|
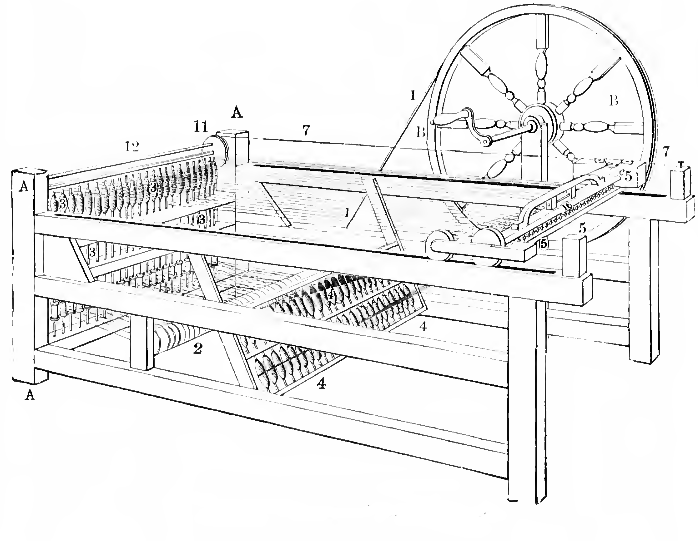
William Radcliffe
William Radcliffe (1761?, in Mellor, Derbyshire – 20 May 1842, in StockportDavid J. Jeremy"Radcliffe, William (1761?–1842)" ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004, accessed 9 July 2008) was a British inventor and author of the essay ''Origin of the New System of Manufacture, Commonly Called Power loom Weaving''. Biography Radcliffe came from a modest family which had made the transition from farming to weaving. His father taught him about carding and spinning. In 1785, he purchased several spinning machines that had been developed by James Hargreaves. Hargreaves machines, called the spinning jenny, were the first wholly successful improvement on the traditional spinning wheel. Its advantage was to multiply many times the amount of yarn that could be spun by a single operator. This development and others such as weavers being able to rely on uninterrupted supplies of yarn led to spinning being concentrated in factories. Powerloom weaving In 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellor, Derbyshire
Mellor is a village in Greater Manchester, England, lying between Marple Bridge and New Mills, Derbyshire. Buildings in the village include St. Thomas' Church, Mellor, St. Thomas' Church, a primary school, golf course, sports club, a riding school, three pubs (the Royal Oak, The Devonshire Arms and The Oddfellows Arms) and the late-17th-century Mellor Hall. The village was a civil parish in the county of Derbyshire until 1936 when it was transferred to Marple, Greater Manchester, Marple Urban District in Cheshire; in 1974, it became part of the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport in Greater Manchester. History The origin of the name ''Mellor'' is uncertain. In one Celtic languages, Celtic dialect, the term would translate to "the bare (or rounded) hill". The name ''Mellor'' does not appear in the Norman-era Domesday Book, although the neighbouring settlement of Ludworth (recorded as ''Lodeuorde'') is listed. It is possible that Ludworth originally included Mellor and that they s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1761 Births
Events January–March * January 14 – Third Battle of Panipat: Ahmad Shah Durrani and his coalition decisively defeat the Maratha Confederacy, and restore the Mughal Empire to Shah Alam II. * January 16 – Siege of Pondicherry (1760) ended: The British capture Pondichéry, India from the French. * February 8 – An earthquake in London breaks chimneys in Limehouse and Poplar. * March 8 – A second earthquake occurs in North London, Hampstead and Highgate. * March 31 – 1761 Portugal earthquake: A magnitude 8.5 earthquake strikes Lisbon, Portugal, with effects felt as far north as Scotland. April–June * April 1 – The Austrian Empire and the Russian Empire sign a new treaty of alliance. * April 4 – A severe epidemic of influenza breaks out in London and "practically the entire population of the city" is afflicted; particularly contagious to pregnant women, the disease causes an unusual number of miscarriages and prema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Inventors
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile Workers
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clothing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The Industrial Revolution
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving Families
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllis Deane
Phyllis Mary Deane FBA (13 October 1918 – 28 July 2012) was a British economic historian and a historian of economic thought. She served as Professor of Economic History at the University of Cambridge from 1981 to 1983. Life and career Deane was born in Hong Kong in October 1918, the daughter of an Admiralty engineer. She attended Chatham County School in Kent, then Hutchesons' Grammar School in Glasgow, before gaining a master's degree (MA) in Economic Science from the University of Glasgow in 1940. She later received an MA from the University of Cambridge. Deane worked as a research officer, first at the National Institute of Economic and Social Research (NIESR) from 1941 to 1945, then at the Colonial Office until 1949. She left in 1950 for Cambridge University, where she was a researcher, then lecturer, in applied economics until 1971. She was then a reader in economic history until 1981, and Professor of Economic History from 1981 to 1983. Among other academic honours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Mathias
Peter Mathias, (10 January 1928 – 1 March 2016) was a British economic historian and the former Chichele Professor of Economic History at the University of Oxford. His research focused on the history of industry, business, and technology, both in Britain and Europe. He is most well known for his publication of ''The First Industrial Nation: an Economic History of Britain 1700–1914'' (1969), which discussed not only the multiple factors that made industrialisation possible, but also how it was sustained. Early life and education Mathias was born in Freshford, Somerset to Jack Mathias (from Plymouth) and Marion (''née'') Love (from Wingfield). He attended Colston's School and Bristol Grammar School where he became interested in history. In December 1945, he applied for a scholarship at King's College, Cambridge; instead he won an Exhibition at Jesus College, Cambridge, during summer 1946. However the college demanded that those coming up from school should have done milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinning Jenny
The spinning jenny is a multi-spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialization of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764 or 1765 by James Hargreaves in Stanhill, Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in England. The device reduced the amount of work needed to produce cloth, with a worker able to work eight or more spools at once. This grew to 120 as technology advanced. The yarn produced by the jenny was not very strong until Richard Arkwright invented the water-powered water frame. The spinning jenny helped to start the factory system of cotton manufacturing. History The spinning jenny was invented by James Hargreaves. He was born in Oswaldtwistle, near Blackburn, around 1720. Blackburn was a town with a population of about 5,000, known for the production of "Blackburn greys," cloths of linen warp and cotton weft initially imported from India. They were usually sent to London to be printed. At the time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, Property rights (economics), property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in Capital market, capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include ''Laissez-faire capitalism, laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_1938.jpg)