|
William II De Soules
William II de Soules (d. 1320/1321), Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland, was a Scottish Border noble during the Wars of Scottish Independence. William was the elder son of Nicholas II de Soules, Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland, and a cousin of Alexander Comyn, Earl of Buchan. He was the nephew of John de Soules, Guardian of Scotland. While still a young man, he was received into the peace of King Edward I of England in 1304. He remained in English service in the following decade, and received reward in 1312 with a knighthood and the lands of Sir Robert Keith although by that time those were in the hands of the Scots. After the victory of the Bruce cause at the Battle of Bannockburn in 1314, he switched to the Scottish side. By 1318 he was Butler of Scotland, and in 1320 he appeared as a signatory to the Declaration of Arbroath with this designation. Later in 1320 he was involved in a conspiracy against King Robert along with Sir David, Lord of Brechin. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soules Arms
Soules is a surname. People with the surname include: * Chris Soules (born 1981), American reality television personality and farmer *Dale Soules (born 1946), American actress *Olivier Soules (born 1967), French tennis player * William Soules (born 1955), American politician See also *Soules (automobile), automotive company founded in Grand Rapids, Michigan in 1905 *Soules College of Business at the University of Texas at Tyler *William II de Soules William II de Soules (d. 1320/1321), Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland, was a Scottish Border noble during the Wars of Scottish Independence. William was the elder son of Nicholas II de Soules, Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland ... (d. 1320/1321), Lord of Liddesdale and Butler of Scotland * John de Soules (other) * Soule (other) * Souls (other) * Soles (other) {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
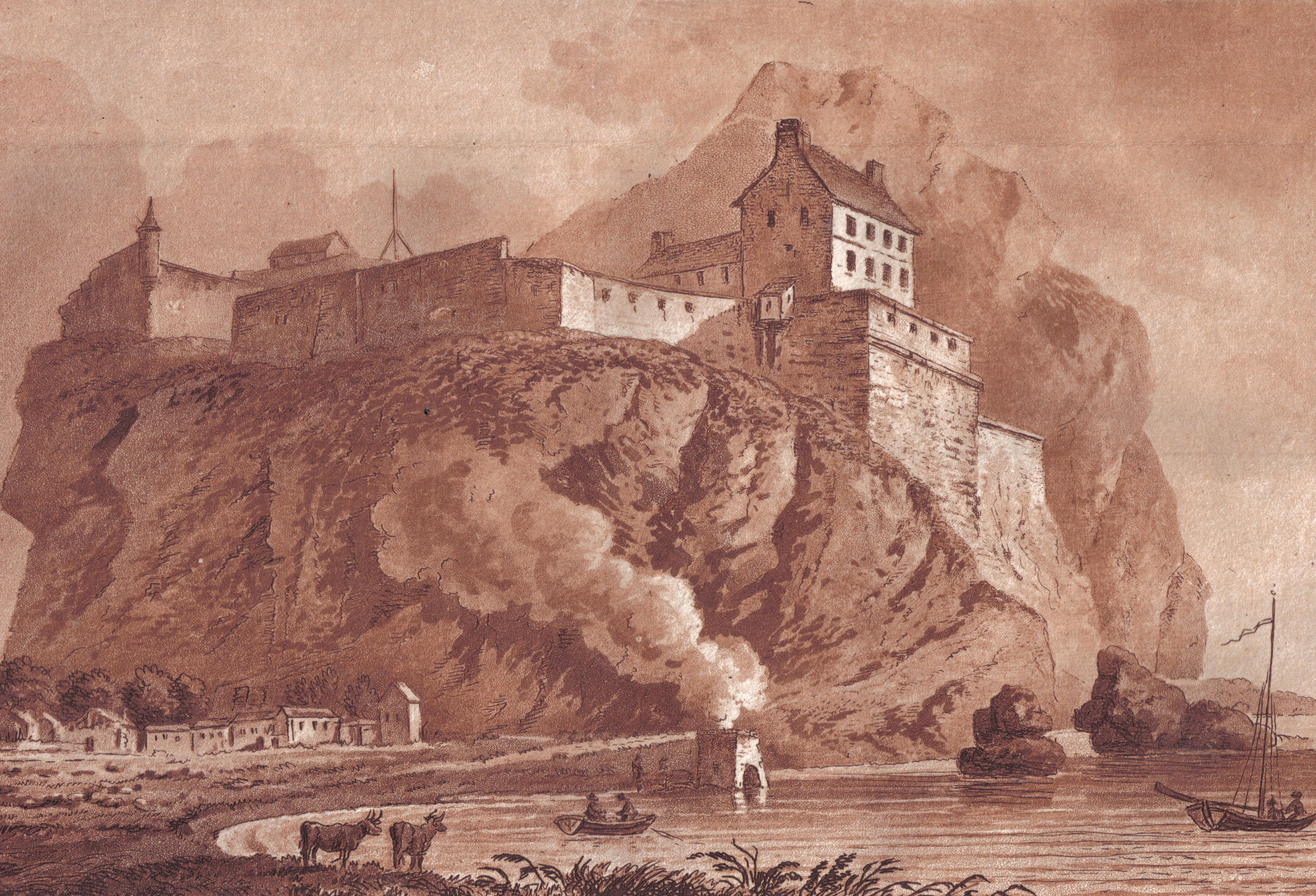
Dumbarton Castle
Dumbarton Castle ( gd, Dùn Breatainn, ; ) has the longest recorded history of any stronghold in Scotland. It sits on a volcanic plug of basalt known as Dumbarton Rock which is high and overlooks the Scottish town of Dumbarton. History Dumbarton Rock was formed between 330 and 340 million years ago, during the Early Carboniferous period, a time of widespread volcanic activity in the area where Glasgow is now situated; over time, the softer exterior of the volcano weathered away, leaving behind a volcanic plug of basalt. Iron Age At least as far back as the Iron Age, this has been the site of a strategically important settlement, as evidenced by archaeological finds. The people that came to reside there in the era of Roman Britain were known to have traded with the Romans. However the first written record about a settlement there was in a letter that Saint Patrick wrote to King Ceretic of Alt Clut in the late 5th century. Early Medieval era David Nash Ford has proposed tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bruce (bastard)
Sir Robert Bruce, Lord of Liddesdale (died 11 August 1332) was an illegitimate son of King Robert the Bruce and an unknown mother. He was knighted and awarded the royal arms at the Battle of Bannockburn in 1314. His father made him Lord of Liddesdale after William II de Soules was found guilty of treason and forfeited the title on 4 August 1320, at the Black Parliament at Scone. It has been suggested that he may have been the father of Thomas Bruce, 1st Baron of Clackmannan, but there is no clear evidence for this. Faced with Edward Balliol's invasion of Scotland, Lord Robert and Duncan IV, Earl of Fife, attempted to prevent Balliol's forces from landing at Kinghorn in Fife on 6 August 1332. The unsuccessful attempt to repel Balliol is called the Battle of Wester Kinghorn, Scottish losses were high and included five or six nobles, one known casualty was Sir Alexander Seton. Succeeding in landing, Balliol's forces marched on Dunfermline, where they looted a Scottish armory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archie Duncan (historian)
Archibald Alexander McBeth Duncan, FBA, FRHistS, FRSE (17 October 1926 – 20 December 2017) was a Scottish historian. From 1962 to 1993 he was Professor of Scottish History and Literature at the University of Glasgow. On giving up his professorship, he became Clerk of Senate and Dean of Faculties, retiring from the university in 2000. From 2001 he was Emeritus Professor of Scottish History and Literature, but continued to publish on the history of Scotland in the Middle Ages In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a .... Select bibliography * ''Scotland: The Making of the Kingdom.'' Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 1973. * ''The Kingship of the Scots: Succession and Independence 842–1292.'' Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2002. References External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitage Castle
Hermitage Castle is a semi-ruined castle in the border region of Scotland. It is under the care of Historic Scotland. The castle has a reputation, both from its history and its appearance, as one of the most sinister and atmospheric castles in Scotland. History Origins of the name It is thought that the name derives from Old French: – guardhouse. The castle was known as ''the guardhouse of the bloodiest valley in Britain'', and the "Strength of Liddesdale". Hermitage Castle was supposedly built by one Nicholas de Soulis around 1240, in a typical Norman Motte and Bailey pattern. It stayed in his family until approximately 1320 when his descendant, William de Soulis, forfeited it because of suspected witchcraft and the attempted regicide of King Robert I of Scotland. Legend has it that Soulis's tenantry, having suffered unbearable depredations, arrested him, and at the nearby Ninestane Rig (a megalithic circle), had him boiled to death in molten lead. In actuality, he died, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninestane Rig
Ninestane Rig ( en, Nine Stone Ridge) is a small stone circle in Scotland near the English border. Located in Roxburghshire, near to Hermitage Castle, it was probably made between 2000 BC and 1250 BC, during the Late Neolithic or early Bronze Age (Bronze Age technology reached the Borders around 1750 BC). It is a scheduled monument (a nationally important archaeological site given special protections) and is part of a group with two other nearby ancient sites, these being Buck Stone standing stone and another standing stone at Greystone Hill. Settlements appear to have developed in the vicinity of these earlier ritual features in late prehistory and probably earlier. The circle (actually slightly oval in form) consists of eight stones fast in the earth (a ninth stone has fallen inwards and lies flat), but six of these are now just stumps of or less. Of the two large standing stones remaining, one is a regular monolith a little under tall and the other, a pointed stone, is a litt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minstrelsy Of The Scottish Border
''Minstrelsy of the Scottish Border'' is an anthology of Border ballads, together with some from north-east Scotland and a few modern literary ballads, edited by Walter Scott. It was first published in 1802, but was expanded in several later editions, reaching its final state in 1830, two years before Scott's death. It includes many of the most famous Scottish ballads, such as '' Sir Patrick Spens'', '' The Young Tamlane'', ''The Twa Corbies'', '' The Douglas Tragedy'', '' Clerk Saunders'', '' Kempion'', ''The Wife of Usher's Well'', '' The Cruel Sister'', '' The Dæmon Lover'', and ''Thomas the Rhymer''. Scott enlisted the help of several collaborators, notably John Leyden, and found his ballads both by field research of his own and by consulting the manuscript collections of others. Controversially, in the editing of his texts he preferred literary quality over scholarly rigour, but ''Minstrelsy of the Scottish Border'' nevertheless attracted high praise from the first. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redcap
The redcap (or powrie) is a type of malevolent, murderous goblin found in Border folklore. He is said to inhabit ruined castles along the Anglo-Scottish border, especially those that were the scenes of tyranny or wicked deeds and is known for soaking his cap in the blood of his victims.Henderson, William (1879). ''Folklore of the Northern Counties of England and the Borders'' (2nd ed.) W. Satchell, Peyton & Co. p. 253.Briggs, Katharine (1976). ''An Encyclopedia of Fairies''. Pantheon Books. p. 339. . He is also known as Redcomb and Bloody Cap. Description and behaviour Redcap is depicted as "a short, thickset old elf with long prominent teeth, skinny fingers armed with talons like eagles, large eyes of a fiery red colour, grisly hair streaming down his shoulders, iron boots, a pikestaff in his left hand, and a red cap on his head". When travellers take refuge in his lair, he flings huge stones at them and if he kills them, he soaks his cap in their blood, giving it a crimson hue. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy'', ''Waverley'', ''Old Mortality'', '' The Heart of Mid-Lothian'' and ''The Bride of Lammermoor'', and the narrative poems '' The Lady of the Lake'' and '' Marmion''. He had a major impact on European and American literature. As an advocate, judge and legal administrator by profession, he combined writing and editing with daily work as Clerk of Session and Sheriff-Depute of Selkirkshire. He was prominent in Edinburgh's Tory establishment, active in the Highland Society, long a president of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1820–1832), and a vice president of the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland (1827–1829). His knowledge of history and literary facility equipped him to establish the historical novel genre as an exemplar of Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Scot
Michael Scot (Latin: Michael Scotus; 1175 – ) was a Scottish mathematician and scholar in the Middle Ages. He was educated at Oxford and Paris, and worked in Bologna and Toledo, where he learned Arabic. His patron was Frederick II of the Holy Roman Empire and Scot served as science adviser and court astrologer to him. Scot translated Averroes and was the greatest public intellectual of his day. Early life and education Scot was born somewhere in the border regions of Scotland. He studied first at the cathedral school of Durham and then at Oxford and Paris, devoting himself to philosophy, mathematics, and astrology. It appears that he had also studied theology and become an ordained priest, as Pope Honorius III wrote to Stephen Langton on 16 January 1223/4, urging him to confer an English benefice on Scot, and nominated Scot as archbishop of Cashel in Ireland. Scot declined this appointment, but he seems to have held benefices in Italy. From Paris, Scot went to Bologna, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Magic
Black magic, also known as dark magic, has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for evil and selfish purposes, specifically the seven magical arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456. During his period of scholarship, A. E. Waite provided a comprehensive account of black magic practices, rituals and traditions in ''The Book of Ceremonial Magic'' (1911). It is also sometimes referred to as the "left-hand path". In modern times, some find that the definition of black magic has been convoluted by people who define magic or ritualistic practices that they disapprove of as black magic. The seven ''Artes prohibitae'' of black magic The seven ''artes prohibitae'' or ''artes magicae'', arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456, their sevenfold partition reflecting that of the artes liberales and artes mechanicae, were: #necromancy #geomancy #hydromancy #aeromancy #pyromancy #chiromancy #scap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
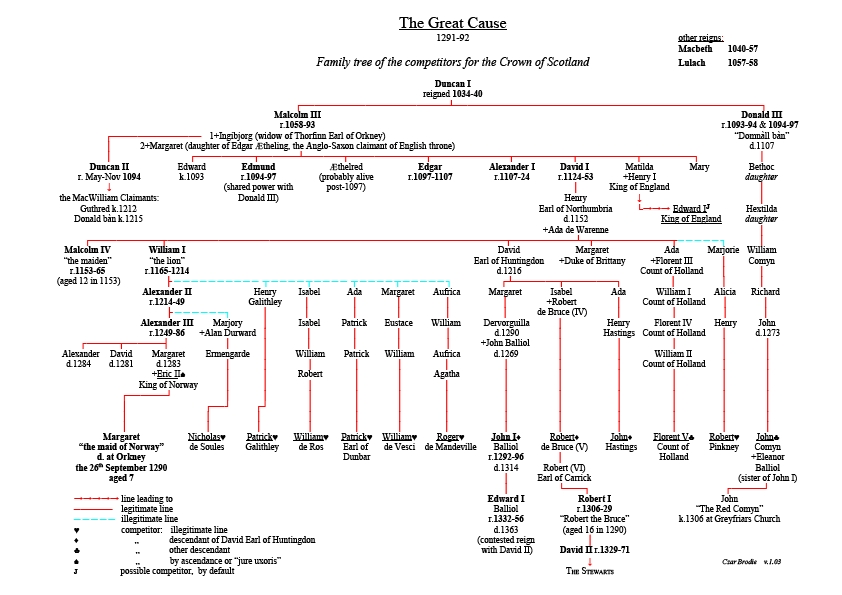
Competitors For The Crown Of Scotland
When the crown of Scotland became vacant in September 1290 on the death of the seven-year-old Queen Margaret, 13 claimants to the throne came forward. Those with the most credible claims were John Balliol, Robert de Brus, 5th Lord of Annandale, John Hastings and Floris V, Count of Holland. Fearing civil war, the Guardians of Scotland asked Edward I of England to arbitrate. Before agreeing, he obtained concessions going some way to revive English overlordship over the Scots. A commission of 104 "auditors" was then appointed—24 by Edward himself, acting as president; and the rest by Bruce and Balliol, in equal numbers. In November 1292, the body decided in favour of John Balliol, whose claim was based on the traditional criterion of primogeniture—inheritance through a line of firstborn sons. The decision was accepted by the majority of the powerful in Scotland, and John ruled as King of Scots from then until 1296. Background With the death of King Alexander III in 1286, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |