|
Winston Cone
A Winston cone is a non-imaging light collector in the shape of an Parabolic_reflector#Off-axis_reflectors, off-axis parabola of revolution with a reflective inner surface. It concentrates the light passing through a relatively large entrance aperture through a smaller exit aperture. The collection of incoming rays is maximized by allowing off-axis rays to make multiple reflections before reaching the exit aperture. Winston cones are used to concentrate light from a large area onto a smaller photodetector or photomultiplier. They are widely used for measurements in the far infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in part because there are no suitable materials to form lenses in the range. Winston cones take their name from their inventor, the physicist Roland Winston. It is commercialized by companies such as Winston Cone Optics References See also * Nonimaging optics Optical devices Nonimaging optics {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-imaging Light Collector
Nonimaging optics (also called anidolic optics)Roland Winston et al., ''Nonimaging Optics'', Academic Press, 2004 R. John Koshel (Editor), ''Illumination Engineering: Design with Nonimaging Optics'', Wiley, 2013 is the branch of optics concerned with the optimal transfer of light radiation between a source and a target. Unlike traditional imaging optics, the techniques involved do not attempt to form an image of the source; instead an optimized optical system for optimal radiative transfer from a source to a target is desired. Applications The two design problems that nonimaging optics solves better than imaging optics are: * solar energy concentration: maximizing the amount of energy applied to a receiver, typically a solar cell or a thermal receiver * illumination: controlling the distribution of light, typically so it is "evenly" spread over some areas and completely blocked from other areas Typical variables to be optimized at the target include the total radiant flux, the angu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabolic Reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface generated by a parabola revolving around its axis. The parabolic reflector transforms an incoming plane wave travelling along the axis into a spherical wave converging toward the focus. Conversely, a spherical wave generated by a point source placed in the focus is reflected into a plane wave propagating as a collimated beam along the axis. Parabolic reflectors are used to collect energy from a distant source (for example sound waves or incoming star light). Since the principles of reflection are reversible, parabolic reflectors can also be used to collimate radiation from an isotropic source into a parallel beam. In optics, parabolic mirrors are used to gather light in reflecting telescopes and solar furnaces, and project a beam of light in flas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
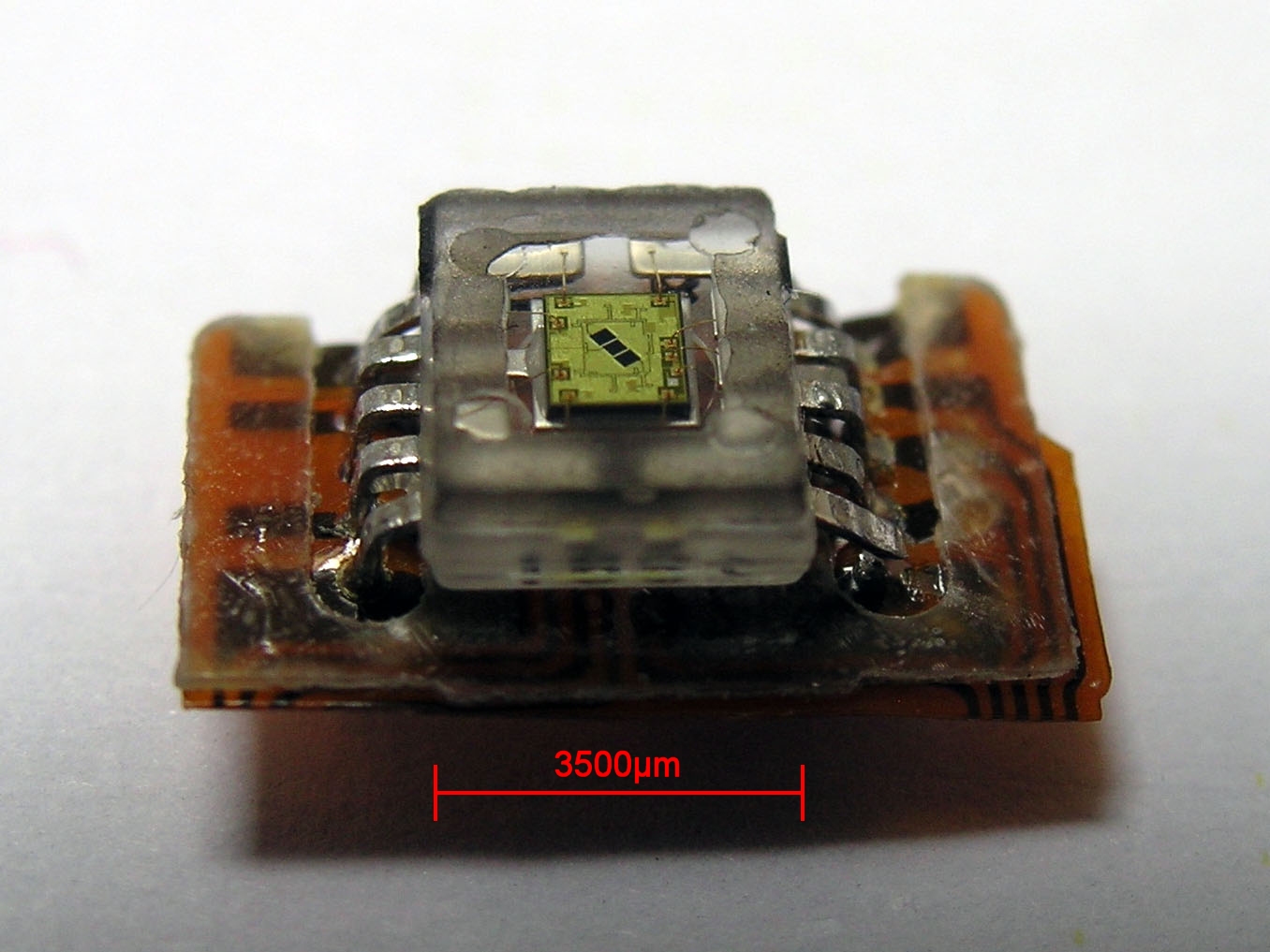
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomultiplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Winston
Roland Winston (born March 12, 1936) is a leading figure in the field of nonimaging optics and its applications to solar energy, and is sometimes termed the "father of non-imaging optics". He is the inventor of the compound parabolic concentrator(CPC), a breakthrough technology in solar energy. He is also a former Guggenheim Fellow, past head of the University of Chicago Department of Physics, a member of the founding faculty of University of California Merced, and as of 2013, head of the California Advanced Solar Technologies Institute. He holds more than 25 patents, chiefly related to solar energy, and has been figuratively said to have a "patent on the sun". Early life and education Winston was born in Moscow, Russia to an American engineer who helped Russians design towns and build an industrial base. In 1942, him and his family had to evacuate Russia when the German military was within artillery range. After fleeing, he attended the Bronx High School of Science. Winston e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonimaging Optics
Nonimaging optics (also called anidolic optics)Roland Winston et al., ''Nonimaging Optics'', Academic Press, 2004 R. John Koshel (Editor), ''Illumination Engineering: Design with Nonimaging Optics'', Wiley, 2013 is the branch of optics concerned with the optimal transfer of light radiation between a source and a target. Unlike traditional imaging optics, the techniques involved do not attempt to form an image of the source; instead an optimized optical system for optimal radiative transfer from a source to a target is desired. Applications The two design problems that nonimaging optics solves better than imaging optics are: * solar energy concentration: maximizing the amount of energy applied to a receiver, typically a solar cell or a thermal receiver * illumination: controlling the distribution of light, typically so it is "evenly" spread over some areas and completely blocked from other areas Typical variables to be optimized at the target include the total radiant flux, the angu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Devices
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: * Interferometer for measuring the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |