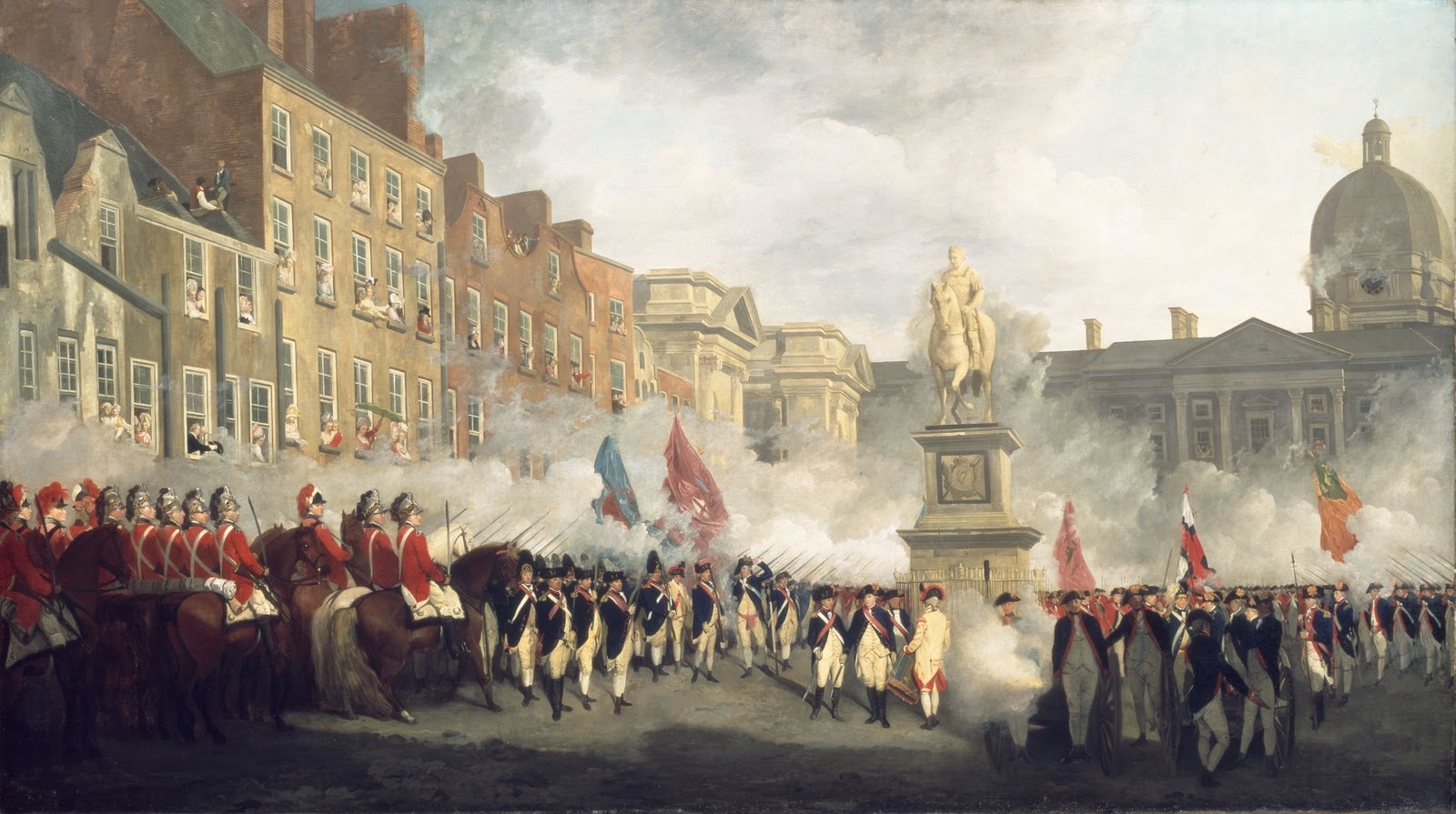|
William FitzGerald, 2nd Duke Of Leinster
William Robert FitzGerald, 2nd Duke of Leinster, KP, PC (Ire) (12/13 March 1749 – 20 October 1804) was an Irish liberal politician and landowner. He was born in London. Career FitzGerald made his Grand Tour between 1768 and 1769. During the same time, he also was Member of Parliament (MP) for Kildare Borough. FitzGerald then sat in the Irish House of Commons for Dublin City until 1773, when he inherited his father's title and estates. He was appointed High Sheriff of Kildare for 1772. Politically he was a liberal supporter of Henry Grattan's Irish Patriot Party and he co-founded the Irish Whig Club in 1789. He controlled about six Kildare members of the Irish House of Commons. In 1779, he was elected colonel of the Dublin Regiment of the Irish Volunteers. In 1770, FitzGerald was chosen Grandmaster of the masonic Grand Lodge of Ireland, which post he held for two years. He was re-elected for another year in 1777. In 1783 he was among the first knights in the newly created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
His Grace
His Grace or Her Grace is an English Style (manner of address), style used for various high-ranking personages. It was the style used to address English monarchs until Henry VIII and the Scottish monarchs up to the Act of Union (1707), Act of Union of 1707, which united the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England. Today, the style is used when referring to archbishops and non-royal dukes and duchesses in the United Kingdom. Examples of usage include His Grace The Duke of Norfolk; His Grace The Lord Archbishop of Canterbury; or "Your Grace" in spoken or written address. As a style of Dukes in the United Kingdom, British dukes it is an abbreviation of the full formal style "The Most High, Noble and Potent Prince His Grace". Royal dukes, for example Prince Edward, Duke of Kent, are addressed with their higher royal style, Royal Highness. The Duchess of Windsor was styled "Your Grace" and not Royal Highness upon marriage to Prince Edward, Duke of Windsor. Ecclesiastical usage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James FitzGerald, 1st Duke Of Leinster
Lieutenant-General James FitzGerald, 1st Duke of Leinster, PC (Ire) (29 May 1722 – 19 November 1773), styled Lord Offaly until 1743 and known as The Earl of Kildare between 1743 and 1761 and as The Marquess of Kildare between 1761 and 1766, was an Anglo-Irish nobleman, soldier and politician. Background Leinster was the son of Robert FitzGerald, 19th Earl of Kildare, and Lady Mary, daughter of William O'Brien, 3rd Earl of Inchiquin. Career Leinster was a member of the Irish House of Commons for Athy from 1741 before succeeding his father as 20th Earl of Kildare in 1743. He was sworn of the Irish Privy Council in 1746 and in 1747, on the occasion of his marriage (see below), he was created Viscount Leinster, of Taplow in the County of Buckingham, in the Peerage of Great Britain, and took his seat in the British House of Lords that same year. From 1749 to 1755 he was one of the leaders of the Popular Party in Ireland, and served as the country's Master-General of the O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Lodge Of Ireland
The Grand Lodge of Ireland is the second most senior Grand Lodge of Freemasons in the world, and the oldest in continuous existence. Since no specific record of its foundation exists, 1725 is the year celebrated in Grand Lodge anniversaries, as the oldest reference to Grand Lodge of Ireland comes from the ''Dublin Weekly Journal'' of 26 June 1725. This describes a meeting of the Grand Lodge to install the new Grand Master, The 1st Earl of Rosse, on 24 June. The Grand Lodge has regular Masonic jurisdiction over 13 Provincial Grand Lodges covering all the Freemasons of the island of Ireland, and another 11 provinces worldwide. History There is considerable evidence of Masonic Lodges meeting in Ireland prior to the 18th century. The story of the "Lady Freemason", Elizabeth St. Leger, dates to a time prior to the existence of the Grand Lodge; also, there are references to Lodge meetings across Dublin in a speech given in Trinity College, Dublin, as far back as 1688. The oldest art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonic
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to Fraternity, fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of Stonemasonry, stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Masonic Lodge, Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that superv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military service. The rank of colonel is typically above the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank above colonel is typically called brigadier, brigade general or brigadier general. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Vatican, colonel is the highest rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Whig Club
Irish may refer to: Common meanings * Someone or something of, from, or related to: ** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ***Éire, Irish language name for the isle ** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ** Republic of Ireland, a sovereign state * Irish language, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family spoken in Ireland * Irish people, people of Irish ethnicity, people born in Ireland and people who hold Irish citizenship Places * Irish Creek (Kansas), a stream in Kansas * Irish Creek (South Dakota), a stream in South Dakota * Irish Lake, Watonwan County, Minnesota * Irish Sea, the body of water which separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain People * Irish (surname), a list of people * William Irish, pseudonym of American writer Cornell Woolrich (1903–1968) * Irish Bob Murphy, Irish-American boxer Edwin Lee Conarty (1922–1961) * Irish McCal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Patriot Party
The Irish Patriot Party was the name of a number of different political groupings in Ireland throughout the 18th century. They were primarily supportive of Whig concepts of personal liberty combined with an Irish identity that rejected full independence, but advocated strong self-government within the British Empire. Due to the discriminatory penal laws, the Irish Parliament at the time was exclusively Anglican Protestant. Their main achievement was the Constitution of 1782, which gave Ireland legislative independence. Early Irish Patriots In 1689 a short-lived "Patriot Parliament" had sat in Dublin before James II, and briefly obtained ''de facto'' legislative independence, while ultimately subject to the English monarchy. The parliament's membership mostly consisted of land-owning Roman Catholic Jacobites who lost the ensuing War of the Grand Alliance in 1689–91. The name was then used from the 1720s to describe Irish supporters of the British Whig party, specifically th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Grattan
Henry Grattan (3 July 1746 – 4 June 1820) was an Irish politician and lawyer who campaigned for legislative freedom for the Irish Parliament in the late 18th century from Britain. He was a Member of the Irish Parliament (MP) from 1775 to 1801 and a Member of Parliament (MP) in Westminster from 1805 to 1820. He has been described as a superb orator and a romantic. With generous enthusiasm he demanded that Ireland should be granted its rightful status, that of an independent nation, though he always insisted that Ireland would remain linked to Great Britain by a common crown and by sharing a common political tradition. Grattan opposed the Act of Union 1800 that merged the Kingdoms of Ireland and Great Britain, but later sat as a member of the united Parliament in London. Early life Grattan was born at Fishamble Street, Dublin, and baptised in the nearby church of St. John the Evangelist in 1746. A member of the Anglo-Irish elite of Protestant background, Grattan was the son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Sheriff Of Kildare
The High Sheriff of Kildare was the British Crown's judicial representative in County Kildare, Ireland from the 16th century until 1922, when the office was abolished in the new Free State and replaced by the office of Kildare County Sheriff. The High Sheriff had judicial, electoral, ceremonial and administrative functions and executed High Court Writs. In 1908, an Order in Council made the Lord Lieutenant the Sovereign's prime representative in a county and reduced the High Sheriff's precedence. However, the sheriff retained his responsibilities for the preservation of law and order in the county. The usual procedure for appointing the sheriff from 1660 onwards was that three persons were nominated at the beginning of each year from the county and the Lord Lieutenant then appointed his choice as High Sheriff for the remainder of the year. Often the other nominees were appointed as under-sheriffs. Sometimes a sheriff did not serve his full term due to death or another event, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish House Of Commons
The Irish House of Commons was the lower house of the Parliament of Ireland that existed from 1297 until 1800. The upper house was the House of Lords. The membership of the House of Commons was directly elected, but on a highly restrictive franchise, similar to the unreformed House of Commons in contemporary England and Great Britain. Catholics were disqualified from sitting in the Irish parliament from 1691, even though they comprised the vast majority of the Irish population. The Irish executive, known as the Dublin Castle administration, under the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, was not answerable to the House of Commons but to the British government. However, the Chief Secretary for Ireland was usually a member of the Irish parliament. In the Commons, business was presided over by the Speaker. From 1 January 1801, it ceased to exist and was succeeded by the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. Franchise The limited franchise was exclusively male. From 1728 until 1793, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tutor or family member) when they had come of age (about 21 years old). The custom—which flourished from about 1660 until the advent of large-scale rail transport in the 1840s and was associated with a standard itinerary—served as an educational rite of passage. Though it was primarily associated with the British nobility and wealthy landed gentry, similar trips were made by wealthy young men of other Protestant Northern European nations, and, from the second half of the 18th century, by some South and North Americans. By the mid-18th century, the Grand Tour had become a regular feature of aristocratic education in Central Europe as well, although it was restricted to the higher nobility. The tradition declined in Europe as enthusiasm fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Volunteers (18th Century)
The Volunteers (also known as the Irish Volunteers) were local militias raised by local initiative in Ireland in 1778. Their original purpose was to guard against invasion and to preserve law and order at a time when British soldiers were withdrawn from Ireland to fight abroad during the American Revolutionary War and the government failed to organise its own militia. Taking advantage of Britain's preoccupation with its rebelling American colonies, the Volunteers were able to pressure Westminster into conceding legislative independence to the Dublin parliament. Members of the Belfast 1st Volunteer Company laid the foundations for the establishment of the United Irishmen organisation. The majority of Volunteer members however were inclined towards the yeomanry, which fought and helped defeat the United Irishmen in the Irish rebellion of 1798.Ulster Museum, History of Belfast exhibition According to Bartlett, it was the Volunteers of 1782 which would launch a paramilitary tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |