiary of American Honda Motor Co. which was established in 1993 and is based in Santa Clarita, California. It is the technical operations center for Honda's American motorsports programs and is involved in the design and development of race engines and chassis for auto racing series such as the IndyCar Series, American Le Mans Series (ALMS), European Le Mans Series (ELMS), FIA World Endurance Championship (WEC) and IMSA SportsCar Championship. IndyCar racing HPD debuted in the CART IndyCar World Series as a works engine manufacturer in 1994. During their first season in 1994, they scored a podium at Toronto, while in 1995 they scored their first victory at New Hampshire. In 1996, HPD won its first manufacturers' and drivers' championships after taking 11 wins from 16 races. HPD took six consecutive drivers championships' as it won the drivers' title again in 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000 and 2001, while it won the manufacturers' tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simulated Environment
Virtual reality (VR) is a simulated experience that employs pose tracking and 3D near-eye displays to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), education (such as medical or military training) and business (such as virtual meetings). Other distinct types of VR-style technology include augmented reality and mixed reality, sometimes referred to as extended reality or XR, although definitions are currently changing due to the nascence of the industry. Currently, standard virtual reality systems use either virtual reality headsets or multi-projected environments to generate realistic images, sounds and other sensations that simulate a user's physical presence in a virtual environment. A person using virtual reality equipment is able to look around the artificial world, move around in it, and interact with virtual features or items. The effect is commonly created by VR headsets consisting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the free-stream flow of the fluid, and the interaction of the fluid ( liquids and gases) with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved, and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows. Initial validation of such software is typically performed using experimental apparatus such as wind tunnels. In addition, previously performed analytical or empirical analysis of a particular problem can be used for comparison. A final validation is often performed using full-scale testing, such as flight tests. CFD is applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad. The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''Energy'', ''Healthcare'' (Siemens Healthineers), and ''Infrastructure & Cities'', which represent the main activities of the corporation. The corporation is a prominent maker of medical diagnostics equipment and its medical health-care division, which generates about 12 percent of the corporation's total sales, is its second-most profitable unit, after the industrial automation division. In this area, it is regarded as a pioneer and the company with the highest revenue in the world. The corporation is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 303,000 people worldwide and reported global revenue of around €62 billion in 2021 according to its earnings release. History 1847 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotesting
Autotesting involves a series of tests, generally around traffic cones, to measure precision driving skill. The tests often include stopping with the front and rear wheels straddling a line, and always end stopping in a garage (usually marked out with cones). Sections of each test are usually completed in reverse. Cars involved can be standard road cars or ones specially built for autotest. In either case, the sport is cheap, with entries to events usually costing between £8 and £25.{{citation needed, date=June 2017 Autotests can take place on either grass or hard surface. Grass Autotests are popular for club events as they are more gentle on tires and transmissions. Many Clubs run their Grass autotests without any reversing. Championship Autotests in the UK are normally on a hard surface. Each event consists of between three and six tests, with each test completed twice with the faster of the two counting for the results. The tests are timed with a stopwatch, with penalti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
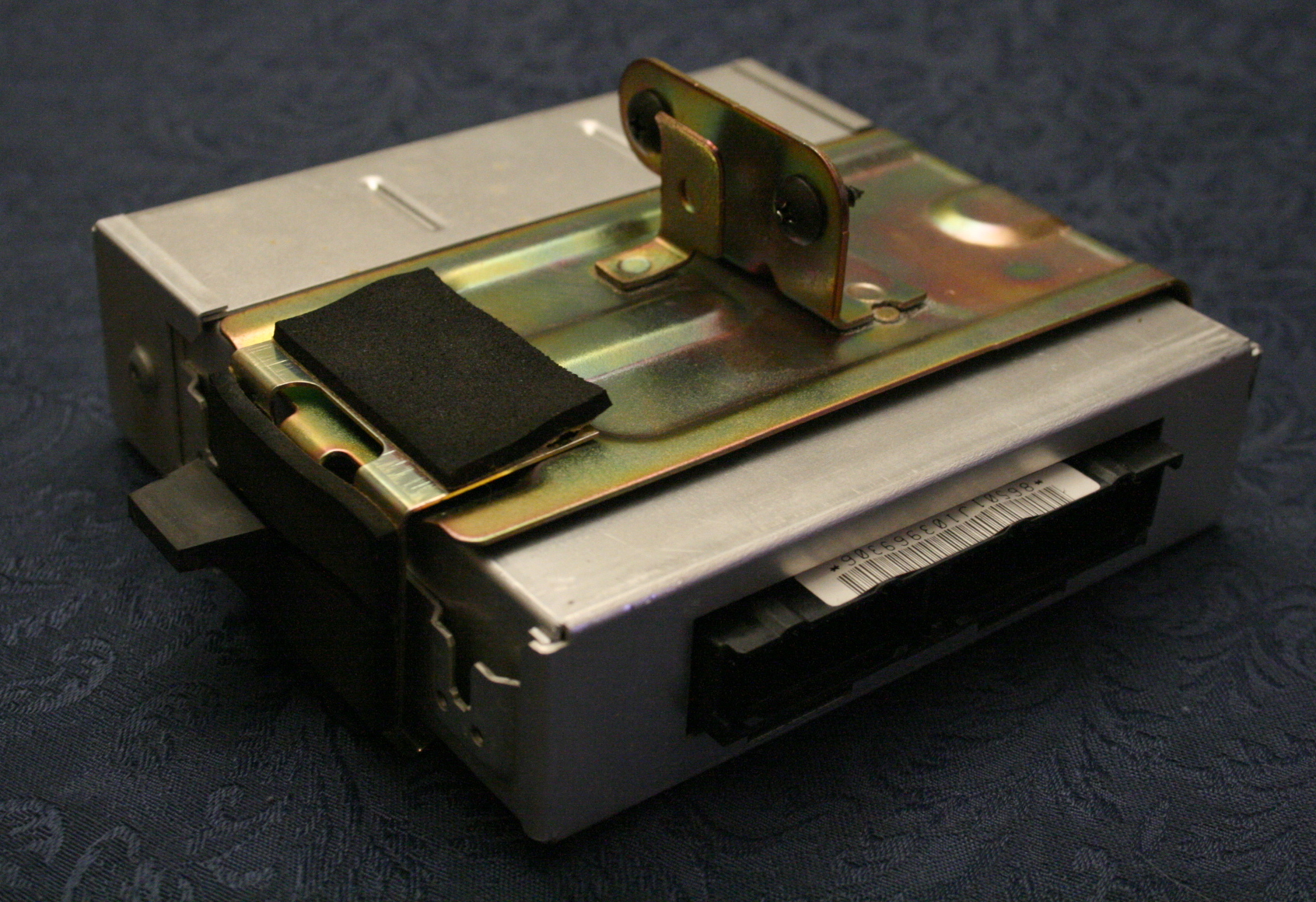
Electronic Control Unit
An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle. Modern vehicles have many ECUs, and these can include some or all of the following: engine control module (ECM), powertrain control module (PCM), transmission control module (TCM), brake control module (BCM or EBCM), central control module (CCM), central timing module (CTM), general electronic module (GEM), body control module (BCM), and suspension control module (SCM). These ECUs together are sometimes referred to collectively as the car's computer though technically they are all separate computers, not a single one. Sometimes an assembly incorporates several individual control modules (a PCM often controls both the engine and the transmission). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Lubrication
Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge (one of the functions of dispersants) and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts. In addition to the aforementioned basic constituents, almost all lubricating oils contain corrosion and oxidation inhibitors. Motor oil may be composed of only a lubricant base stock in the case of non-detergent oil, or a lubricant base stock plus additives to improve the oil's detergency, extreme pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
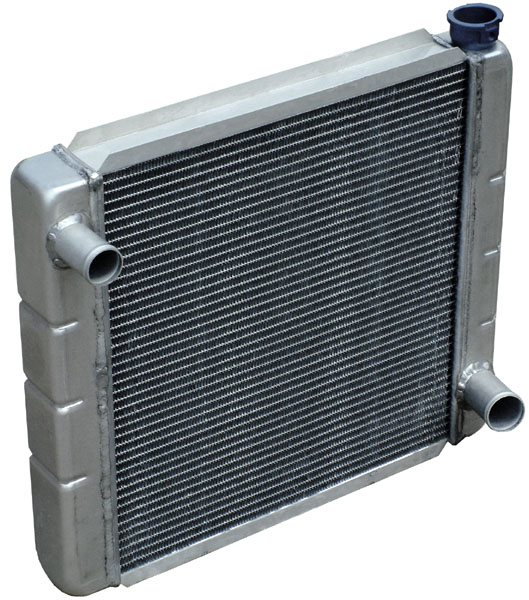
Radiator (engine Cooling)
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine. Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called ''engine coolant'' through the engine block, and cylinder head where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator. Automobiles and motorcycles In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to channels running through the engine and cylinder head, through which a liquid (coolant) is pumped. This liquid may be water (in climates where water is unlik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lakes, estuar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Control Unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by reading values from a multitude of sensors within the engine bay, interpreting the data using multidimensional performance maps (called lookup tables), and adjusting the engine actuators. Before ECUs, air–fuel mixture, ignition timing, and idle speed were mechanically set and dynamically controlled by mechanical and pneumatic means. If the ECU has control over the fuel lines, then it is referred to as an electronic engine management system (EEMS). The fuel injection system has the major role of controlling the engine's fuel supply. The whole mechanism of the EEMS is controlled by a stack of sensors and actuators. Workings Control of air–fuel ratio Most modern engines use some type of fuel injection to deliver fuel to the cylinders. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (mechanics)
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as the speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically (by a control unit). Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |