|
Winston E. Kock
Winston Edward Kock (1909 – November 25, 1982) was an American electrical engineer and musician, who was the first Director of NASA Electronics Research Center (NASA ERC) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, from September 1, 1964 to October 1, 1966. The Center was created for multidisciplinary scientific research, its proximity to certain colleges, its proximity to a local U.S. Air Force research facility, and was perceived as part of the nation's cold war effort. Johnson Space Center News. This article contains public domain information from a NASA document available online. NASA History Program Office. Kock was also a novelist under the pseudonym Wayne Kirk. Kock also wrote books about topics in engineering and acoustics. These included radar, sonar, holography, and lasers. List of science books authored by KocK at the Library of Congress * Kock's seminal research in artificial dielectrics, carried out at AT&T Bell Laboratories in the 1940s, is a historical connection to metamateri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ann Arbor, Michigan
Ann Arbor is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Washtenaw County, Michigan, Washtenaw County. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census recorded its population to be 123,851. It is the principal city of the Ann Arbor List of metropolitan statistical areas, Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Washtenaw County. Ann Arbor is also included in the Metro Detroit, Greater Detroit Combined statistical area, Combined Statistical Area and the Great Lakes megalopolis, the most populated and largest Megaregions of the United States, megalopolis in North America. Ann Arbor is home to the University of Michigan. The university significantly shapes Ann Arbor's economy as it employs about 30,000 workers, including about 12,000 in the University of Michigan Health System, medical center. The city's economy is also centered on high technology, with several companies drawn to the area by the university's research and development infrastructure. Ann A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holography
Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later re-constructed. Holography is best known as a method of generating real three-dimensional images, but it also has a wide range of other applications. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave. A hologram is made by superimposing a second wavefront (normally called the reference beam) on the wavefront of interest, thereby generating an interference pattern which is recorded on a physical medium. When only the second wavefront illuminates the interference pattern, it is diffracted to recreate the original wavefront. Holograms can also be computer-generated by modelling the two wavefronts and adding them together digitally. The resulting digital image is then printed onto a suitable mask or film and illuminated by a suitable source to reconstruct the wavefront of interest. Overview and history The Hungarian- British physicist Dennis Gabor (in Hungarian: ''Gábor Déne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The IRE
The ''Proceedings of the IEEE'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The journal focuses on electrical engineering and computer science. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor of 9.107, ranking it sixth in the category "Engineering, Electrical & Electronic." In 2018, it became fifth with an enhanced impact factor of 10.694. History of the Proceedings The journal was established in 1909, known as the ''Proceedings of the Wireless Institute''. Six issues were published under this banner by Greenleaf Pickard and Alfred Goldsmith. Then in 1911, a merger between the Wireless Institute (New York) and the Society of Wireless Telegraph Engineers (Boston) resulted in a society named the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE). In January 1913 newly formed IRE published the first issue of the ''Proceedings of the IRE''. Later, a 1000-page special issue commemorated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic field, electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Light, (visible) light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Classical electromagnetism, Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric field, electric and magnetic fields. Depending on the frequency of oscillation, different wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum are produced. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, commonly denoted ''c''. In homogeneous, isotropic media, the oscillations of the two fields are perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy and wave propagation, forming a transverse wave. The position of an electromagnetic wave w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasistatic Approximation
Quasistatic approximation(s) refers to different domains and different meanings. In the most common acceptance, quasistatic approximation refers to equations that keep a static form (do not involve time derivatives) even if some quantities are allowed to vary slowly with time. In electromagnetism it refers to mathematical models that can be used to describe devices that do not produce significant amounts of electromagnetic waves. For instance the capacitor and the coil in electrical networks. Overview The quasistatic approximation can be understood through the idea that the sources in the problem change sufficiently slowly that the system can be taken to be in equilibrium at all times. This approximation can then be applied to areas such as classical electromagnetism, fluid mechanics, magnetohydrodynamics, thermodynamics, and more generally systems described by hyperbolic partial differential equations involving both spatial and time derivatives. In simple cases, the quasistati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Antenna
A lens antenna is a microwave antenna that uses a shaped piece of microwave-transparent material to bend and focus the radio waves by refraction, as an optical lens does for light. Typically it consists of a small feed antenna such as a patch antenna or horn antenna which radiates radio waves, with a piece of dielectric or composite material in front which functions as a converging lens to collimate the radio waves into a beam. Conversely, in a receiving antenna the lens focuses the incoming radio waves onto the feed antenna, which converts them to electric currents which are delivered to a radio receiver. They can also be fed by an array of feed antennas, called a focal plane array (FPA), to create more complicated radiation patterns. To generate narrow beams, the lens must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves, so lens antennas are mainly used at the high frequency end of the radio spectrum, with microwaves and millimeter waves, whose small wavelengths allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
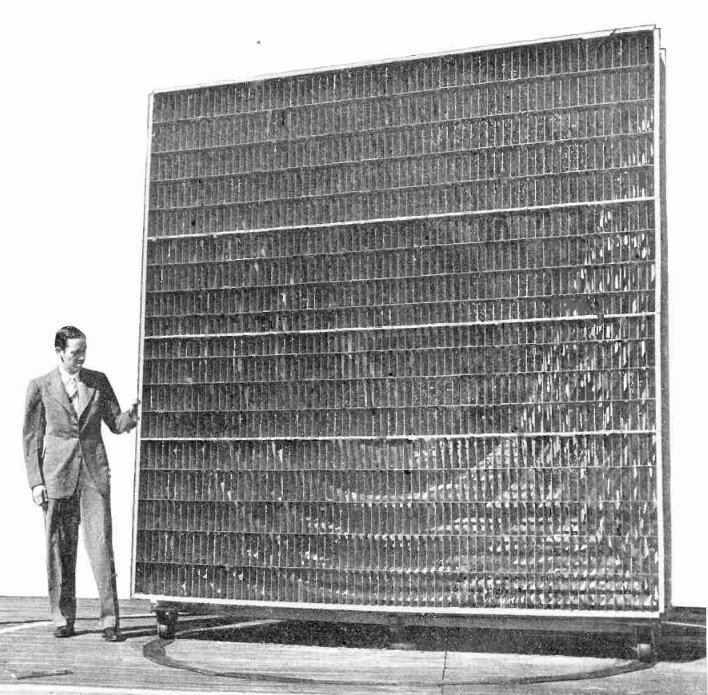
Artificial Dielectric
Artificial dielectrics are fabricated composite materials, often consisting of arrays of conductive shapes or particles in a nonconductive support matrix, designed to have specific electromagnetic properties similar to dielectrics. As long as the lattice spacing is smaller than a wavelength, these substances can refract and diffract electromagnetic waves, and are used to make lenses, diffraction gratings, mirrors, and polarizers for microwaves. These were first conceptualized, constructed and deployed for interaction in the microwave frequency range in the 1940s and 1950s. The constructed medium, the artificial dielectric, has an effective permittivity and effective permeability, as intended. First published in 2004 according to theCRC Press web page for this book. According to the copyright page of this book, accessible via Google Books, it had gone into its tenth printing by sometime in 2005. In addition, some artificial dielectrics may consist of irregular lattices, random mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
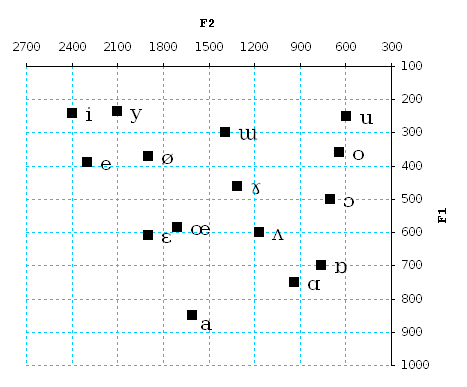
Formant
In speech science and phonetics, a formant is the broad spectral maximum that results from an acoustic resonance of the human vocal tract. In acoustics, a formant is usually defined as a broad peak, or local maximum, in the spectrum. For harmonic sounds, with this definition, the formant frequency is sometimes taken as that of the harmonic that is most augmented by a resonance. The difference between these two definitions resides in whether "formants" characterise the production mechanisms of a sound or the produced sound itself. In practice, the frequency of a spectral peak differs slightly from the associated resonance frequency, except when, by luck, harmonics are aligned with the resonance frequency. A room can be said to have formants characteristic of that particular room, due to its resonances, i.e., to the way sound reflects from its walls and objects. Room formants of this nature reinforce themselves by emphasizing specific frequencies and absorbing others, as exploited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon Tubes
Neon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode at each end, filled with one of a number of gases at low pressure. A high potential of several thousand volts applied to the electrodes ionizes the gas in the tube, causing it to emit colored light. The color of the light depends on the gas in the tube. Neon lights were named for neon Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton ..., a noble gas which gives off a popular orange light, but other gases and chemicals are used to produce other colors, such as hydrogen (red), helium (yellow), carbon dioxide (white), and mercury (element), merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |